Postmodernism presents a threat not only to liberal democracy but to modernity itself. That may sound like a bold or even hyperbolic claim, but the reality is that the cluster of ideas and values at the root of postmodernism have broken the bounds of academia and gained great cultural power in western society. The irrational and identitarian “symptoms” of postmodernism are easily recognizable and much criticized, but the ethos underlying them is not well understood. This is partly because postmodernists rarely explain themselves clearly and partly because of the inherent contradictions and inconsistencies of a way of thought which denies a stable reality or reliable knowledge to exist. However, there are consistent ideas at the root of postmodernism and understanding them is essential if we intend to counter them. They underlie the problems we see today in Social Justice Activism, undermine the credibility of the Left and threaten to return us to an irrational and tribal “pre-modern” culture.
Postmodernism, most simply, is an artistic and philosophical movement which began in France in the 1960s and produced bewildering art and even more bewildering “theory.” It drew on avant-garde and surrealist art and earlier philosophical ideas, particularly those of Nietzsche and Heidegger, for its anti-realism and rejection of the concept of the unified and coherent individual. It reacted against the liberal humanism of the modernist artistic and intellectual movements, which its proponents saw as naïvely universalizing a western, middle-class and male experience.
It rejected philosophy which valued ethics, reason and clarity with the same accusation. Structuralism, a movement which (often over-confidently) attempted to analyze human culture and psychology according to consistent structures of relationships, came under attack. Marxism, with its understanding of society through class and economic structures was regarded as equally rigid and simplistic. Above all, postmodernists attacked science and its goal of attaining objective knowledge about a reality which exists independently of human perceptions which they saw as merely another form of constructed ideology dominated by bourgeois, western assumptions. Decidedly left-wing, postmodernism had both a nihilistic and a revolutionary ethos which resonated with a post-war, post-empire zeitgeist in the West. As postmodernism continued to develop and diversify, its initially stronger nihilistic deconstructive phase became secondary (but still fundamental) to its revolutionary “identity politics” phase.
It has been a matter of contention whether postmodernism is a reaction against modernity. The modern era is the period of history which saw Renaissance Humanism, the Enlightenment, the Scientific Revolution and the development of liberal values and human rights; the period when Western societies gradually came to value reason and science over faith and superstition as routes to knowledge, and developed a concept of the person as an individual member of the human race deserving of rights and freedoms rather than as part of various collectives subject to rigid hierarchical roles in society.

The Encyclopaedia Britannica says postmodernism “is largely a reaction against the philosophical assumptions and values of the modern period of Western (specifically European) history” whilst the Stanford Encyclopaedia of Philosophy denies this and says “Rather, its differences lie within modernity itself, and postmodernism is a continuation of modern thinking in another mode.” I’d suggest the difference lies in whether we see modernity in terms of what was produced or what was destroyed. If we see the essence of modernity as the development of science and reason as well as humanism and universal liberalism, postmodernists are opposed to it. If we see modernity as the tearing down of structures of power including feudalism, the Church, patriarchy, and Empire, postmodernists are attempting to continue it, but their targets are now science, reason, humanism and liberalism. Consequently, the roots of postmodernism are inherently political and revolutionary, albeit in a destructive or, as they would term it, deconstructive way.

The term “postmodern” was coined by Jean-François Lyotard in his 1979 book, The Postmodern Condition. He defined the postmodern condition as “an incredulity towards metanarratives.” A metanarrative is a wide-ranging and cohesive explanation for large phenomena. Religions and other totalizing ideologies are metanarratives in their attempts to explain the meaning of life or all of society’s ills. Lyotard advocated replacing these with “mininarratives” to get at smaller and more personal “truths.” He addressed Christianity and Marxism in this way but also science.
In his view, “there is a strict interlinkage between the kind of language called science and the kind called ethics and politics” (p8). By tying science and the knowledge it produces to government and power he rejects its claim to objectivity. Lyotard describes this incredulous postmodern condition as a general one, and argues that from the end of the 19th century, “an internal erosion of the legitimacy principle of knowledge” began to cause a change in the status of knowledge (p39). By the 1960s, the resulting “doubt” and “demoralization” of scientists had made “an impact on the central problem of legitimization” (p8). No number of scientists telling him they are not demoralized nor any more doubtful than befits the practitioners of a method whose results are always provisional and whose hypotheses are never “proven” could sway him from this.
We see in Lyotard an explicit epistemic relativity (belief in personal or culturally specific truths or facts) and the advocacy of privileging “lived experience” over empirical evidence. We see too the promotion of a version of pluralism which privileges the views of minority groups over the general consensus of scientists or liberal democratic ethics which are presented as authoritarian and dogmatic. This is consistent in postmodern thought.
Michel Foucault’s work is also centered on language and relativism although he applied this to history and culture. He called this approach “archeology” because he saw himself as “uncovering” aspects of historical culture through recorded discourses (speech which promotes or assumes a particular view). For Foucault, discourses control what can be “known” and in different periods and places, different systems of institutional power control discourses. Therefore, knowledge is a direct product of power. “In any given culture and at any given moment, there is always only one ‘episteme’ that defines the conditions of possibility of all knowledge, whether expressed in theory or silently invested in a practice.”[1]

Furthermore, people themselves were culturally constructed. “The individual, with his identity and characteristics, is the product of a relation of power exercised over bodies, multiplicities, movements, desires, forces.”[2] He leaves almost no room for individual agency or autonomy. As Christopher Butler says, Foucault “relies on beliefs about the inherent evil of the individual’s class position, or professional position, seen as ‘discourse’, regardless of the morality of his or her individual conduct.”[3] He presents medieval feudalism and modern liberal democracy as equally oppressive, and advocates criticizing and attacking institutions to unmask the “political violence that has always exercised itself obscurely through them.” [4]
We see in Foucault the most extreme expression of cultural relativity read through structures of power in which shared humanity and individuality are almost entirely absent. Instead, people are constructed by their position in relation to dominant cultural ideas either as oppressors or oppressed. Judith Butler drew on Foucault for her foundational role in queer theory focusing on the culturally constructed nature of gender, as did Edward Said in his similar role in post-colonialism and “Orientalism” and Kimberlé Crenshaw in her development of “intersectionality” and advocacy of identity politics. We see too the equation of language with violence and coercion and the equation of reason and universal liberalism with oppression.
It was Jacques Derrida who introduced the concept of “deconstruction,” and he too argued for cultural constructivism and cultural and personal relativity. He focused even more explicitly on language. Derrida’s best-known pronouncement “There is no outside-text” relates to his rejection of the idea that words refer to anything straightforwardly. Rather, “there are only contexts without any center of absolute anchoring.” [5]
Therefore the author of a text is not the authority on its meaning. The reader or listener makes their own equally valid meaning and every text “engenders infinitely new contexts in an absolutely nonsaturable fashion.” Derrida coined the term différance which he derived from the verb “differer” which means both “to defer” and “to differ.” This was to indicate that not only is meaning never final but it is constructed by differences, specifically by oppositions. The word “young” only makes sense in its relationship with the word “old” and he argued, following Saussure, that meaning is constructed by the conflict of these elemental oppositions which, to him, always form a positive and negative. “Man” is positive and ‘woman’ negative. “Occident” is positive and “Orient” negative. He insisted that “We are not dealing with the peaceful co-existence of a vis-a-vis, but rather with a violent hierarchy. One of the two terms governs the other (axiologically, logically, etc.), or has the upper hand. To deconstruct the opposition, first of all, is to overturn the hierarchy at a given moment.”[6] Deconstruction, therefore, involves inverting these perceived hierarchies, making “woman” and “Orient” positive and “man” and “Occident” negative. This is to be done ironically to reveal the culturally constructed and arbitrary nature of these perceived oppositions in unequal conflict.

We see in Derrida further relativity, both cultural and epistemic, and further justification for identity politics. There is an explicit denial that differences can be other than oppositional and therefore a rejection of Enlightenment liberalism’s values of overcoming differences and focusing on universal human rights and individual freedom and empowerment. We see here the basis of “ironic misandry” and the mantra “reverse racism isn’t real” and the idea that identity dictates what can be understood. We see too a rejection of the need for clarity in speech and argument and to understand the other’s point of view and avoid minterpretation. The intention of the speaker is irrelevant. What matters is the impact of speech. This, along with Foucauldian ideas, underlies the current belief in the deeply damaging nature of “microaggressions” and misuse of terminology related to gender, race or sexuality.
Lyotard, Foucault, and Derrida are just three of the “founding fathers” of postmodernism but their ideas share common themes with other influential “theorists” and were taken up by later postmodernists who applied them to an increasingly diverse range of disciplines within the social sciences and humanities. We’ve seen that this includes an intense sensitivity to language on the level of the word and a feeling that what the speaker means is less important than how it is received, no matter how radical the interpretation. Shared humanity and individuality are essentially illusions and people are propagators or victims of discourses depending on their social position; a position which is dependent on identity far more than their individual engagement with society. Morality is culturally relative, as is reality itself. Empirical evidence is suspect and so are any culturally dominant ideas including science, reason, and universal liberalism. These are Enlightenment values which are naïve, totalizing and oppressive, and there is a moral necessity to smash them. Far more important is the lived experience, narratives and beliefs of “marginalized” groups all of which are equally “true” but must now be privileged over Enlightenment values to reverse an oppressive, unjust and entirely arbitrary social construction of reality, morality and knowledge.
The desire to “smash” the status quo, challenge widely held values and institutions and champion the marginalized is absolutely liberal in ethos. Opposing it is resolutely conservative. This is the historical reality, but we are at a unique point in history where the status quo is fairly consistently liberal, with a liberalism that upholds the values of freedom, equal rights and opportunities for everyone regardless of gender, race and sexuality. The result is confusion in which life-long liberals wishing to conserve this kind of liberal status quo find themselves considered conservative and those wishing to avoid conservatism at all costs find themselves defending irrationalism and illiberalism. Whilst the first postmodernists mostly challenged discourse with discourse, the activists motivated by their ideas are becoming more authoritarian and following those ideas to their logical conclusion. Freedom of speech is under threat because speech is now dangerous. So dangerous that people considering themselves liberal can now justify responding to it with violence. The need to argue a case persuasively using reasoned argument is now often replaced with references to identity and pure rage.

Despite all the evidence that racism, sexism, homophobia, transphobia and xenophobia are at an all-time low in Western societies, Leftist academics and SocJus activists display a fatalistic pessimism, enabled by postmodern interpretative “reading” practices which valorize confirmation bias. The authoritarian power of the postmodern academics and activists seems to be invisible to them whilst being apparent to everyone else. As Andrew Sullivan says of intersectionality:
“It posits a classic orthodoxy through which all of human experience is explained — and through which all speech must be filtered. … Like the Puritanism once familiar in New England, intersectionality controls language and the very terms of discourse.” [7]
Postmodernism has become a Lyotardian metanarrative, a Foucauldian system of discursive power, and a Derridean oppressive hierarchy.
The logical problem of self-referentiality has been pointed out to postmodernists by philosophers fairly constantly but it is one they have yet to address convincingly. As Christopher Butler points out, “the plausibility of Lyotard’s claim for the decline of metanarratives in the late 20th century ultimately depends upon an appeal to the cultural condition of an intellectual minority.” In other words, Lyotard’s claim comes directly from the discourses surrounding him in his bourgeois academic bubble and is, in fact, a metanarrative towards which he is not remotely incredulous. Equally, Foucault’s argument that knowledge is historically contingent must itself be historically contingent, and one wonders why Derrida bothered to explain the infinite malleability of texts at such length if I could read his entire body of work and claim it to be a story about bunny rabbits with the same degree of authority.

This is, of course, not the only criticism commonly made of postmodernism. The most glaring problem of epistemic cultural relativity has been addressed by philosophers and scientists. The philosopher, David Detmer, in Challenging Postmodernism, says
“Consider this example, provided by Erazim Kohak, ‘When I try, unsuccessfully, to squeeze a tennis ball into a wine bottle, I need not try several wine bottles and several tennis balls before, using Mill’s canons of induction, I arrive inductively at the hypothesis that tennis balls do not fit into wine bottles’… We are now in a position to turn the tables on [postmodernist claims of cultural relativity] and ask, ‘If I judge that tennis balls do not fit into wine bottles, can you show precisely how it is that my gender, historical and spatial location, class, ethnicity, etc., undermine the objectivity of this judgement?” [8]
However, he has not found postmodernists committed to explaining their reasoning and describes a bewildering conversation with postmodern philosopher, Laurie Calhoun,
“When I had occasion to ask her whether or not it was a fact that giraffes are taller than ants, she replied that it was not a fact, but rather an article of religious faith in our culture.”
Physicists Alan Sokal and Jean Bricmont address the same problem from the perspective of science in Fashionable Nonsense: Postmodern Intellectuals’ Abuse of Science:
“Who could now seriously deny the ‘grand narrative’ of evolution, except someone in the grip of a far less plausible master narrative such as Creationism? And who would wish to deny the truth of basic physics? The answer was, ‘some postmodernists.’”
and
“There is something very odd indeed in the belief that in looking, say, for causal laws or a unified theory, or in asking whether atoms really do obey the laws of quantum mechanics, the activities of scientists are somehow inherently ‘bourgeois’ or ‘Eurocentric’ or ‘masculinist’, or even ‘militarist.'”
How much of a threat is postmodernism to science? There are certainly some external attacks. In the recent protests against a talk given by Charles Murray at Middlebury, the protesters chanted, as one,
“Science has always been used to legitimize racism, sexism, classism, transphobia, ableism, and homophobia, all veiled as rational and fact, and supported by the government and state. In this world today, there is little that is true ‘fact.'”[9]
When the organizers of the March for Science tweeted:
“colonization, racism, immigration, native rights, sexism, ableism, queer-, trans-, intersex-phobia, & econ justice are scientific issues,”[10] many scientists immediately criticized this politicization of science and derailment of the focus on preservation of science to intersectional ideology. In South Africa, the #ScienceMustFall and #DecolonizeScience progressive student movement announced that science was only one way of knowing that people had been taught to accept. They suggested witchcraft as one alternative. [11]
Despite this, science as a methodology is not going anywhere. It cannot be “adapted” to include epistemic relativity and “alternative ways of knowing.” It can, however, lose public confidence and thereby, state funding, and this is a threat not to be underestimated. Also, at a time in which world rulers doubt climate change, parents believe false claims that vaccines cause autism and people turn to homeopaths and naturopaths for solutions to serious medical conditions, it is dangerous to the degree of an existential threat to further damage people’s confidence in the empirical sciences.
The social sciences and humanities, however, are in danger of changing out of all recognition. Some disciplines within the social sciences already have. Cultural anthropology, sociology, cultural studies and gender studies, for example, have succumbed almost entirely not only to moral relativity but epistemic relativity. English (literature) too, in my experience, is teaching a thoroughly postmodern orthodoxy. Philosophy, as we have seen, is divided. So is history.
Empirical historians are often criticized by the postmodernists among us for claiming to know what really happened in the past. Christopher Butler recalls Diane Purkiss’ accusation that Keith Thomas was enabling a myth that grounded men’s historical identity in “the powerlessness and speechlessness of women” when he provided evidence that accused witches were usually powerless beggar women. Presumably, he should have claimed, against the evidence, that they were wealthy women or better still, men. As Butler says,
“It seems as though Thomas’s empirical claims here have simply run foul of Purkiss’s rival organizing principle for historical narrative – that it should be used to support contemporary notions of female empowerment” (p36)
I encountered the same problem when trying to write about race and gender at the turn of the seventeenth century. I’d argued that Shakespeare’s audience’s would not have found Desdemona’s attraction to Black Othello, who was Christian and a soldier for Venice, so difficult to understand because prejudice against skin color did not become prevalent until a little later in the seventeenth century when the Atlantic Slave Trade gained steam, and that religious and national differences were far more profound before that. I was told this was problematic by an eminent professor and asked how Black communities in contemporary America would feel about my claim. If today’s African Americans felt badly about it, it was implied, it either could not have been true in the seventeenth century or it is morally wrong to mention it. As Christopher Butler says,
“Postmodernist thought sees the culture as containing a number of perpetually competing stories, whose effectiveness depends not so much on an appeal to an independent standard of judgement, as upon their appeal to the communities in which they circulate.”
I fear for the future of the humanities.
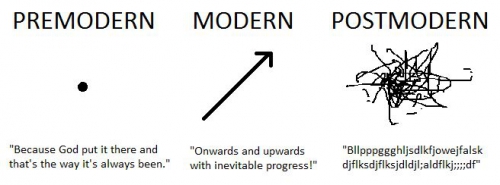
The dangers of postmodernism are not limited to pockets of society which center around academia and Social Justice, however. Relativist ideas, sensitivity to language and focus on identity over humanity or individuality have gained dominance in wider society. It is much easier to say what you feel than rigorously examine the evidence. The freedom to “interpret” reality according to one’s own values feeds into the very human tendency towards confirmation bias and motivated reasoning.
It has become commonplace to note that the far-Right is now using identity politics and epistemic relativism in a very similar way to the postmodern-Left. Of course, elements of the far-Right have always been divisive on the grounds of race, gender and sexuality and prone to irrational and anti-science views but postmodernism has produced a culture more widely receptive to this. Kenan Malik describes this shift,
“When I suggested earlier that the idea of ‘alternative facts’ draws upon ‘a set of concepts that in recent decades have been used by radicals’, I was not suggesting that Kellyanne Conway, or Steve Bannon, still less Donald Trump, have been reading up on Foucault or Baudrillard… It is rather that sections of academia and of the left have in recent decades helped create a culture in which relativized views of facts and knowledge seem untroubling, and hence made it easier for the reactionary right not just to re-appropriate but also to promote reactionary ideas.”[12]
This “set of concepts” threaten to take us back to a time before the Enlightenment, when “reason” was regarded as not only inferior to faith but as a sin. James K. A. Smith, Reformed theologian and professor of philosophy, has been quick to see the advantages for Christianity and regards postmodernism as “a fresh wind of the Spirit sent to revitalize the dry bones of the church” (p18). In Who’s Afraid of Postmodernism?: Taking Derrida, Lyotard, and Foucault to Church, he says,
“A thoughtful engagement with postmodernism will encourage us to look backward. We will see that much that goes under the banner of postmodern philosophy has one eye on ancient and medieval sources and constitutes a significant recovery of premodern ways of knowing, being, and doing.” (p25)
and
“Postmodernism can be a catalyst for the church to reclaim its faith not as a system of truth dictated by a neutral reason but rather as a story that requires ‘eyes to see and ears to hear.” (p125)
We on the Left should be very afraid of what “our side” has produced. Of course, not every problem in society today is the fault of postmodern thinking, and it is not helpful to suggest that it is. The rise of populism and nationalism in the US and across Europe are also due to a strong existing far-Right and the fear of Islamism produced by the refugee crisis. Taking a rigidly “anti-SJW” stance and blaming everything on this element of the Left is itself rife with motivated reasoning and confirmation bias. The Left is not responsible for the far-Right or the religious-Right or secular nationalism, but it is responsible for not engaging with reasonable concerns reasonably and thereby making itself harder for reasonable people to support. It is responsible for its own fragmentation, purity demands and divisiveness which make even the far-Right appear comparatively coherent and cohesive.
In order to regain credibility, the Left needs to recover a strong, coherent and reasonable liberalism. To do this, we need to out-discourse the postmodern-Left. We need to meet their oppositions, divisions and hierarchies with universal principles of freedom, equality and justice. There must be a consistency of liberal principles in opposition to all attempts to evaluate or limit people by race, gender or sexuality. We must address concerns about immigration, globalism and authoritarian identity politics currently empowering the far- Right rather than calling people who express them “racist,” “sexist” or “homophobic” and accusing them of wanting to commit verbal violence. We can do this whilst continuing to oppose authoritarian factions of the Right who genuinely are racist, sexist and homophobic, but can now hide behind a façade of reasonable opposition to the postmodern-Left.
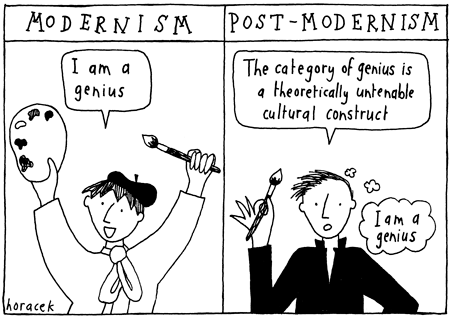
Our current crisis is not one of Left versus Right but of consistency, reason, humility and universal liberalism versus inconsistency, irrationalism, zealous certainty and tribal authoritarianism. The future of freedom, equality and justice looks equally bleak whether the postmodern Left or the post-truth Right wins this current war. Those of us who value liberal democracy and the fruits of the Enlightenment and Scientific Revolution and modernity itself must provide a better option.
—————————
Helen Pluckrose is a researcher in the humanities who focuses on late medieval/early modern religious writing for and about women. She is critical of postmodernism and cultural constructivism which she sees as currently dominating the humanities. You can connect with her on Twitter @HPluckrose
—————————
Notes
[1] The Order of Things: An Archaeology of the Human Sciences (2011) Routledge. p183
[2] ‘About the Beginning of the Hermeneutics of the Self: Two Lectures at Dartmouth.’ Political Theory, 21, 198-227
[3] Postmodernism: A Very Short Introduction. (2002) Oxford University Press. p49
[4] The Chomsky – Foucault Debate: On Human Nature (2006) The New Press. P41
[5] http://hydra.humanities.uci.edu/derrida/sec.html
[6] Positions. (1981) University of Chicago Press p41
[7] http://hotair.com/archives/2017/03/10/is-intersectionality-a-religion/
[8] Challenging Postmodernism: Philosophy and the Politics of Truth (2003) Prometheus Press. p 26.
[9] In Sullivan http://hotair.com/archives/2017/03/10/is-intersectionality-a-religion/
[10] http://dailycaller.com/2017/01/30/anti-trump-march-for-sc...
[11] http://blogs.spectator.co.uk/2016/10/science-must-fall-ti...
[12] https://kenanmalik.wordpress.com/2017/02/05/not-post-trut...









 del.icio.us
del.icio.us
 Digg
Digg




























 Heidegger's thought came to prominence in the post-Soviet era through the work of a remarkable polyglot translator and charismatic philosopher, Vladimir Bibikhin (1938-2004). Not only did Bibikhin translate Being and Time into Russian, he also cultivated a generation of young philosophers through his widely-attended lectures at the University of Moscow. It is difficult to apply a label to Bibikhin's thought, and I shall not try to do so. Suffice it to say that Bibikhin attempted to graft Heidegger onto central currents in Russian thought in such a way as to renovate Russian culture in the post-Soviet era, not as a wholesale rejection of western thought but as an effort at correcting its sometimes baleful influence, especially in regard to the insensate selfishness and venality that made strong inroads into post-Soviet Russia under the guise of promoting a free market and capitalist democracy. Bibikhin fought against the hypocrisy of American democracy as reflected in Russia, the ostensibly principled pursuit of freedom concealing there, as elsewhere, naked greed and exploitation.
Heidegger's thought came to prominence in the post-Soviet era through the work of a remarkable polyglot translator and charismatic philosopher, Vladimir Bibikhin (1938-2004). Not only did Bibikhin translate Being and Time into Russian, he also cultivated a generation of young philosophers through his widely-attended lectures at the University of Moscow. It is difficult to apply a label to Bibikhin's thought, and I shall not try to do so. Suffice it to say that Bibikhin attempted to graft Heidegger onto central currents in Russian thought in such a way as to renovate Russian culture in the post-Soviet era, not as a wholesale rejection of western thought but as an effort at correcting its sometimes baleful influence, especially in regard to the insensate selfishness and venality that made strong inroads into post-Soviet Russia under the guise of promoting a free market and capitalist democracy. Bibikhin fought against the hypocrisy of American democracy as reflected in Russia, the ostensibly principled pursuit of freedom concealing there, as elsewhere, naked greed and exploitation.






 S. T. Joshi
S. T. Joshi






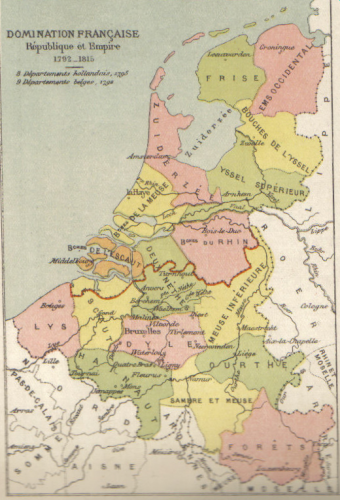

 This tension between the two Bonaparte brothers was exacerbated by the effort of the Emperor Napoleon to defeat Britain by means of economic strangulation. He instituted the Continental System which forbid France and all countries controlled by or allied with France from trading with the British which, as it turned out, proved more ruinous for the continent than it did for Britain and particularly for The Netherlands which had a heavily trade-based economy. Needless to say, smuggling soon reached epidemic proportions because of this and Napoleon was so desperate to stamp it out that in 1810 he simply annexed the Kingdom of Holland and it was absorbed into the French Empire. The former King Ludwig I, by then none too popular with his brother, fled into exile in the Austrian Empire and remained there for the rest of his life. So it was that, until 1813, the Dutch, willingly or not, mostly fought alongside the French under Napoleon. For some, this did not seem all that unnatural given the long history of Anglo-Dutch rivalry and warfare.
This tension between the two Bonaparte brothers was exacerbated by the effort of the Emperor Napoleon to defeat Britain by means of economic strangulation. He instituted the Continental System which forbid France and all countries controlled by or allied with France from trading with the British which, as it turned out, proved more ruinous for the continent than it did for Britain and particularly for The Netherlands which had a heavily trade-based economy. Needless to say, smuggling soon reached epidemic proportions because of this and Napoleon was so desperate to stamp it out that in 1810 he simply annexed the Kingdom of Holland and it was absorbed into the French Empire. The former King Ludwig I, by then none too popular with his brother, fled into exile in the Austrian Empire and remained there for the rest of his life. So it was that, until 1813, the Dutch, willingly or not, mostly fought alongside the French under Napoleon. For some, this did not seem all that unnatural given the long history of Anglo-Dutch rivalry and warfare.

















