jeudi, 28 avril 2016
America’s Long Misguided War to Control the Greater Middle East
THE CONVICTION that invasion, bombing, and special forces benefit large swaths of the globe, while remaining consonant with a Platonic ideal of the national interest, runs deep in the American psyche. Like the poet Stevie Smith’s cat, the United States “likes to gallop about doing good.” The cat attacks and misses, sometimes injuring itself, but does not give up. It asks, as the U.S. should,
What’s the good
Of galloping about doing good
When angels stand in the path
And do not do as they should
Nothing undermines the American belief in military force. No matter how often its galloping about results in resentment and mayhem, the U.S. gets up again to do good elsewhere. Failure to improve life in Vietnam, Lebanon, Somalia, Iraq, Afghanistan, and Libya stiffens the resolve to get it right next time. This notion prevails among politicized elements of the officer corps; much of the media, whether nominally liberal or conservative; the foreign policy elite recycled quadrennially between corporation-endowed think tanks and government; and most politicians on the national stage. For them and the public they influence, the question is less whether to deploy force than when, where, and how.
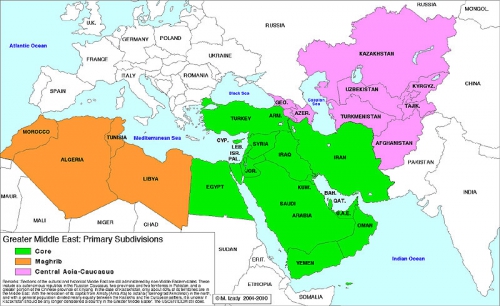
Since 1979, when the Iranians overthrew the Shah and the Soviets invaded Afghanistan, the U.S. has concentrated its firepower in what former U.S. Army colonel Andrew Bacevich calls the “Greater Middle East.” The region comprises most of what America’s imperial predecessors, the British, called the Near and Middle East, a vast zone from Pakistan west to Morocco. In his new book, America’s War for the Greater Middle East, Bacevich writes, “From the end of World War II until 1980, virtually no American soldiers were killed in action while serving in that region. Within a decade, a great shift occurred. Since 1990, virtually no American soldiers have been killed anywhere except the Greater Middle East.” That observation alone might prompt a less propagandized electorate to rebel against leaders who perpetuate policies that, while killing and maiming American soldiers, devastate the societies they touch.
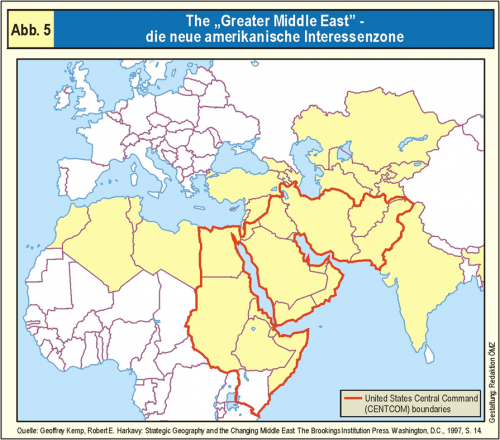
Bacevich describes a loyal cadre of intellectuals and pundits favoring war after war, laying the moral ground for invasions and excusing them when they go wrong. He notes that in 1975, when American imperium was collapsing in Indochina, the guardians of American exceptionalism renewed their case for preserving the U.S. as the exception to international law. An article by Robert Tucker in Commentary that year set the ball rolling with the proposition that “to insist that before using force one must exhaust all other remedies is little more than the functional equivalent of accepting chaos.” Another evangelist for military action, Miles Ignotus, wrote in Harper’s two months later that the U.S. with Israel’s help must prepare to seize Saudi Arabia’s oilfields. Miles Ignotus, Latin for “unknown soldier,” turned out to be the known civilian and Pentagon consultant Edward Luttwak. Luttwak urged a “revolution” in warfare doctrine toward “fast, light forces to penetrate the enemy’s vital centers” with Saudi Arabia a test case. The practical test would come, with results familiar to most of the world, 27 years later in Iraq.
The Pentagon, its pride and reputation wounded in Vietnam as surely as the bodies of 150,000 scarred American soldiers, was slow to take the hint. The end of compulsory military service robbed it of manpower for massive global intervention. Revelations of war crimes and political chicanery from the Senate’s Church Committee and the Pike Committee in the House added to public disenchantment with military adventures and intelligence meddling in other countries’ affairs. It would take years of effort to cure America of its “Vietnam Syndrome,” the preference for diplomatic before military solutions.
In the Middle East, President Gerald Ford saw no reason to rescind his predecessor’s policy, the Nixon Doctrine of reliance on local clients armed by the U.S. to protect Persian Gulf oil for America’s gas-hungry consumers. Nothing much happened, though, until one of the local gendarmes, the Shah of Iran, fell to a popular revolution and the Soviets invaded Afghanistan.
 CHANGE CAME with the Carter Doctrine, enunciated in the president’s January 1980 State of the Union address: “An attempt by any outside force to gain control of the Persian Gulf region will be regarded as an assault on the vital interests of the United States of America, and as such an assault will be repelled by any means necessary, including military force.”
CHANGE CAME with the Carter Doctrine, enunciated in the president’s January 1980 State of the Union address: “An attempt by any outside force to gain control of the Persian Gulf region will be regarded as an assault on the vital interests of the United States of America, and as such an assault will be repelled by any means necessary, including military force.”
Carter’s combative national security adviser, Zbigniew Brzezinski, wrote later, “The Carter Doctrine was modeled on the Truman Doctrine.” Bacevich comments that the Truman Doctrine of ostensibly containing the Soviet Union while absorbing the richer portions of the decolonizing French and British Empires “invited misinterpretation and misuse, with the Vietnam War one example of the consequences.” Carter’s doctrine, modified but not rescinded by his successors, led to similar consequences in Afghanistan and Iraq.
George W. Bush took the Carter Doctrine to fresh lengths when he made the case, prepared for him by national security adviser Condoleezza Rice, for preventive war in a speech at the U.S. Military Academy on June 1, 2002: “If we wait for threats to fully materialize, we will have waited too long.” Bacevich quotes the Nuremberg court’s view of preventive war: “To initiate a war of aggression is the supreme international crime differing only from other war crimes in that it contains within itself the accumulated evil of the whole.” After the failures to impose order in Afghanistan and Iraq, President Barack Obama rather than abandon the policy merely moved its emphasis from Iraq to Afghanistan without achieving any military or political objectives.
Bacevich, a West Point graduate and Vietnam veteran, while conceding his “undistinguished military career,” is more willing than most journalists to question the justice and utility of expanded military operations in the Middle East and to challenge the media-hyped reputations of some of America’s favorite generals, Stormin’ Norman Schwarzkopf, Colin Powell, Wesley Clark, and David Petraeus foremost. One general who comes out well in Bacevich’s assessment is British, Sir Michael Jackson, who resisted Wesley Clark’s order to block a runway at Pristina airport against Russian flights into Kosovo. His answer, worthy of Gen. Anthony McAuliffe’s reply of “Nuts” to the German demand for surrender at Bastogne: “Sir, I’m not starting World War III for you.”
This tour de force of a book covers the modern history of American warfare with sharp criticism of political decisions and rigorous analysis of battlefield strategy and tactics. As such, it should be required reading at the author’s alma mater. It would not hurt for those aspiring to succeed Barack Obama as commander-in-chief to dip into it as well. None of them, with the possible exception of Bernie Sanders, is likely to reject the worldview that led to so many deaths around the world. Watch for more military missions. Be prepared for more assassination by drone, of which even former Afghanistan commander Gen. Stanley McChrystal said, “They are hated on a visceral level, even by people who’ve never seen one or seen the effects of one.” McChrystal pointed out that drone strikes are great recruiters, not for the U.S. military, but for the Taliban, al Qaeda, and ISIS.
Ignoring Bacevich and heeding the call of the intellectual warmongers who guided Bush, Obama’s successor, like Stevie Smith’s cat, is likely “to go on being / A cat that likes to / Gallop about doing good,” expanding rather than limiting the projection of armed might into the Greater Middle East.
Charles Glass, former ABC News chief Middle East correspondent, recently published Syria Burning: A Short History of a Catastrophe (Verso).
Contact the author:
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Géopolitique | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : actualité, géopolitique, politique internationale, états-unis, greater middle east, grand moyen orient, moyen orient, asie, affaires asiatiques, impérialisme |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook