In the geographical area of Syria, as in other parts of the Muslim world, Sufism found itself during the twentieth century under increasing attack. Though accustomed to strictures against their theosophical meditations and popular-ecstatic practices, with the advent of modernity Sufis had to contend with challenges of an altogether different magnitude. These derived not only from the direct impact of the West with its rationalist mode of thinking, but, even more so, from the growing intervention of a secularized State and the concomitant antagonism of a rising Islamic fundamentalism. Under such circumstances, many Sufi brotherhoods declined; yet others were able to develop a variety of strategies from within their divergent traditions to survive, adapt, and at times even thrive. Since the 1980s, with the turn of Muslim governments against the radical upsurge, and the general rise of interest in “Oriental” mysticism in the West, there has been a marked revival in Sufi activities. [1]
This paper focuses on the current manifestations of Sufism and Sufi brotherhoods in the states of Syria and Israel, with occasional references to Lebanon and Jordan. Although subjected to increasingly differentiated socioeconomic and political processes since the later part of the Ottoman period, Sufis in three of the four countries share in a basic situation of living under non-Sunni governments. In Syria, the sectarian-based authoritarian Ba‘th regime, in power since 1963, has been generally hostile toward independent Sufi activity, the more so during the Islamic uprising that culminated in Hamah in 1982. The same regime imposed itself on the Christian-Maronite-dominated political system in Lebanon following the outbreak of civil war in 1976. In the Jewish State of Israel such activity had been almost eliminated by the disruption of the War in 1948, but partly revived after the renewal of contacts with the Palestinians of the West Bank and Gaza in the wake of the 1967 War. Rather than an exhaustive survey, my aim in this paper is to analyze the various ways by which different Sufi brotherhoods in Syria and Israel have responded to the challenges of modernity in general, and to the peculiar political circumstances in which they live in particular.
Among the Syrian brotherhoods that experienced a marked decline or that disappeared during the twentieth century, De Jong includes the major turuq of the Qadiriyya, Khalwatiyya and Mawlawiyya in his mid-1980s survey. [2] The weakening of the Qadiriyya had already become conspicuous by the turn of that century. Essentially an urban brotherhood in Syria, its major branches were led by the notable Kaylani family of Damascus and Hamah, who claimed descent from the founder ‘Abd al-Qadir al-Jilani. In the late Ottoman period leading members of the family became administrators, later turning into influential politicians and entrepreneurs.[3] The last actual shaykh in the family was Muhammad Fariz al-Kaylani, a follower of Ibn ‘Arabi who died in Damascus in 1971 without designating an heir.[4] In Hamah, the Qadiriyya continued to be observed as a family tradition until its open support of the Islamic uprising in 1982 brought upon it the brunt of the regime. Many members of the family were killed by the security forces, while their illustrious lodge (zawiya), and indeed the entire quarter in which they resided, were razed to the ground.[5] In the rural areas local leading Qadiri families, such as the Zu‘bis of the Hawran, have continued to enjoy influence among the peasants even after relinquishing their Sufi identity.[6]
A closer look at this process of decline is provided by Paolo Pinto in a recent anthropological study conducted in Aleppo. One of the focuses of this study is the Hilaliyya brotherhood, which since the eighteenth century has combined the local Qadiri tradition with the then reformist Khalwati import. At present the dhikr is still performed in two lodges in the city, but the brotherhood’s characteristic practice of seclusion (khalwa) is no longer in use because, as its leaders maintain, in modern times people have neither the leisure nor the possibility to set aside their work.[7] Shaykh al-Hilali, a physician, follows his ancestors’ tradition in stressing the primacy of the shari‘a and in combining the religious and secular sciences. Subscribing to the decision of his grandfather to discontinue the path rather than compromise its ideals, he avoids guiding disciples and is content with conducting the dhikr and with providing spiritual advice for the community. In the weekly session (hadra), Pinto reports, around one hundred adherents are assembled, most of them belonging to the old commercial families of Aleppo. Some of the participants are organized into an informal study group in which they discuss their spiritual experiences and read Sufi texts. Among these texts is the Sufi compendium of the local Shadhili-‘Alawi reformist shaykh ‘Abd al-Qadir ‘Isa, which has appeared in several editions since it was first published in 1961.[8]
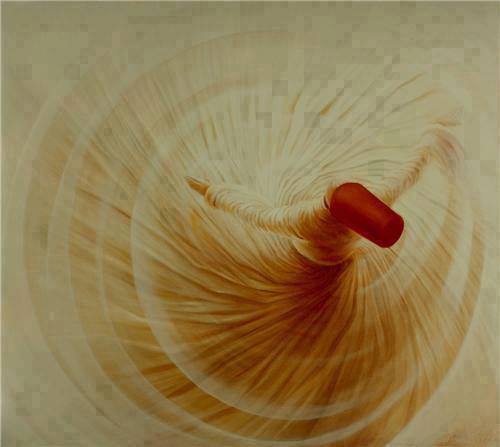
The other major brotherhood that De Jong considers as having lost its ground in Syria, the Mawlawiyya, may have done so in its traditional form. In Aleppo, to where the Great Master moved following the ban on Sufi activity in Turkey in 1925, the tariqa died out in the late 1950s. Yet, as elsewhere in the Muslim world, as well as in the West, groups of Mawlawis have exploited the unique ritual resources of their brotherhood – the whirling dance, musical improvisations, and special clothing – to turn the dhikr into a highly impressive, though often touristic, performance. In Damascus, the leader of the new-style whirling dervishes is Shaykh Hamza Shakkur, the choirmaster of singers (munshidin) in the Umayyad mosque and a vocalist who is much in demand for official religious ceremonies. Shakkur also cooperates with the al-Kindi Ensemble from Aleppo, which was founded in 1983 by Julien Jalaleddin Weiss, a converted Frenchman of Swiss extraction who had studied Arab music and specialized on the qanun. The group holds regular concert tours both in the Arab world and in Europe and America.[9]

As against the general decline of these basically urban-elitist brotherhoods, their rural-popular counterparts have proved more capable of holding to their traditions. Such is the case with the Sa‘diyya, although the spectacular dawsa (the shaykh riding a horse over the backs of his murids) has been long prohibited by the state. Numerous local shaykhs are affiliated with this brotherhood in both the major Syrian cities and in the countryside. Its two centers are the Golan village of Jaba’, the site of the founder’s tomb, and Damascus, where his descendants vie for control over its rich awqaf. The Sa‘diyya in the capital is considerably weakened, but still it is the only brotherhood to take part in the annual procession of laylat al-qadar, in which the first revelation to the Prophet is commemorated by exhibiting one of his hairs in the presence of religious dignitaries and State representatives. In Jaba’ and the neighboring villages, by contrast, hadarat are still regularly conducted with all their traditional vigor, including beating drums, piercing the body with swords and eating burning coal and glass.[10]
Even more popular is the Rifa‘iyya brotherhood, of which the Sa‘diyya is sometimes considered a branch. Rifa‘i zawiyas can be found in most towns of Syria, although, as in the case of the Qadiriyya, the leading families have been incorporated into the local elites; in Damascus rich merchants who are attached to the tariqa are engaged in editing and publishing its basic manuscripts. In Aleppo, however, some of its zawiyas were closed under Shishakli’s military regime in the early 1950s, while in Hamah shaykh Mahmud al-Shaqfa, who was associated with the Muslim Brothers, was killed by Asad’s security forces and his lodge closed in 1979.[11] The mainstay of the Rifa‘iyya has always been in the countryside. The fortunes of the tariqa were enormously enhanced in Syria in the days of the infamous Abu al-Huda al-Sayyadi, who under the patronage of Sultan ‘Abdülhamid II (1876-1909) attracted to the brotherhood a great number of people from the towns, the villages, and the tribes.[12] Considerably reduced during the interwar period, it still persists in many villagers. Thus for instance in Nahjat Brak in the Ghuta the dhikr is held, though only once a year, and is attended by peasants from the adjacent regions.[13] Pinto describes the working of another Rifa‘i lodge in the predominantly Kurdish village of ‘Afrin, north of Aleppo. The head of this zawiya, Shaykh Mahmud, is a descendant of a local family of the brotherhood and has eighteen disciples in various stages of the path. The dhikr of the group includes healing and expulsion of jinns, as well as, like the Sa‘diyya, transpiercing the abdomen with an iron skewer (shish), walking over burning coals and glass eating.[14]
Popular mystical traditions are maintained in contemporary Syria, to some extent or another, also in their non-tariqa forms, particularly around the numerous tombs of prophets and saints which are dispersed throughout the country. The richest locus of sacred sites is naturally Damascus, and it may serve as an illustration of some of the still existing practices. Thus the caves on Mount Qasyun, overlooking the city from the north, are believed to contain the remains of literally hundreds of prophets. Barren women visit Maqam Ibrahim, while wayfarers address themselves to the alleged tomb of al-Khidr, their legendary patron. To this day sixty shaykhs will climb up the mountain in times of drought to perform the traditional prayer for rain. Another important sacred focus is the central Umayyad mosque where, it is claimed, the Prophet Yahya and Imam Husayn’s severed head are interred. At the first, women solicit help in solving problems of motherhood and marriage, and many of them tie a rope to the lattice-work as a symbol of their commitment to fulfill their vow. The second tomb is the starting point of the afore-mentioned solemn procession of laylat al-qadar.[15]
Among the saints (awliya’) buried in Damascus, the most illustrious is Muhyi al-Din ibn ‘Arabi, in whose shrine in the north of the city an impressive hadra is conducted on Friday evenings. Al-Shaykh al-Akbar is visited both by common believers asking for worldly benefits and by mystics who attach themselves to his tomb for spiritual illumination. For the local population, though, even more important is the shrine of Shaykh Arslan, the twelfth-century patron saint and protector of the city. A recent saint is Shaykh Ahmad al-Harun (d. 1962), whose picture adorns many shops and whose miraculous deeds (karamat) are still widely circulated. A stonecutter in Mount Qasyun Harun, who had fiercely fought the French, immersed himself at an advanced age not only in the intricacies of Ibn ‘Arabi’s theosophy but also in the natural sciences, gaining the respect of both ulema and laymen.[16] The “Tales of the Saints” genre is indeed still popular in Syria, as is testified to, for example, by the posthumous publication of a collection of such stories compiled by Muhammad Abu al-Yusr ‘Abidin, the Grand Mufti of the country between 1954 and 1962.[17]
Beyond the unchecked decline of an “elitist”-urban Qadiriyya or the retrograde traditionalism of a “popular”-rural Rifa‘iyya, the Shadhiliyya and Naqshbandiyya Sufi brotherhoods of Syria have tapped into their reformist traditions in an effort to adapt themselves to the modern situation. Such adaptability allows their leaders not only to transcend the urban-rural divide, but – more importantly - to adopt elements from Western culture as well as from Islamic fundamentalist discourse. Moreover, in some cases the Sufi brotherhood appears to have transformed itself into new forms of religious organization in the face of these challenges, notably the educational society and the political movement.
Three Shadhili sub-brotherhoods have had a lasting impact on the Syrian lands in the modern period, all three crossing current political boundaries. The oldest among these branches, and the less effective today, is the Yashrutiyya, which has always stressed its a-political character. Founded in Acre by the Tunisian Shadhili-Madani Shaykh ‘Ali Nur al-Din Yashruti (ca. 1815-1899) in the mid-nineteenth century, the brotherhood spread swiftly throughout the region, from Aleppo in the north to Gaza in the south, attracting both orthodox educated urban elites and disaffected villagers from the countryside with antinomian tendencies.[18] The leadership of the Yashrutiyya has remained within the founder’s family, while its center moved first to Beirut, in the wake of the War of 1948 and then, in 1980, in the midst of the Lebanese civil war, to Amman. In Damascus a regular hadra is still held in the zawiya of Abu al-Shamat, ‘Ali Nur al-Din’s principal deputy (khalifa) in the city, though the once glorious construction is now in a deplorable state. Concentrations of Yashrutis are also found in small towns in the Hawran, in Sirmin near Aleppo, and in the Ghuta villages of Harasta and Daraya. Still a predominantly Palestinian brotherhood, its members are most numerous in the refugee camp of south Damascus, and even more so in the camps near Beirut and Sidon.[19] Another Shadhili sub-brotherhood introduced in Syria in the Second half of the nineteenth century was that of Yashruti’s Madani colleague Muhammad al-Fasi. Brought to Damascus by the celebrated amir ‘Abd al-Qadir al-Jaza’iri, it seems to have remained confined to his elitist circle and died out before the end of the French Mandate.[20]

The second major modern Shadhili branch to strike roots in Syria was the Dandarawiyya, which had been founded toward the end of the nineteenth century by the Egyptian Muhammad al-Dandarawi (1839-1910), a spiritual grandson of the reformist Sufi scholar Ahmad ibn Idris. Spreading to both Damascus and the surrounding Ghuta in the 1890s, the tariqa still has a small presence in these areas, particularly in the village of Jisrin. Its center of activity in the Syrian lands, however, moved to Beirut, where it underwent a major transformation.[21] A glimpse at the working of this brotherhood is provided by Mark Sedgwick in a study of the worldwide spread and “normalization” of Ibn Idris’ legacy. Its current head is the founder’s grandson, Fadl al-Dandarawi (b. 1934), a Cairo-based wealthy businessman who in the early 1970s launched a new project to remold the tariqa. He was assisted by Su‘ad al-Hakim, a Lebanese professor of Arab and Islamic philosophy and author of a celebrated study on Ibn ‘Arabi’s terminology.[22] On one level, Sedgwick argues, the new “Dandarawi thought” represents an attempt to return to the original reformist Ahmadi path; on another it is designed as an inclusive way which combines Sufism and Salafism and is appropriate for the modern world. This is embodied in the “Dandarawi family”, and the history of the Dandarawiyya is reconstructed as having been a social organization in this “family” mold from the outset, rather than a Sufi tariqa. Fadl insists on being addressed as amir and regards the hadra as an “art” or “folklore”. Hakim, a woman, conducts in Beirut, in accordance with this philosophy, a sober hadra for both men and women, as well as an educated discussion group.[23]
No research is as yet available on the Syrian ‘Alawiyya, the third modern Shadhili branch to operate in the country, although the brotherhood as a whole is well known in the West, having been the inspiration for a remarkable group of mystically-minded intellectuals in Europe and North America.[24] Founded by the Darqawi shaykh Ahmad ibn ‘Aliwa of Mustaghanim, Western Algeria, in the early nineteenth century, the ‘Alawiyya was introduced by him in Damascus in the course of a pilgrimage he undertook shortly before his death in 1934. Combining, not unlike the Idrisi tradition, the theosophy of Ibn ‘Arabi with a call to strictly follow the Qur‘an and the Sunna, the brotherhood under the leadership of Muhammad al-Hashimi soon spread to other parts of the country, from Aleppo in the north to Amman in the south, and was very active both in the field of religious education and in the struggle against the French.[25] Similar to the case of the urban Rifa‘iyya, the leaders of the Damascene ‘Alawiyya have been lately engaged in publishing the writings of their masters, but more significant were the shaykhs from the north, who maintained its original militant zeal in supporting the violent struggle against the Ba‘th. Among them were disciples of the above-mentioned Aleppine ‘Abd al-Qadir ‘Isa, who was consequently forced to spend the last years of his life in exile in Jordan, as well as those of ‘Abd al-Ghaffar al-Durubi of Homs, many of whom were killed along with the Muslim Brothers in the notorious massacre in the Tadmur (Palmyra) military prison in June 1980.[26]
The Naqshbandiyya, unquestionably the most active brotherhood in contemporary Syria, has been long characterized by a tradition combining a strong orthodoxy with a sociopolitical orientation. Both traits were reinforced in the early nineteenth century by Shaykh Khalid, the founder of the Khalidi sub-brotherhood whose mausoleum lies in Damascus. Two of his spiritual descendants were responsible for turning the Khalidiyya into the most widespread Sufi organization in Syria in the twentieth century. These were ‘Isa al-Kurdi (1831-1912), an immigrant scholar who ordained a great number of disciples in Damascus and the Ghuta, and Abu al-Nasr Khalaf (1875-1949), who propagated the path in the villages around his hometown Homs, as well as in Aleppo and Hamah.[27] A third center of the Naqshbandiyya-Khalidiyya can be found in the Kurdish areas of the northeast - the Jazira and Dayr al-Zor.[28] These essentially independent local branches adopted different and, in some respects, even opposing attitudes toward the questions of religious renewal, the Salafi challenge and, above all, relations with the Ba‘th regime. Mention should also be made of Nazim al-Qubrusi, founder of the Haqqaniyya branch, who had initially established himself at his master’s shrine in Damascus, but whose brotherhood has now become a truly international organization counting members in many countries around the globe, from Lebanon and Turkey to England and the United States.[29]
The leading Naqshbandi branch in Syria today is that of Ahmad Kuftaro (b. 1915), son of one of ‘Isa al-Kurdi’s principal deputies in Damascus.[30] This is the only Sufi organization in the country to be allowed freedom of action by the regime, with whom it is closely associated. Despite claims for early beginnings, the Kuftariyya seems to have emerged following the Ba‘th takeover in 1963, and the election of Kuftaro a year later to the highest religious position in Syria, that of the Grand Mufti.[31] In 1971, after the rise to power of Hafiz al-Asad who sought to appease the Sunni population, Kuftaro’s mosque in north Damascus was made the basis of the Abu al-Nur Islamic Foundation. The first recognized college within this trust, The College for Islamic Propagation, was inaugurated in 1982, at the height of the Islamic uprising. The Kuftariyya appeals to social strata generally higher than other Sufi brotherhoods in Syria, especially small merchants and junior functionaries. It has a female wing under Kuftaro’s younger daughter, Wafa’, who propagate his message among women in weekly lectures in the Abu al-Nur Foundation, where she also conducts the dhikr, and in various mosques in Damascus.[32] Kuftaro regards himself in addition as the spiritual father of the more independent female Sufi organization of the Qubaysiyya, which directs its attention to women from higher social classes. Members of this organization run highly appreciated private schools in Syria, and it has lately spread to other countries of the Middle East.
Faithful to the reformist tradition of the Naqshbandiyya, Ahmad Kuftaro seeks to adapt its path to the modern situation by propagating a learned and discreet form of Sufism which is based on the Qur’an and the shari‘a. Particularly under the inspiration of the Indian scholar Abu al-Hasan al-Nadwi, he also stresses engagement in social affairs and rejects monastic mysticism (rahbaniyya) as a major cause of the social and cultural weakening of Islam.[33] The focus of Kuftaro’s reformist activity lies in the sphere of education. On the basis of the Abu al-Nur Foundation, where he himself continues to deliver a weekly lesson in front of thousands of people, Kuftaro has founded numerous religious institutions, from private schools for boys and girls to an Islamic center of higher education which since 1992 has provided Ph.D. degrees in Islamic Law. To enhance the prestige of the foundation, he formed connections with various universities in the Muslim world – in Libya, Pakistan and Sudan – as well as in North America, where an Abu al-Nur Institute was opened in 1993 in Baltimore, Maryland. In view of the great importance that Kuftaro attaches to modern technology, the foundation also supports students of high-status professions, while inculcating in them its religious values. Some of his close relatives are themselves engineers trained in the West, and they helped him develop the Abu al-Nur Foundation beyond its strictly religious functions into an effective economic, social and political organization.
Yet in face of the fierce Salafi critique of Sufism, Ahmad Kuftaro has proved ready to go beyond the traditional reformism of the Naqshbandiyya and eventually adopt much of the discourse and argumentation of his rivals. In this endeavor, he downplays his relation to the great Naqshbandi masters of the past, including Shaykh Khalid,[34] while stressing his good relations with most moderate Islamists.[35] Moreover, once again in the footsteps of Nadwi,[36] Kuftaro suggests to do away with the Sufi terminology in favor of a strictly Qur’anic vocabulary. In this scheme of “spiritual education” (tarbiya ruhiyya) the terms tasawwuf and tariqa themselves are to be substituted by the less controversial ihsan and tazkiyat al-nafs.[37] Kufatro explicitly follows the Salafis in denouncing legal school partisanship and the practice of imitation (taqlid) in favor of individual reasoning (ijtihad). He likewise stresses the need to interpret Islam in relation to the present, and of being guided by reason, often declaring that religion is nothing but “mature reason”. On the other hand, Kuftaro and his associates are keen to demonstrate to the Salafis that the Sufis’ inner search of God has not diverted them from active participation in jihad.[38] Muhammad Sa‘id Ramadan al-Buti, a highly popular doctor of Islamic Law from the University of Damascus who is also affiliated to the Naqshbandiyya,[39] fully supports Kuftaro’s approach. In a book dedicated to the refutation of extreme Salafi positions, Buti approves of the shaykh’s terminology while showing, by way of ijtihad, that the dhikr and other Sufi practices are fully compatible with the Qur’an and the Sunna.[40]
Another aspect in which Ahmad Kuftaro departs from the traditional way of the Naqshbandiyya, in this case even beyond the reformism of the Salafis, concerns his propagation of the religion. As already mentioned, the Abu al-Nur Foundation has an active da‘wa department, which uses modern devices - from videotapes and audio cassettes to the Internet - to spread the shaykh’s message among both Muslim and non-Muslim audiences. For the latter, a collection of lectures translated into English was published in 1993 under the title “The Way of Truth”, and was expanded in a second edition in 1997. Kuftaro himself has exploited his extensive travels in an official capacity to present Islam and Sufism, his earliest visit being as early as 1966 to the United States.[41] His da‘wa is nevertheless characterized by an intentional ambiguity. On the one hand, Kuftaro adheres to the orthodox position, held by Naqshbandis and Salafis alike, that Islam is the final and most perfect religion; on the other hand, however, he points out that the three monotheistic religions stem from a common source, and further maintains that all denominations are different traditions of the one universal religion. In harmony with the latter position, also indicated in the title of his official website – Abrahamic religions - Kuftaro has been long engaged in interfaith dialogue, taking part in various conferences around the world and hosting delegations of clergymen, particularly Christian, in the Abu al-Nur mosque. In recent years his interests have expanded to include other issues of international concern, notably those of human rights and the environment.[42]

Students of the Syrian religious scene assess differently the special relations between Ahmad Kuftaro and the Asad regime. Thus the more affirmative Geoffroy counts the shaykh among those resilient men of religion, mostly from Damascus, who have sought to assuage the hostility of the Ba‘th and avoid complete rupture. The accusations against his compromising stands are, according to this interpretation, nothing but the age-old claim about the corruption of ulema in the service of rulers.[43] Stenberg, on his part, stresses the fact that although Kuftaro may be allied with – or even controlled by – the Syrian regime, he also can influence the political leadership through his position as the highest religious authority at the head of a large religious movement.[44] He however concurs with Böttcher’s view of Kuftaro as a tool in the Islamic policy of the regime,[45] and with De Jong’s assertion that the cultivation of the Kuftariyya seems to have been designed to weaken the position of the politically unreliable Naqshbandi shaykhs of the north and northeast.[46] In my view, its cultivation was more specifically aimed at offsetting the influence of Sa‘id Hawwa, the foremost ideologue of the Islamic opposition in Syria, who was deeply attached to Sufism in general, and to the northern branch of the Naqshbandiyya in particular.[47]
The affinity between the ideas and discourse of the Naqshbandi brotherhood of Syria and its Salafis-Islamists, which has been noted even in the case of the state-backed Kuftaro, was much more pronounced in the north, where disciples of Abu al-Nasr Khalaf were instrumental in founding local branches of the Muslim Brothers in the 1930s and 1940s. Outstanding among these Naqshbandi-oriented Brothers were Muhammad al-Hamid (1910-1969) in Hamah and ‘Abd al-Fattah Abu-Ghudda (1917-1997) in Aleppo.[48] Under the rule of the Ba‘th, Abu-Ghudda emerged as the leader of the Islamists’ northern faction, while Sa‘id Hawwa (1935-1989) perpetuated Hamid’s work on the national level. Sufism permeates Hawwa’s entire oeuvre, one of the expressed aims of which was to familiarize the Islamic movement with the reformist Sufi tradition and thus provide it with a spiritual “depth”. In a series of books he dedicated to the subject, notably Tarbiyatuna al-ruhiyya and al-Mustakhlas fi tazkiyat al-anfus, Hawwa in all probability preceded Kuftaro in deemphasizing the Sufi vocabulary.[49] Indignant, though, at the Damascene shaykh’s complicity with the un-Islamic Ba‘th, he went beyond the latter’s rejection of rahbaniyya to elaborate upon Nadwi’s complementary concept of rabbaniyya, making it the basis for a sociopolitical alternative. Through this concept, Hawwa conceived of a grass-roots organization, a popular supra-brotherhood as it were, that would unite all the Islamic forces in the country and lead them in the struggle for religious revival in general, and against the secular tendencies of the Ba‘th in particular.[50] The Hamah uprising of 1982, and its brutal suppression by Asad’s regime, left Kufatro’s accommodating collaboration the only alternative open before the Syrian Naqshbandiyya.
Sufi manifestations in contemporary Israel differ considerably from those in Syria in both their scope and the identity of the brotherhoods involved. The differences go back to Ottoman Palestine, in which the Sufi brotherhoods were less organized and of a more limited social significance. The Naqshbandiyya has never struck roots here, its presence being generally restricted to a zawiya run by Uzbeks in Jerusalem, while the Mawlawiyya and Rifa‘iyya had practically disappeared, the first already by the beginning of the twentieth century, the other in 1948.[51] Three brotherhoods - The Qadiriyya, Yashrutiyya and Khalwatiyya-Rahmaniyya were able to adapt themselves to the Israeli realities, in ascending order of success. Various local groups of the Qadiriyya were active in Palestine during Ottoman times, in both towns and villages. These groups disintegrated in 1948, but in recent years new ones appeared, in the same fragmented manner, under leaders who received the path from different shaykhs in the West Bank and Gaza. They include Sa‘id Abu-Laban, a descendant from the leading Qadiri family of Ottoman Ramla which was responsible for the ziyara at Nabi Salih’s tomb; ‘Abd al-Salam Manasara, an ex-Communist from Nazareth who adheres to a more sober type of Sufism; and the charismatic though controversial Abu Filastin from Sahnin in the Lower Galilee. In some cases, to fortify their standing, the shaykhs combine with the Qadiriyya other affiliations such as the Rifa‘iyya and ‘Alawiyya.[52]
The Yashrutiyya, whom we met in the refugee camps of Syria and Lebanon, introduced into Palestine a more organized type of Sufism during the last decades of Ottoman rule. Retaining its essentially centralized structure, the brotherhood was able to attract a wide membership throughout the country well into the British Mandate. Its fortunes were severely affected, however, by the events of 1948, when Muhammad al-Hadi, the founder’s grandson, moved with many of his followers to Beirut. Several zawiyas were lost during the battles, and in 1952 the economic basis of the mother lodge in Acre was further undermined as most of its awqaf were confiscated. After 1967, the Yashrutis in Israel regained some of their former strength as they were allowed to establish contacts with adherents in the West Bank and Gaza, as well as in other parts of the Muslim world. The main figure in this renewed activity was Ibrahim Abu al-Hashish of Umm al-Fahm, where the largest concentration of Yashrutis is found today. With contributions from abroad the zawiya in Acre was also renovated, al-Hadi being buried there beside his fathers in 1981 with Israel’s permission.[53] His son Ahmad occasionally visits the lodge and conducts a celebrated dhikr, but otherwise activity is limited to the religious festivals, notably the Prophet’s mawlid.[54]
Much more successful in its accommodation to the Israeli realities is the Rahmani branch of the Khalwatiyya, a brotherhood that eventually disappeared in other parts of the Syrian lands. This branch was founded immediately after World War I by ‘Abd al-Rahman al-Sharif, a former deputy (muqaddam) of the Yashrutiyya in Hebron who switched to the Khalwati silsila returning to the great reviver of the brotherhood in the eighteenth century, Mustafa al-Bakri. In his footsteps, the Rahmaniyya has propagated, possibly as a counterbalance to the antinomian tendencies among the rural Yashrutiyya, a reformist type of Sufism combining strictly following the Qur’an and the Sunna with the pursuit of worldly concerns.[55] Splitting after the founder’s death in 1925, his most outstanding khalifa, Husni al-Din al-Qasimi, established himself in the village of Zayta, and further spread the path to the villages that now form the Triangle area in Israel.[56] Most important among these is the lodge in Baqa al-Gharbiyya, which four successive sons of Husni al-Din, the last being the present shaykh ‘Abd al-Rauf al-Qasimi, managed by keeping cordial relations with Israeli authorities to develop after 1967 into an impressive religious-educational complex. It includes both a large mosque-zawiya where a regular dhikr is held for both men and women in separate rooms, and a rapidly expanding Islamic College, which was opened in 1989 and is served by a modern academic library. Enjoying the official recognition of the Ministry of Education, the college has currently more than five hundred students.[57]

Finally attention should be drawn to an Israeli version of the tariqa Ibrahimiyya. Although, as in Syria, this way aims at enhancing an interfaith dialogue, in Israel it was founded by a Jewish group, including a conservative Rabbi and academic scholars, who relate themselves to the Jewish Sufi tradition inaugurated by Rabbi Abraham son of Maimonides in the thirteenth century. The members used to meet to read Sufi texts and perform the dhikr under the guidance of Muslim Sufi shaykhs. These activities were interrupted following the break of the last Intifada in 2000, but recently they have been renewed.[58]
Although clearly losing ground in the face of the multi-faceted challenge mounted against it through the twentieth century, Sufism is still conspicuously present in many countries of the contemporary Muslim world. As the cases of Syria and Israel show, among the diverse Sufi traditions, it was primarily the reformist brotherhoods of the pre-modern era, particularly the Naqshbandiyya but also the Shadhiliyya and the Khalwatiyya, which proved most capable of adjusting to the modern circumstances. Adopting a seemingly paradoxical strategy of accommodating one agent of modernity or another - western rationalism, Islamic fundamentalism or, most importantly, the all-powerful State – by the close of the century branches from these brotherhoods have managed not merely to preserve their mystical traditions, but also at times to expand into new enterprises in the educational, socioeconomic and political realms.
-------------------
[1] For a general discussion of the debate on Sufism in the twentieth century, see Carl W. Ernst, Sufism: An Essential Introduction to the Philosophy and Practice of
the Mystical Tradition of Islam (Boston: Shambhala, 1997), 199-228; Elizabeth Sirriyeh, Sufis and Anti-Sufis: The Defence, Rethinking and Rejection of Sufism in the Modern World (Richmond, Surrey: Curzon Press, 1999), chs. 4-6.
[2] Fred de Jong, “Les confréries mystiques musulmanes au Machreq arabe,” in Alexandre Popovic and Gilles Veinstein (eds.), Les Ordres mystiques dans l’Islam: Cheminements et situation actuelle (Paris: Editions de l’EHESS, 1986), 214.
[3] Linda Schatkowski Schilcher, Families in Politics: Damascene Factions and Estates of the 18th and 19th Centuries (Stuttgart: Steiner Verlag, 1985), 194-196; Zaim Khenchelaoui and Thierry Zarcone, “La Famille Jilânî de Hama – Syrie (Bayt al- Jilânî),” Journal of the History of Sufism, 1-2 (2000), 61-71.
[4] On Fariz al-Kaylani, see Muhammad Muti‘ al-Hafiz and Nizar Abaza, Tarikh ‘ulama’ Dimashq fi al-qarn al-rabi‘ ‘ashar al-hijri, (3 vols. Damascus: Dar al-fikr, 1986-1991), 3: 363-365.
[5] Eric Geoffroy, “Sufism, réformisme et pouvoir en Syrie contemporaine,” Égypte/Monde arabe 29 (1997), 17.
[6] Hanna Batatu, Syria’s Peasantry, the Descendants of its Lesser Rural Notables, and their Politics (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1999), 107-108.
[7] On the Hilaliyya, see Julia Gonnella, Islamischer Heiligenverherung im urbanen Kontext am Beispiel von Aleppo (Syrien) (Berlin: Klaus Schwartz Verlag, 1995), 248-250, 261-263. Similar reasons are given for the actual disappearance of the Khalwatiyya from its once thriving center of Tripoli, see Daphne Habibis, “Change and Continuity: A Sufi Order in Contemporary Lebanon,” Social Analysis 31 (1992), 49-50.
[8] Paolo Pinto, “Proof and Experience: the Construction of Religious Identity in the Sufi Zawiyas of Aleppo, Syria,” a paper read at the 16th Middle East History and Theory Conference, University of Chicago, May 11-12, 2001, 3-8; ‘Abd al-Qadir ‘Isa, Haqa‘iq ‘an al-tasawwuf (5th ed. Damascus: Mu’assasat al-Sham lil-tiba‘a wal-tajlid, 1993).
[9] www.turath.org/Events/Dervishes.htm. See also the discussion in Ernst, 191-194.
[10] De Jong, “Machreq arabe,” 212-214; Pierre-Jean Luizard, “Le Moyen-Orient arabe,” in Alexandre Popovic and Gilles Veinstein (eds.), Les voies d’Allah (Paris: Fayard, 1996), 361-362.
[11] De Jong, ibid., 215-216; Gonnella, 118-119, 263-268. For Mahmud al-Shaqfa, see Johannes Reissner, Ideologie und politik der Muslimbrüder Syriens von den Wahlen 1947 bis zum Verbot unter Adīb aš-Šišaklī 1952 (Freiburg: Klaus Schwarz Verlag, 1980), 427-428.
[12] Butrus Abu-Manneh, “Sultan Abdulhamid II and Shaikh Abulhuda al-Sayyadi,” Middle Eastern Studies, 15 (1979), 131-153; Batatu, 107-108.
[13] Ibid., 105-108.
[14] Pinto, 8-14. For the practice of piercing the body with a shish, see also Gonnella, 74-76.
[15] Eric Geoffroy, “L’empreinte de la sainteté,” in Anne-Marie Bianquis (ed.), Damas: Miroir brise d’un Orient arabe (Paris: Éditions Autrement, 1993), 166-169.
[16] Ibid, 169-174. On Ahmad al-Harun see also Hafiz and Abaza, 753-762.
[17] Muhammad Abu al-Yusr ‘Abidin, Hakaya al-Sufiyya (Damascus: Dar al-basha’ir, 1993).
[18] On the history of the brotherhood see Josef Van Ess, “Libanesische Miszellen, 6: Die YašruÔīya,” Die Welt des Islams, 16 (1975), 1-103; Itzchak Weismann, Taste of Modernity: Sufism, Salafiyya, and Arabism in Late Ottoman Damascus (Leiden: Brill, 2000), 219-224, 252-255.
 [19] De Jong, “Machreq arabe,” 217-218.
[19] De Jong, “Machreq arabe,” 217-218.
[20] Weismann, Taste of Modernity, 197-198.
[21] Ibid., 255-256; De Jong, ibid., 216.
[22] Su‘ad al-Hakim, al-Mu‘jam al-sufi: al-hikma fi hudud al-kalima (Beirut: Dandara lil-tiba‘a wal-nashr, 1981).
[23] Mark J.R. Sedgwick, “The Heirs of Ahmad Ibn Idris: The Spread and Normalization of a Sufi Order, 1799-1996,” (Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Bergen, 1998), 235-247, 266-277.
[24] See Martin Lings, A Sufi Saint of the Twentieth Century - Shaykh Ahmad al-‘Alawi: His Spiritual Heritage and Legacy (2nd ed. London: George Allen & Unwin, 1971); Mark Sedgwick, “Traditional Sufism”, Aries 22 (1999), 3-24.
[25] See the entries on Muhammad al-Hashimi and Muhammad Sa‘id al-Burhani in Hafiz and Abaza, 747-751, 794-804; as well as ‘Isa, 618-631, and Muhammad Riyad al-Malih, al-‘Allama Muhammad Sa‘id al-Burhani: Arba‘un ‘amm fi mihrab al-tawba (Damascus: n.p., 1387 A.H.).
[26] Geoffroy, “Sufism, réformisme et pouvoir,” 17-18.
[27] See my two articles, “The Forgotten Shaykh: ‘Isa al-Kurdi and the Transformation of the Naqshbandi-Khalidi Order in Twentieth Century Syria,” Die Welt des Islams 43 (2003), 273-293; and “Sa‘id Hawwa: The Making of a Radical Muslim Thinker in Modern Syria,” Middle Eastern Studies 29 (1993), 607-611.
[28] De Jong, “Machreq arabe,” 214-215; Gonnella, 224, 269-270.
[29] On Nazim al-Qubrusi and his international activity, see Muhammad Hisham Kabbani, The Naqshbandi Sufi Way: History and Guidebook of the Saints of the Golden Chain (Chicago: Kazi Publications, 1995), 375-408; Habibis, 44-78; Annabelle Böttcher, “The Naqshbandiyya in the United States”, www. naqshbandi.net/haqqani/features/ Naqshbandiyya_in_us.htm.
[30] For biographical details, see Muhammad Habash, al-Shaykh Amin Kuftaru fi dhikra khamsin ‘am ‘ala wafatihi (Damascus: Dar al-ma‘rifa, 1989); idem, al-Shaykh Ahmad Kuftaru wa-minhajuhu fi al-tajdid wal-islah (Damascus: Dar al-nur, 1996).
[31] My description of the Kuftariyya and its working is mainly based on the following sources: Annabelle Böttcher, Syrische Religionspolitik unter Asad (Freiburg, 1998), 147-223; Leif Stenberg, “Naqshbandiyya in Damascus: Strategies to Establish and Strengthen the Order in a Changing Society,” in Elisabeth Özdalga (ed.), Naqshbandis in Western and Central Asia (Istanbul: Swedish Research Institute, 1999), 101-116; Geoffroy, “Sufism, réformisme et pouvoir,” 11-18.
[32] See also Annabelle Böttcher, “L’élite féminine kurde de la Kaftariyya: une confrérie Naqshbandi Damascène,” in Martin van Bruinessen (ed.), Islam des Kurdes (Paris: ERISM, 1998), 125-139.
[33] See Abu al-Hasan ‘Ali al-Hasani al-Nadwi, Rabbaniyya la rahbaniyya (4th ed. Beirut: Mu’assasat al-risala, 1986). On his acquaintance with Kuftaro see idem, Mudhakkirat sa’ih fi al-sharq al-‘arabi (2nd ed. Beirut: Mu’assasat al-risala, 1975), 224-225, 236-238.
[34] Stenberg, 109.
[35] ‘Imad ‘Abd al-Latif Naddaf, Al-Shaykh Ahmad Kuftaru yatahaddath (Beirut: Dar al-rashid, 1997), 150-192. Stenberg reports that among Kuftaro’s young adherents the ideas of Hasan al-Banna are well-known and widely discussed.
[36] Nadwi, 7-11.
[37] For an exposition of this doctrine in the context of the anti-Salafi debate, see Muhammad al-Shaykhani, al-Tarbiya al-ruhiyya bayn al-Sufiyyin wal-Salafiyyin (Damascus: Dar Qutayba, 1990), esp. 191-195, 287-297.
[38] Ibid., 299-303. For a widely acclaimed historical exposition of the Sufi’s contribution to jihad struggles, see As‘ad al-Khatib, al-Butula wal-fida’ ‘inda al-Sufiyya (Damascus: Maktab al-Ghazali, 1995).
[39] See Andreas Christmann, “Islamic Scholar and Religious Leader: a Portrait of Shaykh Muhammad Sa‘id Ramadan al-Buti,” Islam and Christian-Muslim Relations 9 (1998), 149-169.
[40] Muhammad Sa‘id Ramadan al-Buti, Al-Salafiyya: marhala zamaniyya mubaraka, la madhhab Islami (Damascus: Dar al-fikr, 1988), 189-209.
[41] On Kuftaro’s philosophy of da‘wa, see Wahid Taja, al-Khitab al-Islami al-mu‘asir: muhawarat fikriyya (Aleppo: Fussilat lil-dirasat wal-tarjama wal-nashr, 2000), 21-34.
[42] See Naddaf, 120-149; www.abrahamicreligions.com/kuftaro/Interfaith.htm and www.abrahamicreligions.com/kuftaro/Environment.htm. For meetings with German and Swiss delegations see Naddaf, 295-309, and with an American delegation, see Syria Times, 18 December 1999, www.islamic-study.org/new
[43] Geoffroy, “Sufism, réformisme et pouvoir,” 17.
[44] Stenberg, 106-107.
[45] Böttcher, 149.
 [46] Frederick De Jong, “The Naqshbandiyya in Egypt and Syria. Aspects of its History, and Observations Concerning its Present-Day Condition,” in Marc Gaborieau, Alexandre Popovic and Thierry Zarcone (eds.), Naqshbandis: cheminements et situation actuelle d’un ordre mystique musulman (Istanbul and Paris: ISIS, 1990), 600.
[46] Frederick De Jong, “The Naqshbandiyya in Egypt and Syria. Aspects of its History, and Observations Concerning its Present-Day Condition,” in Marc Gaborieau, Alexandre Popovic and Thierry Zarcone (eds.), Naqshbandis: cheminements et situation actuelle d’un ordre mystique musulman (Istanbul and Paris: ISIS, 1990), 600.
[47] For his biography, see Itzchak Weismann, “Radical Muslim Thinker”, 601-623.
[48] For Abu-Ghudda, who was a disciple of Khalaf’s deputy ‘Isa al-Bayanuni, see Hanna Batatu, “Syria’s Muslim Brethren,” Merip Reports 110 (1982), 14; Muhammad ibn ‘Abdallah Al Rashid, Imdad al-fattah bi-asanid wa-muruyyat al-Shaykh ‘Abd al-Fattah (Riyadh: Maktabat al-Imam al-Shafi‘i, 1999), esp. 149-150, 152; and www.aboghodda.com. For Hamid see my, “Religious Strife on the Periphery: Sufi Populists, Salafi Ideologues, and Muslim Brothers in Twentieth-Century Hamah,” forthcoming in International Journal of Middle East Studies.
[49] Sa‘id Hawwa, Tarbiyyatuna al-ruhiyya (2nd ed. Amman: Maktabat al-risala al-haditha, 1981), 6-8. See also the discussion in Geoffroy, “Sufism, Réformisme et Pouvoir,” 12-13.
[50] Itzchak Weismann, “Sa‘id Hawwa and Islamic Revivalism in Ba‘thist Syria,” Studia Islamica 85 (1997), 131-154.
[51] F. De Jong, “The Sufi Orders in Nineteenth and Twentieth-Century Palestine,” Studia Islamica 58 (1983), 149-158, 167-174.
[52] De Jong, “Machreq arabe,” 221-223; Luizard, 364-365; Arnon Dancho, “Ha-techiya shel ha-Sufim (The Revival of the Sufis),” Eretz ve-Teva 53 (1999), 45-53.
[53] De Jong, “Palestine,” 179-180.
[54] Interview with Ibrahim Satal, attendant at the Shadhiliyya-Yashrutiyya complex in Acre, 7 August, 2002.
[55] ‘Afif ibn Husni al-Din al-Qasimi, Adwa’ ‘ala al-tariqa al-Khalwatiyya al-Jami‘a al-Rahmaniyya (n.p., 1997).
[56] De Jong, “Palestine,” 175; idem, “Machreq arabe,” 220. For the Rahmani silsila see Qasimi, 4-7. For the activities of its successive shaykhs, ibid., 59-63.
[57] Interview with ‘Adil Badran, chief librarian of the Islamic College, Baqa al-Gharbiyya, 28 October, 2002.
[58] Zohara Ron, “Be-Darko shel Avraham (In the Path of Abraham),” Masa Akher 111 (2000), 83-88.






 del.icio.us
del.icio.us
 Digg
Digg

 Myth is, in traditional cultures, a great antithesis as well, where, as it was shown in the capital work of J. J. Bachofen, Mother Right: An Investigation of the Religious and Juridical Character of Matriarchy in the Ancient World, the two major and irreconcilable principles are confronted: uranic and htonic, patriarchal and matriarchal, and this is projected to all second modalities of state and social order through to the arts and culture.
Myth is, in traditional cultures, a great antithesis as well, where, as it was shown in the capital work of J. J. Bachofen, Mother Right: An Investigation of the Religious and Juridical Character of Matriarchy in the Ancient World, the two major and irreconcilable principles are confronted: uranic and htonic, patriarchal and matriarchal, and this is projected to all second modalities of state and social order through to the arts and culture.







 [19] De Jong, “Machreq arabe,” 217-218.
[19] De Jong, “Machreq arabe,” 217-218.  [46] Frederick De Jong, “The Naqshbandiyya in Egypt and Syria. Aspects of its History, and Observations Concerning its Present-Day Condition,” in Marc Gaborieau, Alexandre Popovic and Thierry Zarcone (eds.), Naqshbandis: cheminements et situation actuelle d’un ordre mystique musulman (Istanbul and Paris: ISIS, 1990), 600.
[46] Frederick De Jong, “The Naqshbandiyya in Egypt and Syria. Aspects of its History, and Observations Concerning its Present-Day Condition,” in Marc Gaborieau, Alexandre Popovic and Thierry Zarcone (eds.), Naqshbandis: cheminements et situation actuelle d’un ordre mystique musulman (Istanbul and Paris: ISIS, 1990), 600. 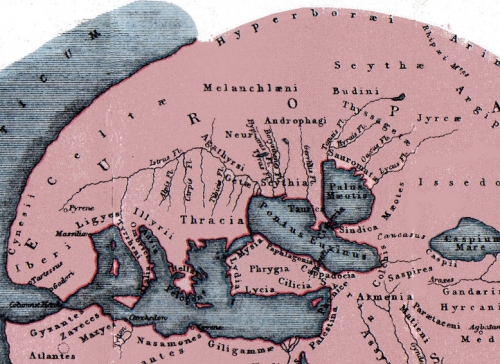

 Quant au judaïsme, non seulement il n’échapperait pas à cette opposition interne, mais celle-ci se retrouverait aussi dans les formes séculières de la pensée juive. Douguine analyse les branches mystiques du judaïsme (hassidisme, sabbataïsme, kabbalisme) comme l’expression de l’aspect terrestre de cette religion. Au contraire, le talmudisme en représenterait l’aspect atlantiste notamment par l’accent mis sur la rigueur dogmatique et le rationalisme. Par ailleurs, rappelant l’influence du messianisme juif sur le développement du marxisme et du bolchevisme, Douguine voit dans ces derniers des formes séculières du judaïsme terrestre. Au contraire, le judaïsme atlantiste sécularisé aurait contribué à l’essor du capitalisme et de l’esprit bourgeois. Le géopoliticien russe voit dans cette tension interne au judaïsme l’explication d’un récurrent « antisémitisme juif ». Les propos de Karl Marx, affirmant notamment que l’argent serait le Dieu profane du judaïsme (La question juive), seraient l’incarnation empirique du juif mystique s’attaquant au juif talmudiste, soit une émanation de la tradition contre une forme de la modernité.
Quant au judaïsme, non seulement il n’échapperait pas à cette opposition interne, mais celle-ci se retrouverait aussi dans les formes séculières de la pensée juive. Douguine analyse les branches mystiques du judaïsme (hassidisme, sabbataïsme, kabbalisme) comme l’expression de l’aspect terrestre de cette religion. Au contraire, le talmudisme en représenterait l’aspect atlantiste notamment par l’accent mis sur la rigueur dogmatique et le rationalisme. Par ailleurs, rappelant l’influence du messianisme juif sur le développement du marxisme et du bolchevisme, Douguine voit dans ces derniers des formes séculières du judaïsme terrestre. Au contraire, le judaïsme atlantiste sécularisé aurait contribué à l’essor du capitalisme et de l’esprit bourgeois. Le géopoliticien russe voit dans cette tension interne au judaïsme l’explication d’un récurrent « antisémitisme juif ». Les propos de Karl Marx, affirmant notamment que l’argent serait le Dieu profane du judaïsme (La question juive), seraient l’incarnation empirique du juif mystique s’attaquant au juif talmudiste, soit une émanation de la tradition contre une forme de la modernité.


 One thing which became clear to the Ahnenerbe, early on, was that all pre-Christian Indo-European cultures seemed to conceive of history as being cyclical rather than linear. In other words, all ancient “pagan” Indo-European cultures believed in an organic rhythmical order to both Time and Space. This conception of cyclical history – first expounded upon in modern times by Nikolai Danilevsky (1822-1885) and then Oswald Spengler (1880-1936) – stands in stark contrast to the Semitic-derived, “Abrahamic” belief in a purely linear or teleological conception of Time.
One thing which became clear to the Ahnenerbe, early on, was that all pre-Christian Indo-European cultures seemed to conceive of history as being cyclical rather than linear. In other words, all ancient “pagan” Indo-European cultures believed in an organic rhythmical order to both Time and Space. This conception of cyclical history – first expounded upon in modern times by Nikolai Danilevsky (1822-1885) and then Oswald Spengler (1880-1936) – stands in stark contrast to the Semitic-derived, “Abrahamic” belief in a purely linear or teleological conception of Time.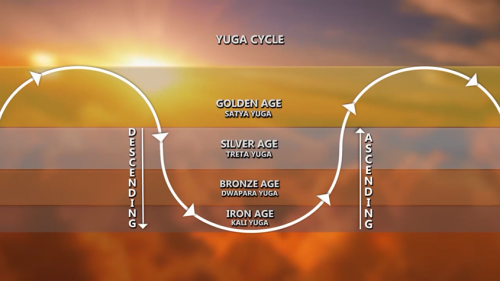


 At the turn of the twentieth century there was a Catholic monk in Vienna who was a member of the old Teutonic Order. Disillusioned and disgusted with mainstream Christian dogma, he eventually left the monastery and assumed the name of “Lanz von Liebenfels.” He is most famous for writing Theozoology – a philosophical work that centers on the perennial earthly Struggle between Man(created in the image of God) and the hominid/apeling masses of the soulless, material world. It is said that von Liebenfels had an epiphany in his native Austria upon seeing a statue of a knight standing victoriously on top of a primate. Of course the knight symbolized a Noble, a true Man, a Man of the divine – and the primate symbolized the great bulk of animalistic humanity.
At the turn of the twentieth century there was a Catholic monk in Vienna who was a member of the old Teutonic Order. Disillusioned and disgusted with mainstream Christian dogma, he eventually left the monastery and assumed the name of “Lanz von Liebenfels.” He is most famous for writing Theozoology – a philosophical work that centers on the perennial earthly Struggle between Man(created in the image of God) and the hominid/apeling masses of the soulless, material world. It is said that von Liebenfels had an epiphany in his native Austria upon seeing a statue of a knight standing victoriously on top of a primate. Of course the knight symbolized a Noble, a true Man, a Man of the divine – and the primate symbolized the great bulk of animalistic humanity.


 Konfuzius geht es nicht um eine abstrakt definierte Moral, sondern um eine individuelle, durch persönliches Beispiel gelebte Sittlichkeit. Er lehrte nicht durch logische Erklärungen, sondern Umschreibungen. „Als der Stall niederbrannte und Konfuzius zurück kehrte, fragte er: ‚Wurde jemand verletzt?‘ Er fragte nicht nach den Pferden.“ Dieses berühmte Zitat beleuchtet die Lehrweise Konfuzius und wie er Menschlichkeit definiert. Er sorgt sich nicht um den Besitz – die Pferde. Aber er sagt es nicht direkt, das Gleichnis umschreibt es nur. Es ist eben kein Kantianischer Imperativ, sondern eine Ermutigung zum persönlichen Vorbild. Von ihm stammt die berühmte Goldene Regel: „Füge anderen nicht zu, was du nicht willst, dass dir zugefügt wird.“ Dabei steht der Konfuzianismus zwischen den Extremen des Universalismus und Tribalismus. Es gibt eine Moral, eben die Menschlichkeit, die man allen Menschen gegenüber walten lässt; dennoch ist das Verhältnis der Einzelnen zueinander wichtig. Man verhält sich den Obigen gegenüber mit Respekt, den Unteren gegenüber mit Milde. Die Eltern leiten die Kinder mit Strenge und Güte, die Kinder achten die Eltern mit Respekt. Dies setzt sich in allen Bereichen fort: es gibt eben keine Gleichheit, aus der die Moral entspringt, sondern was sittlich ist, bestimmt das Verhältnis der Menschen, wie sie zueinander stehen. Damit wird die gesellschaftliche Ordnung aufrecht erhalten. Die Rollen der Menschen sind eben unterschiedlich, und das Urbild dazu ist die Familie. Der Vater als Beschützer und Leiter, die Mutter als nährend und umsorgend, die Kinder folgsam und respektvoll. Auch die Rollen von Mann und Frau können nicht die gleichen sein, sie sind Abbilder von Yin und Yang, dem männlichen Himmelsprinzip und dem weiblichen der Erde: der Himmel beleuchtet und überwölbt, die Erde trägt und nährt. Es ist keine Unfreiheit, keine Ungleichheit der Würde, aber es sind sich ergänzende Rollen, wie eben im Yin-Yang Symbol: zwei Teile deren gegensätzliche Rollen einander zu einem Ganzen ergänzen, da sie sich ihren natürlichen Anlagen entsprechend einbringen. Ethik von der Familie als Kern aus zu denken, ist die Balance zwischen Universalismus und Tribalismus. Die Familie steht einem näher als alle anderen, ihr ist man zuhöchst verpflichtet, danach kommt die eigene Region, und dann die Nation, der Staat, und erst danach die Menschheit als Ganzes. Es ist aber auch kein Tribalismus, in dem nur dem eigenen Stamm moralische Pflicht gilt. Die Menschlichkeit und Gerechtigkeit gelten gegen alle, aber die moralische Pflicht ist vom inneren Kreise, von der Familie ausgehend, abgestuft. Dem Eigenen gilt die höhere Pflicht als dem Fremden.
Konfuzius geht es nicht um eine abstrakt definierte Moral, sondern um eine individuelle, durch persönliches Beispiel gelebte Sittlichkeit. Er lehrte nicht durch logische Erklärungen, sondern Umschreibungen. „Als der Stall niederbrannte und Konfuzius zurück kehrte, fragte er: ‚Wurde jemand verletzt?‘ Er fragte nicht nach den Pferden.“ Dieses berühmte Zitat beleuchtet die Lehrweise Konfuzius und wie er Menschlichkeit definiert. Er sorgt sich nicht um den Besitz – die Pferde. Aber er sagt es nicht direkt, das Gleichnis umschreibt es nur. Es ist eben kein Kantianischer Imperativ, sondern eine Ermutigung zum persönlichen Vorbild. Von ihm stammt die berühmte Goldene Regel: „Füge anderen nicht zu, was du nicht willst, dass dir zugefügt wird.“ Dabei steht der Konfuzianismus zwischen den Extremen des Universalismus und Tribalismus. Es gibt eine Moral, eben die Menschlichkeit, die man allen Menschen gegenüber walten lässt; dennoch ist das Verhältnis der Einzelnen zueinander wichtig. Man verhält sich den Obigen gegenüber mit Respekt, den Unteren gegenüber mit Milde. Die Eltern leiten die Kinder mit Strenge und Güte, die Kinder achten die Eltern mit Respekt. Dies setzt sich in allen Bereichen fort: es gibt eben keine Gleichheit, aus der die Moral entspringt, sondern was sittlich ist, bestimmt das Verhältnis der Menschen, wie sie zueinander stehen. Damit wird die gesellschaftliche Ordnung aufrecht erhalten. Die Rollen der Menschen sind eben unterschiedlich, und das Urbild dazu ist die Familie. Der Vater als Beschützer und Leiter, die Mutter als nährend und umsorgend, die Kinder folgsam und respektvoll. Auch die Rollen von Mann und Frau können nicht die gleichen sein, sie sind Abbilder von Yin und Yang, dem männlichen Himmelsprinzip und dem weiblichen der Erde: der Himmel beleuchtet und überwölbt, die Erde trägt und nährt. Es ist keine Unfreiheit, keine Ungleichheit der Würde, aber es sind sich ergänzende Rollen, wie eben im Yin-Yang Symbol: zwei Teile deren gegensätzliche Rollen einander zu einem Ganzen ergänzen, da sie sich ihren natürlichen Anlagen entsprechend einbringen. Ethik von der Familie als Kern aus zu denken, ist die Balance zwischen Universalismus und Tribalismus. Die Familie steht einem näher als alle anderen, ihr ist man zuhöchst verpflichtet, danach kommt die eigene Region, und dann die Nation, der Staat, und erst danach die Menschheit als Ganzes. Es ist aber auch kein Tribalismus, in dem nur dem eigenen Stamm moralische Pflicht gilt. Die Menschlichkeit und Gerechtigkeit gelten gegen alle, aber die moralische Pflicht ist vom inneren Kreise, von der Familie ausgehend, abgestuft. Dem Eigenen gilt die höhere Pflicht als dem Fremden. Den fünften Grundpfeiler macht die Bildung, sie ist für Konfuzius Mittel und Selbstzweck zugleich. Unbildung war für ihn ein großer Fluch. „Ein Volk ohne Bildung in den Krieg führen, das heißt, es dem Untergang weihen.“ Hier kommen zwei Übel zusammen: ein ungebildetes Volk und eine Führung in Krieg und Gewalt: das kann nur schlecht ausgehen. Nur Bildung ermöglicht Verstehen, ermöglicht, seinen Platz und seinen Weg in der Gemeinschaft finden. Aber für Konfuzius, der sein Leben lang nicht den Erfolg seiner Lehre erlebte, war Bildung auch ein Trost, etwas um das man sich immer bemüht, um sein Wissen und seinen Charakter immer zu bessern. Für Konfuzius bezeichnet der Weg des Edlen Fleiß, Hingabe und immer wieder Selbstverbesserung, Lernen und Bildung erlangen. „Wer sich nie schämt, wie kann der sich bessern?“ Es ist diese Scham, die den Menschen heute abhanden gekommen ist im Westen. Man will sich nicht bessern, ja man kann sich gar nicht mehr bessern, weil keiner mehr ein rechtes Gefühl für die eigenen Unzulänglichkeiten hat. Jeder ist ein kleiner König, von Kindesbeinen an werden Menschen ermutigt, sich nicht zu ändern, dass alles was sie tun recht und billig sei. Wir wurden überschwemmt mit Ratgebern, die uns sagen, wir sind ok, egal wie wir sind, wir müssen alles akzeptieren und eine kritische Selbst-Befragung, die Notwendigkeit sich zu bessern, haben wir damit verloren. Es wurde den Menschen aberzogen sich zu schämen. Dumme, rohe, derbe Menschen werden uns überall vorgeführt, im Fernsehen, in der Politik ebenso. Es sind oben wie unten Menschen unfähig der Scham, eine schamlose Gesellschaft, die keinen Sinn für die eigenen Charakterschwächen mehr hat, die eigene Unbildung und Primitivität. „Die Alten hielten mit ihren Worten zurück, denn sie schämten sich, mit ihren Taten hinter ihren Worten zurück zu bleiben.“ Heute agieren die Leute im Westen genau umgekehrt: wer am lautesten Schreit und am größten angibt, der bekommt. Damit kommen die Dummen und die Primitiven nach oben.
Den fünften Grundpfeiler macht die Bildung, sie ist für Konfuzius Mittel und Selbstzweck zugleich. Unbildung war für ihn ein großer Fluch. „Ein Volk ohne Bildung in den Krieg führen, das heißt, es dem Untergang weihen.“ Hier kommen zwei Übel zusammen: ein ungebildetes Volk und eine Führung in Krieg und Gewalt: das kann nur schlecht ausgehen. Nur Bildung ermöglicht Verstehen, ermöglicht, seinen Platz und seinen Weg in der Gemeinschaft finden. Aber für Konfuzius, der sein Leben lang nicht den Erfolg seiner Lehre erlebte, war Bildung auch ein Trost, etwas um das man sich immer bemüht, um sein Wissen und seinen Charakter immer zu bessern. Für Konfuzius bezeichnet der Weg des Edlen Fleiß, Hingabe und immer wieder Selbstverbesserung, Lernen und Bildung erlangen. „Wer sich nie schämt, wie kann der sich bessern?“ Es ist diese Scham, die den Menschen heute abhanden gekommen ist im Westen. Man will sich nicht bessern, ja man kann sich gar nicht mehr bessern, weil keiner mehr ein rechtes Gefühl für die eigenen Unzulänglichkeiten hat. Jeder ist ein kleiner König, von Kindesbeinen an werden Menschen ermutigt, sich nicht zu ändern, dass alles was sie tun recht und billig sei. Wir wurden überschwemmt mit Ratgebern, die uns sagen, wir sind ok, egal wie wir sind, wir müssen alles akzeptieren und eine kritische Selbst-Befragung, die Notwendigkeit sich zu bessern, haben wir damit verloren. Es wurde den Menschen aberzogen sich zu schämen. Dumme, rohe, derbe Menschen werden uns überall vorgeführt, im Fernsehen, in der Politik ebenso. Es sind oben wie unten Menschen unfähig der Scham, eine schamlose Gesellschaft, die keinen Sinn für die eigenen Charakterschwächen mehr hat, die eigene Unbildung und Primitivität. „Die Alten hielten mit ihren Worten zurück, denn sie schämten sich, mit ihren Taten hinter ihren Worten zurück zu bleiben.“ Heute agieren die Leute im Westen genau umgekehrt: wer am lautesten Schreit und am größten angibt, der bekommt. Damit kommen die Dummen und die Primitiven nach oben.












 Si Evola naît dans une famille catholique et bourgeoise, il en rejette rapidement ces deux aspects. Le catholicisme, moral et sentimental, lui semble étranger à une véritable sacralité et une haute ascèse, loin de l’idéal « viril et aristocratique » du bouddhisme aryen. Son mépris de la vie bourgeoise lui fait refuser une chaire universitaire.
Si Evola naît dans une famille catholique et bourgeoise, il en rejette rapidement ces deux aspects. Le catholicisme, moral et sentimental, lui semble étranger à une véritable sacralité et une haute ascèse, loin de l’idéal « viril et aristocratique » du bouddhisme aryen. Son mépris de la vie bourgeoise lui fait refuser une chaire universitaire. Son ouvrage Chevaucher le tigre est un bilan de ses expériences, et un constat de réalisme ferme : rien ne peut être fait, ni artistiquement, ni religieusement, ni politiquement, pour provoquer un bouleversement positif au sein du monde moderne. Le seul horizon, c’est le chaos. Ce livre s’adresse aux hommes différenciés, ceux qui n’appartiennent pas intérieurement au monde moderne, qui sont de l’autre civilisation. Selon une image extrême-orientale, « si l’on réussit à chevaucher un tigre, on l’empêche de se jeter sur vous et, […] en outre, si l’on ne descend pas, si l’on maintient la prise, il se peut que l’on ait, à la fin, raison de lui. » Evola s’adresse aux « convives de pierre », aux Individus absolus, ceux qui ne peuvent ou ne veulent pas se détacher du monde actuel, et qui sont prêts à y vivre « sous les formes les plus paroxystiques ». Evola y examine, sous formes d’orientations existentielles, les possibilités d’émancipation totale de l’être par la mise en confrontation avec les processus destructeurs du monde moderne.
Son ouvrage Chevaucher le tigre est un bilan de ses expériences, et un constat de réalisme ferme : rien ne peut être fait, ni artistiquement, ni religieusement, ni politiquement, pour provoquer un bouleversement positif au sein du monde moderne. Le seul horizon, c’est le chaos. Ce livre s’adresse aux hommes différenciés, ceux qui n’appartiennent pas intérieurement au monde moderne, qui sont de l’autre civilisation. Selon une image extrême-orientale, « si l’on réussit à chevaucher un tigre, on l’empêche de se jeter sur vous et, […] en outre, si l’on ne descend pas, si l’on maintient la prise, il se peut que l’on ait, à la fin, raison de lui. » Evola s’adresse aux « convives de pierre », aux Individus absolus, ceux qui ne peuvent ou ne veulent pas se détacher du monde actuel, et qui sont prêts à y vivre « sous les formes les plus paroxystiques ». Evola y examine, sous formes d’orientations existentielles, les possibilités d’émancipation totale de l’être par la mise en confrontation avec les processus destructeurs du monde moderne.






 Sin lugar a dudas, a primera vista, el ojo inexperto sería incapaz de distinguir a una persona aleví del resto de musulmanes. Incluso sus centros de culto, decorados en ocasiones con cúpulas y minaretes, podrían pasar, vistos desde el exterior, como una mezquita más. No obstante, a medida que se curiosea con mayor detalle, se dará cuenta de las enormes diferencias existentes entre la comunidad alevi y los suníes y shiíes. Pero, ¿quiénes son los alevíes?
Sin lugar a dudas, a primera vista, el ojo inexperto sería incapaz de distinguir a una persona aleví del resto de musulmanes. Incluso sus centros de culto, decorados en ocasiones con cúpulas y minaretes, podrían pasar, vistos desde el exterior, como una mezquita más. No obstante, a medida que se curiosea con mayor detalle, se dará cuenta de las enormes diferencias existentes entre la comunidad alevi y los suníes y shiíes. Pero, ¿quiénes son los alevíes?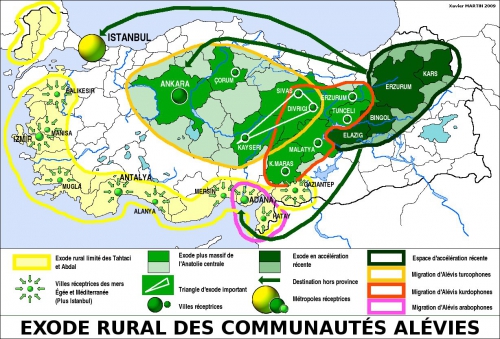



 Posteriormente, tras la década de 1990, los movimientos islamistas articularían una identidad nacional alternativa que definiría la nación como una civilización otomana esencialmente islámica, en contraste con la identidad oficial, laica y occidentalizada. De esta nueva concepción de la república turca nacería, en agosto de 2001, el Partido de la Justicia y el Desarrollo (AKP por sus siglas en turco), liderado por el actual presidente, Recep Tayyip Erdogan. Quince meses después se celebrarían las elecciones,
Posteriormente, tras la década de 1990, los movimientos islamistas articularían una identidad nacional alternativa que definiría la nación como una civilización otomana esencialmente islámica, en contraste con la identidad oficial, laica y occidentalizada. De esta nueva concepción de la república turca nacería, en agosto de 2001, el Partido de la Justicia y el Desarrollo (AKP por sus siglas en turco), liderado por el actual presidente, Recep Tayyip Erdogan. Quince meses después se celebrarían las elecciones, 
 On retrouve nettement dans ses écrits l’influence de trois philosophes : Carlo Michelstaedter, sur la question de l’autonomie de l’être (Phénoménologie de l’Individu Absolu) ; Otto Weininger, sur sa lecture de la déviation matriarcale de la spiritualité (Révolte contre le monde moderne) ; et enfin Friedrich Nietzsche, dans sa vision antibourgeoise de l’homme différencié (Chevaucher le tigre).
On retrouve nettement dans ses écrits l’influence de trois philosophes : Carlo Michelstaedter, sur la question de l’autonomie de l’être (Phénoménologie de l’Individu Absolu) ; Otto Weininger, sur sa lecture de la déviation matriarcale de la spiritualité (Révolte contre le monde moderne) ; et enfin Friedrich Nietzsche, dans sa vision antibourgeoise de l’homme différencié (Chevaucher le tigre). Evola emprunte à Johann Jakob Bachofen sa lecture de la morphologie des civilisations, en rejetant l’aspect évolutionniste, y préférant la thèse involutive de Guénon. Tout au long de l’histoire connue, on a assisté à une altération du monde de la Tradition, avec notamment la dissociation entre autorité spirituelle et pouvoir temporel, inséparables aux origines. La civilisation, à l’origine, est patriarcale, héroïque, solaire, olympienne, virile ; elle se détériore sous les influences altératrices de la civilisation matriarcale, lunaire, tellurique, chtonienne, et aboutit à l’âge sombre, au kali-yuga.
Evola emprunte à Johann Jakob Bachofen sa lecture de la morphologie des civilisations, en rejetant l’aspect évolutionniste, y préférant la thèse involutive de Guénon. Tout au long de l’histoire connue, on a assisté à une altération du monde de la Tradition, avec notamment la dissociation entre autorité spirituelle et pouvoir temporel, inséparables aux origines. La civilisation, à l’origine, est patriarcale, héroïque, solaire, olympienne, virile ; elle se détériore sous les influences altératrices de la civilisation matriarcale, lunaire, tellurique, chtonienne, et aboutit à l’âge sombre, au kali-yuga. Son ouvrage Chevaucher le tigre est un bilan de ses expériences, et un constat de réalisme ferme : rien ne peut être fait, ni artistiquement, ni religieusement, ni politiquement, pour provoquer un bouleversement positif au sein du monde moderne. Le seul horizon, c’est le chaos. Ce livre s’adresse aux hommes différenciés, ceux qui n’appartiennent pas intérieurement au monde moderne, qui sont de l’autre civilisation. Selon une image extrême-orientale, « si l’on réussit à chevaucher un tigre, on l’empêche de se jeter sur vous et, […] en outre, si l’on ne descend pas, si l’on maintient la prise, il se peut que l’on ait, à la fin, raison de lui. » Evola s’adresse aux « convives de pierre », aux Individus absolus, ceux qui ne peuvent ou ne veulent pas se détacher du monde actuel, et qui sont prêts à y vivre « sous les formes les plus paroxystiques ». Evola y examine, sous formes d’orientations existentielles, les possibilités d’émancipation totale de l’être par la mise en confrontation avec les processus destructeurs du monde moderne.
Son ouvrage Chevaucher le tigre est un bilan de ses expériences, et un constat de réalisme ferme : rien ne peut être fait, ni artistiquement, ni religieusement, ni politiquement, pour provoquer un bouleversement positif au sein du monde moderne. Le seul horizon, c’est le chaos. Ce livre s’adresse aux hommes différenciés, ceux qui n’appartiennent pas intérieurement au monde moderne, qui sont de l’autre civilisation. Selon une image extrême-orientale, « si l’on réussit à chevaucher un tigre, on l’empêche de se jeter sur vous et, […] en outre, si l’on ne descend pas, si l’on maintient la prise, il se peut que l’on ait, à la fin, raison de lui. » Evola s’adresse aux « convives de pierre », aux Individus absolus, ceux qui ne peuvent ou ne veulent pas se détacher du monde actuel, et qui sont prêts à y vivre « sous les formes les plus paroxystiques ». Evola y examine, sous formes d’orientations existentielles, les possibilités d’émancipation totale de l’être par la mise en confrontation avec les processus destructeurs du monde moderne.

 Durante estos años, y bajo el influjo permanente de los escritos de
Durante estos años, y bajo el influjo permanente de los escritos de  Evola mantiene un discurso constante en el que asocia todas las formas de
Evola mantiene un discurso constante en el que asocia todas las formas de  El otro gran representante de la Tradición Romana es Guido De Giorgio, el principal discípulo del pensamiento de René Guénon en Italia, un hombre oscuro, tanto en su trayectoria vital como en aquella intelectual, de una moral espartana, y definido por el propio Evola como un «iniciado en estado salvaje». Su principal obra, La Tradición Romana, fue publicada póstumamente, en el año 1973, y todavía a día de hoy existen obras inéditas del autor, que no han visto la luz todavía. Las premisas del pensamiento de Giorgio, como ocurre con Guénon, parten de un punto de vista absoluto, metafísico, sacro y Tradicional. No obstante su visión de la Tradición como tal cuenta con la confluencia de muy variadas influencias, entre las cuales podemos encontrar a los neoplatónicos, cristianos, hinduistas y musulmanes. A las citadas fuentes que nutren su pensamiento podemos añadir una peculiar forma de escribir, muchas veces teñida de una cierta iluminación, de una intuición muy sutil, y lo enigmáticos que resultan muchos de los pasajes de su obra. Un ejemplo de esta confluencia de ideas y doctrinas la vemos en sus consideraciones, de matiz claramente cristiano, en las que habla de la fe como la base de la Tradición por excelencia, al tiempo que contempla la concepción no dualista del Principio Supremo en lo que es un concepto de impronta hinduista. Sin embargo, la perspectiva islámica es la que toma mayor protagonismo en el conjunto de sus ideas, y es precisamente en base a esta
El otro gran representante de la Tradición Romana es Guido De Giorgio, el principal discípulo del pensamiento de René Guénon en Italia, un hombre oscuro, tanto en su trayectoria vital como en aquella intelectual, de una moral espartana, y definido por el propio Evola como un «iniciado en estado salvaje». Su principal obra, La Tradición Romana, fue publicada póstumamente, en el año 1973, y todavía a día de hoy existen obras inéditas del autor, que no han visto la luz todavía. Las premisas del pensamiento de Giorgio, como ocurre con Guénon, parten de un punto de vista absoluto, metafísico, sacro y Tradicional. No obstante su visión de la Tradición como tal cuenta con la confluencia de muy variadas influencias, entre las cuales podemos encontrar a los neoplatónicos, cristianos, hinduistas y musulmanes. A las citadas fuentes que nutren su pensamiento podemos añadir una peculiar forma de escribir, muchas veces teñida de una cierta iluminación, de una intuición muy sutil, y lo enigmáticos que resultan muchos de los pasajes de su obra. Un ejemplo de esta confluencia de ideas y doctrinas la vemos en sus consideraciones, de matiz claramente cristiano, en las que habla de la fe como la base de la Tradición por excelencia, al tiempo que contempla la concepción no dualista del Principio Supremo en lo que es un concepto de impronta hinduista. Sin embargo, la perspectiva islámica es la que toma mayor protagonismo en el conjunto de sus ideas, y es precisamente en base a esta 




 Descartes, amongst other seminal Modern thinkers, provided the philosophical impetus for the forces which would reduce human life to a set of Cartesian coördinates plotted within Weber’s Iron Cage along an x-axis: Reason, and a y-axis: Will—a parody of the Axis Mundi or the double Axe of the ancient god-kings (the prehistoric Cross) which served as the central symbols of the Traditional world. Philosophy was converted from a pursuit of eternal truths into a secular science which emphasized the power of human reason to manipulate the world. Nietzsche was perfectly justified in concluding, if flippantly, that “reason is only an instrument, and Descartes was superficial.”2
Descartes, amongst other seminal Modern thinkers, provided the philosophical impetus for the forces which would reduce human life to a set of Cartesian coördinates plotted within Weber’s Iron Cage along an x-axis: Reason, and a y-axis: Will—a parody of the Axis Mundi or the double Axe of the ancient god-kings (the prehistoric Cross) which served as the central symbols of the Traditional world. Philosophy was converted from a pursuit of eternal truths into a secular science which emphasized the power of human reason to manipulate the world. Nietzsche was perfectly justified in concluding, if flippantly, that “reason is only an instrument, and Descartes was superficial.”2
 From the Indo-Europeans to Mesoamerica, we find that the great traditional civilisations divided world history into Four Ages, a cosmic cycle between Creation and final destruction in which the overall trend is one of inevitable entropy and degeneration. Hesiod, Ovid, and the ancient Iranians, amongst others, identify the successive ages with Gold, Silver, Bronze (or Copper), and Iron. The Traditionalist conception of time is helical: neither linear (contra the myth of Eternal Progress) nor an endless cycle of Eternal Returns—pacĕ Nietzsche, Eliade, and modern Hinduism). The helix is made up of a succession of ever-decreasing cycles of cultural and spiritual disintegration, like the diminishing periods of a free-swinging pendulum) around a central axis. Heraclitus never stepped twice in the same river, and history never exactly repeats itself, but the beginning of a cycle foreshadows its end.15
From the Indo-Europeans to Mesoamerica, we find that the great traditional civilisations divided world history into Four Ages, a cosmic cycle between Creation and final destruction in which the overall trend is one of inevitable entropy and degeneration. Hesiod, Ovid, and the ancient Iranians, amongst others, identify the successive ages with Gold, Silver, Bronze (or Copper), and Iron. The Traditionalist conception of time is helical: neither linear (contra the myth of Eternal Progress) nor an endless cycle of Eternal Returns—pacĕ Nietzsche, Eliade, and modern Hinduism). The helix is made up of a succession of ever-decreasing cycles of cultural and spiritual disintegration, like the diminishing periods of a free-swinging pendulum) around a central axis. Heraclitus never stepped twice in the same river, and history never exactly repeats itself, but the beginning of a cycle foreshadows its end.15

 The North is the land where the sun never sets, a place of undying light. Every sacred tradition honours the Centre, the point where contrasts are resolved, the symbolic place not subject to the laws of cosmic entropy. The North was the cardinal point chosen whereby the primæval Logos would reveal itself in History. Every divine revelation in human history represents a reëstablishment of that Centre.
The North is the land where the sun never sets, a place of undying light. Every sacred tradition honours the Centre, the point where contrasts are resolved, the symbolic place not subject to the laws of cosmic entropy. The North was the cardinal point chosen whereby the primæval Logos would reveal itself in History. Every divine revelation in human history represents a reëstablishment of that Centre. The Indian nationalist scholar, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, came to the same conclusion based on his analysis of the most ancient Hindu scriptures, the Vedas: “the poets of the Rig-Veda were acquainted with the climatic conditions witnessible only in the Arctic regions […] described by them […] directly in plain and simple words.”36
The Indian nationalist scholar, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, came to the same conclusion based on his analysis of the most ancient Hindu scriptures, the Vedas: “the poets of the Rig-Veda were acquainted with the climatic conditions witnessible only in the Arctic regions […] described by them […] directly in plain and simple words.”36 The Sun—with its qualities of immobility, immutability, and stability—symbolized the supreme God, and the positive, masculine principles of his divine nature.42 The axial motif of the Sun radiating from the summit of the Tree at the world’s Centre symbolized the Saviour or divine Son. For example, the Orphic Hymn to Apollo—grandson of the Titan Polus, ‘Pole’—praises the god for harmonizing the opposite poles of the cosmos with his lyre. This imagery harks back to the falcon Horus—god of the sun and the Pole—king and messiah of Egypt, who is depicted as alighting upon the Djed or column of Stability at the creation of the Earth.
The Sun—with its qualities of immobility, immutability, and stability—symbolized the supreme God, and the positive, masculine principles of his divine nature.42 The axial motif of the Sun radiating from the summit of the Tree at the world’s Centre symbolized the Saviour or divine Son. For example, the Orphic Hymn to Apollo—grandson of the Titan Polus, ‘Pole’—praises the god for harmonizing the opposite poles of the cosmos with his lyre. This imagery harks back to the falcon Horus—god of the sun and the Pole—king and messiah of Egypt, who is depicted as alighting upon the Djed or column of Stability at the creation of the Earth. Charles Upton, a student of Guénon, observed that the success of the Theosophists of yesterday and neopagans of today, in repackaging Hermetic teachings stripped of their religious and traditional context—along with, for example, belief “in UFOs and alien entities that bear all the marks of classical demons”—merely adds an ‘esoteric flavour’ to the Modern habit of explaining the mysteries of the world by reference to purely material causes: psychic powers, biological race, astronomical events and the like.46
Charles Upton, a student of Guénon, observed that the success of the Theosophists of yesterday and neopagans of today, in repackaging Hermetic teachings stripped of their religious and traditional context—along with, for example, belief “in UFOs and alien entities that bear all the marks of classical demons”—merely adds an ‘esoteric flavour’ to the Modern habit of explaining the mysteries of the world by reference to purely material causes: psychic powers, biological race, astronomical events and the like.46 Traditionalism posits that all religions are derived from a body of core truths, a Divine Revelation, known as the Philosophia Perennis or ‘Perennial Philosophy.’ The Philosophia Perennis is fundamentally monotheistic, as can be seen in its Semitic and even its apparently polytheistic Indo-European branches; this has been argued most cogently by Ananda Coomaraswamy.51 The Traditional doctrine—that monotheism belongs to the earliest, primordial layer of every religion, only later degenerating into polytheism and idolatry—was proven by Pater Wilhelm Schmidt, founder of the Vienna School of ethnology.52
Traditionalism posits that all religions are derived from a body of core truths, a Divine Revelation, known as the Philosophia Perennis or ‘Perennial Philosophy.’ The Philosophia Perennis is fundamentally monotheistic, as can be seen in its Semitic and even its apparently polytheistic Indo-European branches; this has been argued most cogently by Ananda Coomaraswamy.51 The Traditional doctrine—that monotheism belongs to the earliest, primordial layer of every religion, only later degenerating into polytheism and idolatry—was proven by Pater Wilhelm Schmidt, founder of the Vienna School of ethnology.52

 The subject of Nicolás Gómez Dávila’s Text Implicite is democracy. According to the Author, democracy is a new religion; more precisely, an anthropotheistic religion in which Man is presented as God. The Catholic Thinker therefore concludes that the ultimate consequence can only be to treat democracy as if it were a form of Satanism.
The subject of Nicolás Gómez Dávila’s Text Implicite is democracy. According to the Author, democracy is a new religion; more precisely, an anthropotheistic religion in which Man is presented as God. The Catholic Thinker therefore concludes that the ultimate consequence can only be to treat democracy as if it were a form of Satanism. According to Nicolás Gómez Dávila, the sovereign Will reigns in liberal and individualistic democracies, while the authentic Will reigns in collective and despotic democracies. In his characterisation of the democratic religion, the Author of the Scholia holds that “the transformation of a liberal and individualistic democracy, into a collective and despotic democracy, does not molest the democratic intention, nor does it depart from its promised objectives.”23 This is because the law of the democratic Will has the mandate to coerce the obedience of the individual Will, due to the fact that the individual Will “sins against its [i.e. the democratic Will’s] own being.”24 Summarising thus far, the Bogotán writes that “continued faith in the democratic ideal interferes with the immediate objectives of the authoritarian democrat, who enslaves in the name of freedom and awaits the coming of a god from without the depraved masses.”25 Thus in the context of Man’s supposed omnipotence, Gómez recalls democracy’s resulting abuse of technology and the “inexorable industrial exploitation of the planet.”26
According to Nicolás Gómez Dávila, the sovereign Will reigns in liberal and individualistic democracies, while the authentic Will reigns in collective and despotic democracies. In his characterisation of the democratic religion, the Author of the Scholia holds that “the transformation of a liberal and individualistic democracy, into a collective and despotic democracy, does not molest the democratic intention, nor does it depart from its promised objectives.”23 This is because the law of the democratic Will has the mandate to coerce the obedience of the individual Will, due to the fact that the individual Will “sins against its [i.e. the democratic Will’s] own being.”24 Summarising thus far, the Bogotán writes that “continued faith in the democratic ideal interferes with the immediate objectives of the authoritarian democrat, who enslaves in the name of freedom and awaits the coming of a god from without the depraved masses.”25 Thus in the context of Man’s supposed omnipotence, Gómez recalls democracy’s resulting abuse of technology and the “inexorable industrial exploitation of the planet.”26 The geneology of Gnosticism is not foreign to Gómez: “the birth of gnosis can evidently be traced to the pre-Christian era, yet its poison has evolved in the shadow of Christianity.”46 Thus the Bogotán ceases to associate Platonism – to which he is endeared – with Gnosticism and directs his suspicions towards Stoicism47 – which he despises: “The Greek roots of Gnosticism spätantike are not found in Platonic dualism but in Stoic monism.”48
The geneology of Gnosticism is not foreign to Gómez: “the birth of gnosis can evidently be traced to the pre-Christian era, yet its poison has evolved in the shadow of Christianity.”46 Thus the Bogotán ceases to associate Platonism – to which he is endeared – with Gnosticism and directs his suspicions towards Stoicism47 – which he despises: “The Greek roots of Gnosticism spätantike are not found in Platonic dualism but in Stoic monism.”48 In the second century A.D., Gnosticism was customarily concerned with the Fall of the divine entity; Manicheanism, associated with the gnostic dualist religious currents begotten by Mani in the third century A.D., concerned itself with the duality of and struggle between Good and Evil. After contact with Christianity, Gnosticism assumed the religious elements of Judaism and Christianity, e.g. revelation per se, and in particular the revelation of Christ and the revelation contained in the Scriptures. In the womb of Christianity, Gnosticism stimulates numerous heresies (e.g. Valentinius of Phrebonis and his disciples). Manichaeism is presented as a continuation of Gnosticism, and the inheritors of both currents are the Pualines, Bogomils and Cathars. Gómez does not fully agree with this classification and seems to contradict it, as he earlier writes in Textos I:
In the second century A.D., Gnosticism was customarily concerned with the Fall of the divine entity; Manicheanism, associated with the gnostic dualist religious currents begotten by Mani in the third century A.D., concerned itself with the duality of and struggle between Good and Evil. After contact with Christianity, Gnosticism assumed the religious elements of Judaism and Christianity, e.g. revelation per se, and in particular the revelation of Christ and the revelation contained in the Scriptures. In the womb of Christianity, Gnosticism stimulates numerous heresies (e.g. Valentinius of Phrebonis and his disciples). Manichaeism is presented as a continuation of Gnosticism, and the inheritors of both currents are the Pualines, Bogomils and Cathars. Gómez does not fully agree with this classification and seems to contradict it, as he earlier writes in Textos I: Another famous Gnostic is Valentine, who studied Platonism and the secret wisdom of Egypt in Alexandria, and who attended Isidore’s lectures. He established two schools: the Eastern (Alexandria) and the Italian (Rome). The Eastern School interprets the Book of Genesis and the Evangelia, and develops the theory of the Eons which emanate in primordial pairs (Jesus is here one of the greatest Eons). There is a fundamental difference between the ‘good god’ (the Most High primordial Absolute71) and the Demiurge of the world. Equally, Man is represented dualistically. Within him co-exist two elements: the first, originating from the Evil Demiurge and his Angels (impulses are the bad spirits); the second originate from the ‘good god’. Redemption is necessary. It is made possible through the revelation of Jesus Christ. The Eastern School speaks of three types of Man:
Another famous Gnostic is Valentine, who studied Platonism and the secret wisdom of Egypt in Alexandria, and who attended Isidore’s lectures. He established two schools: the Eastern (Alexandria) and the Italian (Rome). The Eastern School interprets the Book of Genesis and the Evangelia, and develops the theory of the Eons which emanate in primordial pairs (Jesus is here one of the greatest Eons). There is a fundamental difference between the ‘good god’ (the Most High primordial Absolute71) and the Demiurge of the world. Equally, Man is represented dualistically. Within him co-exist two elements: the first, originating from the Evil Demiurge and his Angels (impulses are the bad spirits); the second originate from the ‘good god’. Redemption is necessary. It is made possible through the revelation of Jesus Christ. The Eastern School speaks of three types of Man:


