Ex: http://www.counter-currents.com
I have known Jaroslaw for a long time. He always impressed me as a highly erudite individual. We are both active in writing articles on the New Right and in various metapolitical organizations. We agreed to exchange interviews, so I will provide an interview for Szturm magazine and Jaroslaw for Reconquista.
Jaroslaw is a very interesting personality. We first met at the black metal festival Asgardsrei [2], from where Jaroslaw wrote reports on the popular American website Counter-Currents (CC). In addition to black metal and alternative music in general, Jaroslaw also engages in other activities, writes articles at CC [3], and translates longer essays for the Polish Szturm magazine.
Until recently, he also worked at the university, but due to the excessive political correctness of this environment and personal dissatisfaction, he moved to the private sphere. Today he pursues a professional career, travels the world, and tries to cultivate the Polish patriotic scene. He himself devotes a lot of space to historical novels and poetry, which is rather rare in the circles where we both move. Jaroslaw does what he considers right in life and takes a positively realistic approach.
In the first part of the interview, he will tell us something about Polish politics, contemporary nationalist organizations, the EU and possible Polexit, the most important patriotic event Marszi Niepodległości, the magazine and organization Szturm, the geopolitics of Intermarium, contemporary censorship, and how different religious denominations come together.

Ondrej Mann: What is the actual political situation in Poland?
Jaroslaw Ostrogniew: First of all, thank you for sending me the questions and for giving me a chance to present Szturm to the readers of your magazine! And now back to the question — I see you want to jump into the deepest waters right away. So let’s try — the political situation in Poland is quite complicated, but I will talk about the most important points. The ruling party is Prawo I Sprawiedliwość (though they are actually in a coalition with smaller conservative parties), who are ruling now for the second term. In the foreign media they are portrayed as “evil nationalists,” but this is completely not the case. They are a kind of conservative populist mild party, and as is always the case with such parties, they are generally less to the Right than their constituency. Some of their policies are good, some are bad, and some are terrible and disastrous. You have to remember that the previous ruling party (the center-liberal Platforma Obywatelska) reached unbelievable levels of corruption, hubris, EU ass-kissing, liberal stupidity, and unwillingness to do anything besides cling to political power, that it eventually collapsed under its own weight. So anything that came afterward seemed to be better. The coronavirus pandemic is also something that keeps the popularity of the government high, as they are rather effective in their actions, especially compared to “old EU” countries, such as Italy or Spain.

Prawo I Sprawiedliwość enjoys large popularity in Polish society, but it is a kind of “pragmatic relationship without love.” People see the positive impact of the pro-social policies introduced by Prawo I Sprawiedliwość and they believe that there is no better alternative, but most of them do not really like the party, and the leader, Jarosław Kaczyński, is widely disliked even by the people who vote for his party. There are two very important and very good things that Prawo I Sprawiedliwość introduced. The first one is the introduction of pro-family social policies, namely the program 500+. The idea is very simple: every family gets 500 PLN [Polish złoty] per month per every non-adult child in the family from the state’s budget, regardless of the parents’ income. You have to remember Poland had one of the lowest social support systems in Europe. For instance, the only support a family would get would be a one-time payment of 1000 PLN when the child was born, and that was it. The second good accomplishment is that the government managed to strengthen the Polish tax system, especially the VAT tax, which was being avoided by large companies on a massive scale. This tax reform provided the funds for the social programs. The bad things about the current government are that it is rather “cuckservative”: they support civic nationalism, mass immigration, they are powerless against international corporations (which still do not pay any taxes in Poland), they tolerate Leftist extremism in the universities, they keep virtue signaling to the liberal media, and attacking the nationalists. They are also very pro-EU (they have some small feuds with EU, but mostly follow the general line in the most important matters), very pro-US (the American ambassador even dictates policies which are later being enabled by the government) and extremely pro-Zionist.

There are two terrible and disastrous things that the Prawo I Sprawiedliwość government has enabled. The first one is mass immigration to Poland. It is interesting, because one of the main slogans of this party is not accepting Muslim refugees into Poland (but on the other hand spending a large amount of public funds on help for refugees in Middle Eastern countries). However, the same government has opened the Polish job market to workers from outside of the EU. The government makes sure that the official figures are lowered, but it can be estimated that now there are more immigrants in Poland than there have ever been combined in our contemporary history. Most of the workers are coming from Ukraine — I must emphasize I have nothing against Ukrainians, I think this is one of the countries Poland has most connections with and I spend time and effort to strengthen the ties between nationalists in these two countries. However, accepting over one million people from another country in one year is not a good idea. As usual, the economically worse-off workers from Ukraine have been used by capital to keep wages low and working conditions bad in Poland. Mass immigration is the reserve army of capital and it has been used for this sole purpose again and again — this was the case with Yugoslav and Turkish workers in former West Germany, with Polish workers in the United Kingdom, and now with the Ukrainian workers in Poland. It is harmful to both Ukraine and Poland. What is even worse is that capital is never satisfied — both international corporations and large Polish companies have successfully pushed for accepting workers from outside of Europe, mostly India and the Philippines. Before Prawo I Sprawiedliwość came to power, Poland had been an almost completely ethnically homogeneous country. Now we have an extremely large European minority and growing large non-European minorities. Right now, in the largest Polish cities, Uber Eats and such services are dominated by non-whites. Ethnically speaking, Warsaw looks pretty much like Berlin, Paris, or London. And we know that we can expect another wave of non-European immigrants right after this pandemic is over.
The second disastrous thing “achieved” by our current government is the onslaught of Leftist extremism in Poland. It is another paradox, because Prawo I Sprawiedliwość presents itself as a conservative party. They even use the public media to attack Leftists and liberals. However, they are a dog that barks a lot but never bites. Leftist organizations still receive funds from the state (and funding from outside has really increased lately), Leftists can freely abuse the education system and the academia to push their agenda and attack their opponents, as well as organize their demonstrations and marches unharmed by the state and protected by the police from the wrath of the people. Just to give you an example: under the current government, there were “LGBT pride parades” (legal and actively protected by the police) organized in every Polish major city. Something like this has never happened before, not even in the time when Poland was ruled by the post-Communist social democrats.

So, as you see from this summary, our current political situation is complicated, and the ruling party is a very mixed bag. I personally think that Prawo I Sprawiedliwość is in some aspects better than the previous ruling party, that the pro-social policies and the better tax system are real accomplishments, but many of their policies, especially pushing mass immigration, are already bringing disastrous consequences to Poland, and will have even worse consequences in the future.
OM: What is your opinion on Polish conservative and nationalist parties? Ruch Narodowy, Kukiz ’15, Konfederacja Wolność i Niepodległość, and currently the strongest Prawo i Sprawiedliwość?
JO: Well, I think I said enough about Prawo I Sprawiedliwość in the previous answer. Ruch Narodowy is an initiative that started out as a new expression of the Polish tradition of national democracy. However, it gradually softened its message to appeal to the more “common people” — or, to use a better expression, to the normies of all ages — to gain more votes and get into Parliament. Eventually, it became a conservative movement with some national flavor (mostly petty chauvinism and civic nationalism), but it is definitely not a nationalist initiative. Once their representatives got into Parliament, they mostly became interested in keeping their seats and got engaged in some pretty weird virtue-signaling. For instance, they proposed a strengthening of the infamous Article 256 of the Polish penal code, which is the basis of persecution of Polish nationalists. They also get into the “anti-fascists are the real fascists” and “Muslims threaten our modern way of life” cuckservative stuff all the time. So basically speaking, Ruch Narodowy is not a nationalist initiative and is an example of another wasted opportunity in Polish politics.

Kukiz ‘15 was an interesting phenomenon, as it was the first Polish populist initiative that really gained popular support. It was a coalition of various groups and individuals, representing the whole political spectrum, but united in their opposition to the existing political system. The leader of this movement, Paweł Kukiz, is an interesting figure, as he is a musician coming from the Polish punk rock scene (which always had a strong anti-communist aspect), who started emphasizing patriotic (but definitely not nationalist) themes in his later songs and who was a supporter of the liberal Platforma Obywatelska, but later became one of their main opponents. As usual with such populist initiatives, they live for a very short moment, kept together only by a charismatic leader and the goal to overthrow or reform the system — and Kukiz ’15 started to dissolve right after it got into Parliament. Now, to stay active, they cooperate with the Polish agrarian party: Polskie Stronnictwo Ludowe.
Konfederacja is a kind of attempt at repeating the success of Kukiz ’15: creating a loose populist coalition of various organizations opposing the existing system. However, Konfederacja became dominated by free-market liberals (whose leader is Janusz Korwin-Mikke, whom your readers might know from various YouTube clips), and right now their main slogan is “fighting socialism” (and they consider anyone who is not libertarian to be a socialist, so. . .) by reducing or removing taxes and public services. It is not a nationalist initiative at all, and it definitely does not have anything to do with the new nationalism Szturm represents.
OM: There is a lot of discussion in the Czech Republic that as soon as Poland brings more money into the EU than it receives, it will leave the EU. Is Polexit possible?
JO: First of all, it is a good question — whether Poland gets more from the EU than it gives. And the answer depends on how you count the money. The second thing is that Poland is one of the most pro-EU countries in Europe. Many people do not like the whole ideological aspect of the EU, the push for LGBT propaganda, or the “refugees” quotas, but they consider Polish membership in the EU as a huge achievement and associate it with better infrastructure and the possibility to travel without passports. When talking to normies (especially those of the older generation) the most difficult issue is to convince them that we need a Polexit. I became involved in nationalism at the time Poland was entering the EU, so it is quite obvious I have been anti-EU for some time, but once I started working on the EU project, I truly understood that the EU is the main obstacle to solving all of the main problems of Europe. The EU is a barely-working bureaucracy, which has the power only to counteract anything productive, and it uses enormous amounts of money to create and maintain a whole class of parasites living on EU funds. Unfortunately, Poland is one of these countries, where this parasitic class is relatively strong and has a big influence on public opinion.
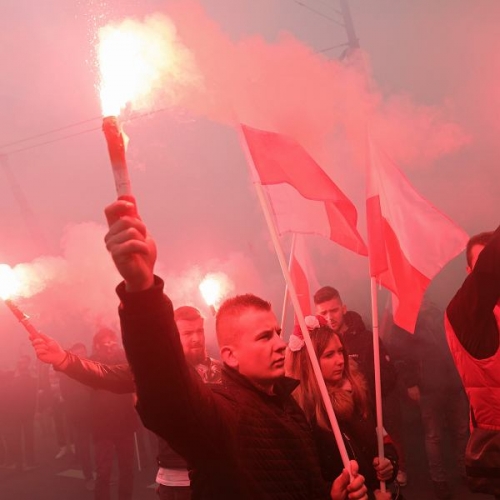

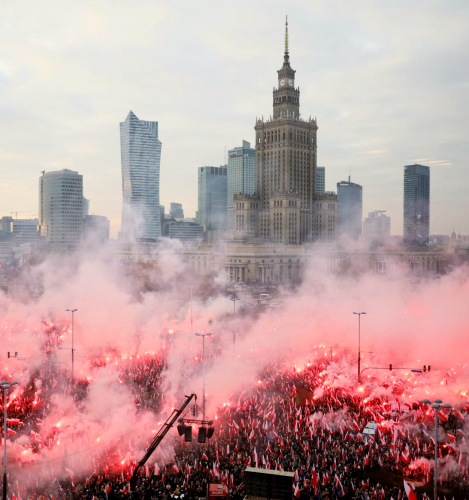
OM: Do you have any comments about Marsz Niepodległości?
JO: This is a complicated issue. Marsz Niepodległości was at first a strictly nationalist event, with very low attendance. This started to change when football fans and later more regular young people began attending this event. You have to remember, that in Poland since the change of regime in 1989, there was a phenomenon of “pedagogy of shame.” It was promoted by Leftist and liberal circles (also more pro-EU oriented central circles). The basic idea was that Poles are an evil nation, responsible for the persecution of various minorities throughout our history culminating after the First World War in Polish antisemitism, and that Poles need to atone for their sins as the “specter of Polish nationalism” can rise anytime soon. Any kind of display of national pride was scorned by our liberal elites and any form of Polish patriotism was associated with antisemitism or Nazism. This “pedagogy of shame” was present in all mainstream Polish media, in our school system, in our political discourse, even in the disputes among the common Poles. When Marsz Niepodległości began to attract more people, especially the regular people, the media and the politicians attacked it on all fronts, branding it as an expression of the returning Polish antisemitism, etc. However, this worked the opposite way, since many more regular people started to attend the event every year. The ruling party at the time (the liberal Platforma Obywatelska) decided to use force against the march (including regular police violence, lots of police provocations, and outright persecution of both organizers and attendants of the march). Again, this attracted more and more regular people, and Marsz Niepodległości became the main anti-establishment event in Poland. However, once the conservative Prawo I Sprawiedliwość party gained power, police stopped attacking the event, and Marsz Niepodległości gradually became a more regular patriotic event. The ruling party does all it can do that the march not become a nationalist event. For example, every year, editors of Szturm are arrested under false accusations right before the march and later released without any charges right after the event. To sum it all up: on the one hand, Marsz Niepodległości is an interesting, large patriotic event, which can be especially impressive to people from other countries. On the other hand, it has lost much of its nationalist color: it is a regular patriotic event, with an ever-stronger “cuckservative” flavor. Lots of the energy of past marches has gone to waste. However, Polish nationalists such as Szturm or Nacjonalistyczne Południe (with the help of our comrades from other countries) are making sure that there is a strong nationalist presence during the event by forming a nationalist bloc in the march.

OM: Does Szturm also have a geopolitical vision? Intermarium, V4, Eurosibirsk?
JO: Yes, geopolitics and international relationships are one of our key focus points. Our main idea is to overcome prejudice among European nations and ethnic chauvinism among European nationalists. This means both standing against chauvinist attitudes among Polish nationalists, but also against anti-Polish resentments among nationalists from other countries. Szturm is first and foremost a ground for discussion of various ideas among Polish nationalists, not a loudspeaker for promoting one and only “correct” vision of nationalism. Many articles published in Szturm are dedicated to the problem of geopolitics and international relationships and the authors do not agree on everything. However, there is no doubt among us that in contemporary circumstances all European nations need to awaken and stand together against the common threats: both eternal (such as non-European immigration) and internal (such as liberalism). The most popular position among our writers is Intermarium. I personally am a proponent of looking further West and East and making the Intermarium bloc not an opposition against Western Europe or Russia, but a rallying point for European nationalists, whose ultimate goal is the establishment of nationalism in all European countries. For me, the goal is the united Europe of nations, which will form an autarchy — a self-sustainable economic and political bloc independent of other geopolitical blocs. This cannot be achieved only in one part of Europe. Another idea I promote in Szturm is that the Americans are another European nation (but living on a different continent) that is being occupied by an alien government, and our enemy is the contemporary American system with its liberal imperialism, not the American nation (understood as a nation of European Americans).
OM: What is the purpose of Szturmowcy? And what means do you use for it?
JO: Szturmowcy was an organization connected with the ideas propagated by the Szturm magazine. The brand of nationalism represented by Szturm is quite original, it even gained a name of its own: “szturmowy nacjonalizm,” so it was only a matter of time that such an organization would emerge. However, the organization and the magazine are not the same thing, and the organization wanted to become more independent, so they are now unaffiliated with the magazine, and some chapters even rebranded or disbanded. I cannot comment on the details as I was not a part of this organization. As is often the case, organizations are temporal while ideas are longer-lasting, which might have something to do with the fact that ideas are more about setting the goals (let’s say they belong to the level of strategy), while organizations are more about achieving these goals (let’s say they belong to the level of tactics) and need to adapt to the changing circumstances, which in Poland are difficult due to the rising persecution of nationalists by the state.

OM: Is there any persecution of dissidents, dismissal from work, bans on publishing books, censorship, doxing, concert cancellation in Poland?
JO: Yes. It is a serious problem and I have discussed it a little answering the previous questions. The basis of this persecution is Article 256 of the Polish penal code. And the persecution is now growing. One of the main reasons is the changing attitude of the politicians, persecutors, judges, or police — they believe in the false idea of the “hate crime”: namely, that words and thoughts are as important as actions and even a small comment in social media can lead to “another holocaust.” And this persecution has accelerated under the current government, which tries to virtue-signal the liberal media by persecuting nationalists. So any time there is any kind of nationalist event condemned by the media, the government will enforce fierce persecution to show that they have nothing to do with nationalism. Another problem is that the current government understands that the only alternative to the system that could be supported by Polish society is the nationalist movement, so they try to eradicate this real opposition. They especially target any forms of international cooperation — and they are right, because as we both know, the growing “nationalist international” is real, getting stronger both metapolitically and politically, and has already become a real challenge to the liberal system. In Poland, the state mostly focuses on active legal persecution of nationalists, while media and NGOs focus on finding and pointing out “wrongthink” in social media. The whole phenomenon of doxing in Poland has got to a whole new level — there are organizations dedicated only to this aim, and they focus not on actual nationalists, but some random people writing mean comments on social media. So they dox and harass literally hundreds of people every month for writing things like “fuck Muslims” on Facebook. The leader of one of these organizations is an interesting person — he had an NGO and ran a theater, but he used this as an opportunity to steal money from his Leftist colleagues. He was convicted of fraud and theft by the court, and he ran away to Norway where he successfully pleaded for refugee status, claiming that he was persecuted for his sexual orientation (he is married and has children, so. . .). He is also morbidly obese — so now you have the whole picture of what kind of people organize online doxing in Poland.
OM: Does the state regulate censorship from the side of Facebook, YouTube, etc.?
JO: No. The Polish state cannot or does not want to do anything against international corporations. For instance, Amazon runs many of its stores in Poland, but like all corporations, they evade almost all taxes, and Poles cannot even order anything from these stores (we can only do it via Amazon Germany). The commodities and “sense” of late capitalism. . . But back to the question. As usual on corporate social media: the nationalists are persecuted, the Leftists are not. And as I mentioned, social media are the main tool of doxing and harassing by the Leftists and our courts refuse to do anything against it. Welcome to the brave new world.

Is there an Arktos-type publishing house or any New Right organization in Poland?
Unfortunately not, but we are working on it. There is no typically nationalist or New Right-focused publishing house in Poland, but there are nationalist and New Right books published by other publishing houses. For instance, Capitalbooks (which is a typically patriotic publisher) published the Polish translation of Daniel Friberg’s The Real Right Returns. There is a small publishing house, Arte, that publishes translations of Leon Degrelle and Robert Brasillach. Its main focus is on historical books. Szturm also publishes books: anthologies of the best essays first published online, booklets dealing with certain contemporary problems from the nationalist perspective, and new editions of some classics of the Polish nationalist thought. There are also interesting books by nationalist or New Right writers published by completely mainstream publishers, such as translations of Ernst Jünger, Yukio Mishima, Louis-Ferdinande Celine, Martin Heidegger, Carl Schmitt, Oswald Spengler, Carl Gustav Jung, Mircea Eliade, Knut Hamsun, Ezra Pound, or Gottfried Benn. The Polish translation of Kevin MacDonald’s Culture of Critique was published by one of the main publishers of humanist books. However, we definitely need a Polish publishing house similar to Arktos.
OM: Poland is quite a Catholic country, how do nationalists of different confessions come together?
JO: Poland is not such a Catholic country as most people assume. It is true that 95% of Poles officially belong to the Roman Catholic church, but most of them do not actively take part in religious life, except for such occasions as weddings or funerals. Another aspect of Polish Catholicism is that it is really shallow, and even many of the people who take part in religious ceremonies do it on an external level but do not have very strong religious convictions. So the really believing and really practicing Catholics are a minority in Poland. Another thing you have to remember is that Poland is quite a large country with some visible differences. There is a difference between Western and Eastern Poland, with Western Poland being more liberal and secular and Eastern Poland being more conservative and religious. It is similar to large cities and towns and villages. Religion is a subject taught in Polish public schools (even in kindergartens) but it is not obligatory, though most of the students attend these lessons. However, the secular tendencies in Polish society are more common especially among these generations, which attended religion in school. Also, Poles are famous for having very little knowledge about the Catholic faith, which may be connected with how these religious lessons are organized. There are also very strong anti-clerical tendencies in Poland, even among people who attend church. When it comes to teachings of the Church on such issues as sexuality, contraception, marriage and divorce, or abortion, the vast majority of Catholics in Poland do not agree with the church.

The case of Polish nationalism is also not so obvious, as the early Polish nationalists (the national democrats) were coming from the positivist and Darwinist circles, so they had a negative attitude towards religion. Even Roman Dmowski had this attitude at first; he just changed his mind when he realized how strong folk Catholicism was at that time and the importance of religion in the national identity of the masses, so he decided to use this to spread nationalism among the common people. But even then, for a long time, he was rather pro-Catholic than pro-Christian. Even one of the main Polish conservatives Stanisław Cat-Mackiewicz stated that the only problem with Catholicism is that there is no God, but apart from that, he is all for it. In Polish nationalism, we have a strong strain of non-Christian pagan nationalism connected with Jan Stachniuk and the Zadruga movement, who claimed that Catholicism is not a necessary part of Polish identity, and even went further — that it was against Polish identity. Stachniuk was right in reminding everyone that during the rule of the Jagiellonian dynasty, at the peak of the power of Poland, many of the elites, the whole nobility (szlachta) were leaning towards Reformation, with many of the most famous Polish humanists such as Jan Kochanowski or Mikołaj Rej being Protestants. Back then, Poland was on the brink of proclaiming a national church and cutting ties with Rome. Though I personally think that it would not have changed much in our history.
Getting back to the point of your question, I think nationalists of different confessions can come together. The four main tendencies we see among Polish nationalists are: Orthodox Catholics, “mild” Catholics, atheists, and pagans. All of these tendencies are represented in Szturm — but we do not pretend they do not exist. We talk about them openly and agree to disagree on certain issues. Among the young nationalists, we see the same tendency as among the youth in Europe as a whole — they care less about religion, and tend not to think about it too much or just consider this a personal issue. Personally, I am an adherent of the Slavic native faith, a practicing pagan if you would like, but I have more in common with many of the Catholic nationalists than with the “liberal pseudo-pagans.” We have a nation to save and an enemy to defeat. We can talk more about religion afterward.
This interview was conducted by Ondrej Mann of Reconquista and originally printed in Reconquista number XXXIII [4].
If you want to support Counter-Currents, please send us a donation by going to our Entropy page [5] and selecting “send paid chat.” Entropy allows you to donate any amount from $3 and up. All comments will be read and discussed in the next episode of Counter-Currents Radio, which airs every weekend on DLive [6].
Don’t forget to sign up [7] for the twice-monthly email Counter-Currents Newsletter for exclusive content, offers, and news.




 « Tout ce qui est moderne est du démon », écrit Léon Bloy, le 7 Août 1910. C'était, il nous semble, bien avant les guerres mondiales, les bombes atomiques et les catastrophes nucléaires, les camps de concentration, les manipulations génétiques et le totalitarisme cybernétique. En 1910, Léon Bloy pouvait passer pour un extravagant; désormais ses aperçus, comme ceux du génial Villiers de L’Isle-Adam des Contes Cruels, sont d'une pertinence troublante. L'écart se creuse, et il se creuse bien, entre ceux qui somnolent à côté de leur temps et ne comprennent rien à ses épreuves et à ses horreurs, et ceux-là qui, à l'exemple de Léon Bloy vivent au cœur de leur temps si exactement qu'ils touchent ce point de non-retour où le temps est compris, jugé et dépassé. Léon Bloy écrit dans l'attente de l'Apocalypse. Tous ces événements, singuliers ou caractéristiques qui adviennent dans une temporalité en apparence profane, Léon Bloy les analyse dans une perspective sacrée. L'histoire visible, que Léon Bloy est loin de méconnaître, n'est pour lui que l'écho d'une histoire invisible. « Tout n'est qu'apparence, tout n'est que symbole, écrit Léon Bloy. Nous sommes des dormants qui crient dans leur sommeil. Nous ne pouvons jamais savoir si telle chose qui nous afflige n'est pas le principe de notre joie ultérieure. »
« Tout ce qui est moderne est du démon », écrit Léon Bloy, le 7 Août 1910. C'était, il nous semble, bien avant les guerres mondiales, les bombes atomiques et les catastrophes nucléaires, les camps de concentration, les manipulations génétiques et le totalitarisme cybernétique. En 1910, Léon Bloy pouvait passer pour un extravagant; désormais ses aperçus, comme ceux du génial Villiers de L’Isle-Adam des Contes Cruels, sont d'une pertinence troublante. L'écart se creuse, et il se creuse bien, entre ceux qui somnolent à côté de leur temps et ne comprennent rien à ses épreuves et à ses horreurs, et ceux-là qui, à l'exemple de Léon Bloy vivent au cœur de leur temps si exactement qu'ils touchent ce point de non-retour où le temps est compris, jugé et dépassé. Léon Bloy écrit dans l'attente de l'Apocalypse. Tous ces événements, singuliers ou caractéristiques qui adviennent dans une temporalité en apparence profane, Léon Bloy les analyse dans une perspective sacrée. L'histoire visible, que Léon Bloy est loin de méconnaître, n'est pour lui que l'écho d'une histoire invisible. « Tout n'est qu'apparence, tout n'est que symbole, écrit Léon Bloy. Nous sommes des dormants qui crient dans leur sommeil. Nous ne pouvons jamais savoir si telle chose qui nous afflige n'est pas le principe de notre joie ultérieure. »  Pour Léon Bloy, qui se définit lui-même comme « un esprit intuitif et d'aperception lointaine, par conséquent toujours aspiré en deçà ou au-delà du temps », la fonction de l'auteur écrivant son journal n'est pas de se soumettre à l'aléa de la temporalité, du passager ou du fugitif, mais tout au contraire « d'envelopper d'un regard unique la multitude infinie des gestes concomitants de la Providence ». Le Journal, - tout en marquant le pas, en laissant retentir en soi, et dans l'âme du lecteur ami, la souffrance ou la joie, plus rare, de chaque jour, les « nouveautés » menues ou grandioses du monde, ne s'inscrit pas moins dans une rébellion contre le fragmentaire, le relatif ou l'éphémère. Ce Journal, et c'est en quoi il décontenance un lecteur moderne, n'a d'autre dessein que de déchiffrer la grammaire de Dieu.
Pour Léon Bloy, qui se définit lui-même comme « un esprit intuitif et d'aperception lointaine, par conséquent toujours aspiré en deçà ou au-delà du temps », la fonction de l'auteur écrivant son journal n'est pas de se soumettre à l'aléa de la temporalité, du passager ou du fugitif, mais tout au contraire « d'envelopper d'un regard unique la multitude infinie des gestes concomitants de la Providence ». Le Journal, - tout en marquant le pas, en laissant retentir en soi, et dans l'âme du lecteur ami, la souffrance ou la joie, plus rare, de chaque jour, les « nouveautés » menues ou grandioses du monde, ne s'inscrit pas moins dans une rébellion contre le fragmentaire, le relatif ou l'éphémère. Ce Journal, et c'est en quoi il décontenance un lecteur moderne, n'a d'autre dessein que de déchiffrer la grammaire de Dieu.  Léon Bloy s'est nommé lui-même « Le Pèlerin de l'Absolu ». Chaque jour qui advient, et que l'auteur traverse comme une nouvelle épreuve où se forge son courage et son style, le rapproche du moment crucial où apparaîtront dans une lumière parfaite la concordance de l'histoire visible et de l'histoire invisible. Cette quête que Léon Bloy partage avec Joseph de Maistre et Balzac le conduit à une vision du monde littéralement liturgique. L'histoire de l'univers, comme celle de l'auteur esseulé dans son malheur et dans son combat, est « un immense Texte liturgique. » Les Symboles, ces « hiéroglyphes divins », corroborent la réalité où ils s'inscrivent, de même que les actes humains sont « la syntaxe infinie d'un livre insoupçonné et plein de mystères. »
Léon Bloy s'est nommé lui-même « Le Pèlerin de l'Absolu ». Chaque jour qui advient, et que l'auteur traverse comme une nouvelle épreuve où se forge son courage et son style, le rapproche du moment crucial où apparaîtront dans une lumière parfaite la concordance de l'histoire visible et de l'histoire invisible. Cette quête que Léon Bloy partage avec Joseph de Maistre et Balzac le conduit à une vision du monde littéralement liturgique. L'histoire de l'univers, comme celle de l'auteur esseulé dans son malheur et dans son combat, est « un immense Texte liturgique. » Les Symboles, ces « hiéroglyphes divins », corroborent la réalité où ils s'inscrivent, de même que les actes humains sont « la syntaxe infinie d'un livre insoupçonné et plein de mystères. »  Contre ce sinistre état de fait, qui pervertit l'esprit humain, l'œuvre de Léon Bloy dresse un grandiose et intarissable réquisitoire. Or, c'est bien ce réquisitoire que les Modernes ne veulent pas entendre et qu'ils cherchent à minimiser en le réduisant à la « singularité » de l'auteur. Certes Léon Bloy est singulier, mais c'est d'abord parce qu'il se veut religieusement « un Unique pour un Unique ». La situation dans laquelle il se trouve enchaîné n'en est pas moins réelle et la description qu'il en donne particulièrement pertinente en ces temps où face à la marchandise mondiale le Pauvre est devenu encore beaucoup plus radicalement pauvre qu'il ne l'était au dix-neuvième siècle. La morale désormais se confond avec le Marché, et l'on pourrait presque dire que, pour le Moderne libéral, la notion d'immoralité et celle de non-rentabilité ne font plus qu'une. Refuser ce règne de l'économie, c'est à coup sûr être ou devenir pauvre et accueillir en soi les gloires du Saint-Esprit, dont la nature dispensatrice, effusive et lumineuse ne connaît point de limite.
Contre ce sinistre état de fait, qui pervertit l'esprit humain, l'œuvre de Léon Bloy dresse un grandiose et intarissable réquisitoire. Or, c'est bien ce réquisitoire que les Modernes ne veulent pas entendre et qu'ils cherchent à minimiser en le réduisant à la « singularité » de l'auteur. Certes Léon Bloy est singulier, mais c'est d'abord parce qu'il se veut religieusement « un Unique pour un Unique ». La situation dans laquelle il se trouve enchaîné n'en est pas moins réelle et la description qu'il en donne particulièrement pertinente en ces temps où face à la marchandise mondiale le Pauvre est devenu encore beaucoup plus radicalement pauvre qu'il ne l'était au dix-neuvième siècle. La morale désormais se confond avec le Marché, et l'on pourrait presque dire que, pour le Moderne libéral, la notion d'immoralité et celle de non-rentabilité ne font plus qu'une. Refuser ce règne de l'économie, c'est à coup sûr être ou devenir pauvre et accueillir en soi les gloires du Saint-Esprit, dont la nature dispensatrice, effusive et lumineuse ne connaît point de limite.
 del.icio.us
del.icio.us
 Digg
Digg
 La maison d'édition Diana propose la réimpression d'un essai de Marcel Gauchet "Droite/Gauche - histoire d'une dichotomie", enrichi d'une introduction de Marco Tarchi et d'une postface de l'auteur, annexe nécessaire à une publication datant déjà de 1992.
La maison d'édition Diana propose la réimpression d'un essai de Marcel Gauchet "Droite/Gauche - histoire d'une dichotomie", enrichi d'une introduction de Marco Tarchi et d'une postface de l'auteur, annexe nécessaire à une publication datant déjà de 1992. Les finalités, les contenus et les programmes changent mais l'"ordre de bataille" de la politique française reste formellement inchangé : dans un mélange de conflit et de fragmentation, les modérés et les alternances du centre continuent à gouverner, laissant "libre cours" aux doctrinaires des extrêmes et à un dualisme aussi élémentaire que manichéen, virulent et implacable.
Les finalités, les contenus et les programmes changent mais l'"ordre de bataille" de la politique française reste formellement inchangé : dans un mélange de conflit et de fragmentation, les modérés et les alternances du centre continuent à gouverner, laissant "libre cours" aux doctrinaires des extrêmes et à un dualisme aussi élémentaire que manichéen, virulent et implacable. Cette approche contraste avec celle "essentialiste" (identifiable, en grande partie, dans les écrits de Norberto Bobbio), qui échappe au test empirique d'une discrimination claire entre les deux catégories et n'explique pas les transformations que le passage du temps et l'évolution des circonstances ont imposées aux pratiques des partis et mouvements politiques traditionnellement placés dans l'un ou l'autre domaine.
Cette approche contraste avec celle "essentialiste" (identifiable, en grande partie, dans les écrits de Norberto Bobbio), qui échappe au test empirique d'une discrimination claire entre les deux catégories et n'explique pas les transformations que le passage du temps et l'évolution des circonstances ont imposées aux pratiques des partis et mouvements politiques traditionnellement placés dans l'un ou l'autre domaine.










 L'homme qui plantait des arbres est un livre de Jean Giono dans lequel l’auteur se rend compte, comme en ces temps-ci, qu'il n’a que deux alliés qui ne le trahissent pas et qui lui sont toujours fidèles : Dieu et la nature.
L'homme qui plantait des arbres est un livre de Jean Giono dans lequel l’auteur se rend compte, comme en ces temps-ci, qu'il n’a que deux alliés qui ne le trahissent pas et qui lui sont toujours fidèles : Dieu et la nature. L'homme qui plantait des arbres, un berger provençal, personnage principal du livre, a travaillé humblement pendant 37 ans, en se penchant sur le sol pour planter des glands, même s'il savait que seuls 20 % d'entre eux deviendraient des chênes. Il a ainsi transformé des collines stériles en forêts de chênes et de hêtres. Il avait décidé d'atteindre ce but premier dans la vie sans se poser trop de questions sur sa réussite ou non. Mais la persévérance d'un homme simple, faite d'amour et de dévouement, durant toutes ces années, va conduire à révolutionner un lieu désert et abandonné en le transformant en un village orné de forêts et de ruisseaux.
L'homme qui plantait des arbres, un berger provençal, personnage principal du livre, a travaillé humblement pendant 37 ans, en se penchant sur le sol pour planter des glands, même s'il savait que seuls 20 % d'entre eux deviendraient des chênes. Il a ainsi transformé des collines stériles en forêts de chênes et de hêtres. Il avait décidé d'atteindre ce but premier dans la vie sans se poser trop de questions sur sa réussite ou non. Mais la persévérance d'un homme simple, faite d'amour et de dévouement, durant toutes ces années, va conduire à révolutionner un lieu désert et abandonné en le transformant en un village orné de forêts et de ruisseaux.



 Mais pour réaliser tout cela, l'économie de marché avait besoin de l'État, qui, cependant, avait été déclaré mort à bord du navire de guerre HMS Prince of Wales au large des côtes de Terre-Neuve lorsque non seulement la Charte de l'Atlantique a été stipulée, mais où les funérailles de cet État-nation ont été organisées, Etat-nation qui était le symbole même de la primauté universelle d'une Europe - elle-même une Nation - qui a cessé d'être une idée pour devenir une Banque. Et de la pire espèce.
Mais pour réaliser tout cela, l'économie de marché avait besoin de l'État, qui, cependant, avait été déclaré mort à bord du navire de guerre HMS Prince of Wales au large des côtes de Terre-Neuve lorsque non seulement la Charte de l'Atlantique a été stipulée, mais où les funérailles de cet État-nation ont été organisées, Etat-nation qui était le symbole même de la primauté universelle d'une Europe - elle-même une Nation - qui a cessé d'être une idée pour devenir une Banque. Et de la pire espèce.




 Le WEF et les cercles d'élite connectés ne semblent d'ailleurs pas être arrivés au rendez-vous avec la pandémie sans préparation: le 18 octobre 2019, quelques mois avant l'explosion de Covid, l'exercice "
Le WEF et les cercles d'élite connectés ne semblent d'ailleurs pas être arrivés au rendez-vous avec la pandémie sans préparation: le 18 octobre 2019, quelques mois avant l'explosion de Covid, l'exercice " 




















 Bien sûr, la question de l'antifascisme est absolument décisive. Je voudrais résumer la question comme suit : à l'époque de Gramsci ou de Gobetti, en nous limitant au contexte italien, l'antifascisme était indispensable et fondamental, et il avait, du moins chez Gramsci, un but politique communiste, patriotique et anticapitaliste. Le problème, cependant, se pose lorsque l'antifascisme continue à se développer en l'absence de fascisme ou, plus précisément, lorsque le fascisme, si par cette expression nous entendons le pouvoir de manière générique, change de visage.
Bien sûr, la question de l'antifascisme est absolument décisive. Je voudrais résumer la question comme suit : à l'époque de Gramsci ou de Gobetti, en nous limitant au contexte italien, l'antifascisme était indispensable et fondamental, et il avait, du moins chez Gramsci, un but politique communiste, patriotique et anticapitaliste. Le problème, cependant, se pose lorsque l'antifascisme continue à se développer en l'absence de fascisme ou, plus précisément, lorsque le fascisme, si par cette expression nous entendons le pouvoir de manière générique, change de visage. Par conséquent, la gauche, qui ne défend plus les idées de Gramsci et de Marx, mais qui défend directement le capital, du moins la plus grande partie de celui-ci, a besoin de maintenir l'antifascisme en vie pour se légitimer, afin que la contradiction ne soit pas visible et évidente ; c'est-à-dire que cette gauche veut dissimuler le fait pourtant patent que la gauche est restée antifasciste, alors que le fascisme n'existe plus mais n'est pas pour autant anticapitaliste, alors que le capitalisme progresse plus que jamais. Au contraire, les hommes de gauche utilisent l'antifascisme comme prétexte pour adhérer complètement au "fascisme" de la civilisation consumériste, à l'atout invisible de l'économie de marché. Je pense au cas français où la gauche forme un front antifasciste uni contre Le Pen pour accepter pleinement le "fascisme de marché" et l'élite financière cooptée par Rothschild, représentée par le libéral Macron.
Par conséquent, la gauche, qui ne défend plus les idées de Gramsci et de Marx, mais qui défend directement le capital, du moins la plus grande partie de celui-ci, a besoin de maintenir l'antifascisme en vie pour se légitimer, afin que la contradiction ne soit pas visible et évidente ; c'est-à-dire que cette gauche veut dissimuler le fait pourtant patent que la gauche est restée antifasciste, alors que le fascisme n'existe plus mais n'est pas pour autant anticapitaliste, alors que le capitalisme progresse plus que jamais. Au contraire, les hommes de gauche utilisent l'antifascisme comme prétexte pour adhérer complètement au "fascisme" de la civilisation consumériste, à l'atout invisible de l'économie de marché. Je pense au cas français où la gauche forme un front antifasciste uni contre Le Pen pour accepter pleinement le "fascisme de marché" et l'élite financière cooptée par Rothschild, représentée par le libéral Macron. Il n'y a pas d'autre réalité, dans la modernité, pour les droits sociaux et les démocraties en dehors des États souverains nationaux. C'est pourquoi l'expression de Che Guevara "la patrie ou la mort" a sa propre validité aujourd'hui encore, non seulement parce qu'elle revendique l'identité contre l'anonymat impersonnel des marchés, mais aussi parce qu'elle revendique l'idée de souveraineté nationale contre les processus de déracinement voulus par le capitalisme mondialiste. La classe dominante est de gauche en matière de coutumes et de culture parce qu'elle n'a pas fait sien l'impératif de la gauche anticapitaliste de Gramsci ou de Lénine, qu'elle a d'ailleurs répudié, mais a adopté celui de la gauche rose de 1968, qui identifie le communisme à la libéralisation individualiste de la consommation et des coutumes ; c'est-à-dire à la société de libre-service des consommateurs individuels qui ont toute la liberté qu'ils peuvent concrètement acheter et se sentir libres comme des atomes de Nietzsche, comme des surhommes avec une volonté de pouvoir illimitée, c'est-à-dire qu'ils conçoivent la liberté comme la propriété de l'individu déraciné par rapport aux communautés sédentaires qu’ils posent comme autoritaires : la communauté familiale, la communauté politique, la communauté religieuse.
Il n'y a pas d'autre réalité, dans la modernité, pour les droits sociaux et les démocraties en dehors des États souverains nationaux. C'est pourquoi l'expression de Che Guevara "la patrie ou la mort" a sa propre validité aujourd'hui encore, non seulement parce qu'elle revendique l'identité contre l'anonymat impersonnel des marchés, mais aussi parce qu'elle revendique l'idée de souveraineté nationale contre les processus de déracinement voulus par le capitalisme mondialiste. La classe dominante est de gauche en matière de coutumes et de culture parce qu'elle n'a pas fait sien l'impératif de la gauche anticapitaliste de Gramsci ou de Lénine, qu'elle a d'ailleurs répudié, mais a adopté celui de la gauche rose de 1968, qui identifie le communisme à la libéralisation individualiste de la consommation et des coutumes ; c'est-à-dire à la société de libre-service des consommateurs individuels qui ont toute la liberté qu'ils peuvent concrètement acheter et se sentir libres comme des atomes de Nietzsche, comme des surhommes avec une volonté de pouvoir illimitée, c'est-à-dire qu'ils conçoivent la liberté comme la propriété de l'individu déraciné par rapport aux communautés sédentaires qu’ils posent comme autoritaires : la communauté familiale, la communauté politique, la communauté religieuse. Une économie sans politique et sans État ne sera jamais démocratique ou socialiste, elle sera toujours l'humus idéal pour le capital cosmopolite, qui est tout sauf socialiste et démocratique. D'où l'importance de ce que j'appelle le souverainisme internationaliste et populiste. Souveraineté parce que la souveraineté nationale est pleinement récupérée comme base des droits et des démocraties, du socialisme et des conquêtes sociales. Internationaliste parce que ce n'est pas le nationalisme de la droite réactionnaire, xénophobe et autoritaire, c'est une souveraineté internationaliste ouverte aux autres nations socialistes et démocratiques, elle crée un internationalisme prolétarien, comme on l'appelait autrefois, qui est à l'opposé du nationalisme individualiste et réactionnaire et du cosmopolitisme libéral auxquels la gauche rose a vendu sa tête et son cœur, comme je l'ai dit précédemment.
Une économie sans politique et sans État ne sera jamais démocratique ou socialiste, elle sera toujours l'humus idéal pour le capital cosmopolite, qui est tout sauf socialiste et démocratique. D'où l'importance de ce que j'appelle le souverainisme internationaliste et populiste. Souveraineté parce que la souveraineté nationale est pleinement récupérée comme base des droits et des démocraties, du socialisme et des conquêtes sociales. Internationaliste parce que ce n'est pas le nationalisme de la droite réactionnaire, xénophobe et autoritaire, c'est une souveraineté internationaliste ouverte aux autres nations socialistes et démocratiques, elle crée un internationalisme prolétarien, comme on l'appelait autrefois, qui est à l'opposé du nationalisme individualiste et réactionnaire et du cosmopolitisme libéral auxquels la gauche rose a vendu sa tête et son cœur, comme je l'ai dit précédemment. Par conséquent, quiconque s'oppose à cette vision, revendiquant la primauté de l'humain et du politique, défendant la nécessité de réguler, réclamant la primauté du politique et de la démocratie sur les flux de capitaux, de personnes, de désirs, de consommation, est automatiquement calomnié comme fasciste par la gauche rose-fuchsia, pour qui tout ce qui ne se met pas au diapason avec le seigneur cosmopolite, dont ils sont les idiots utiles, est fasciste. Le paradoxe est le suivant, je le résume ainsi, cette gauche diffame tout ce qui s'oppose à l'ordre de la classe dominante sans-frontiériste, de la classe globocratique du capital, elle diffame comme fasciste l'idée de l'intervention de l'État dans l'économie, elle diffame comme fasciste le réveil des classes dominées, des opprimés qui, comme le disait Fichte, sont au-dessus de toute autorité qui prétend être supérieure.
Par conséquent, quiconque s'oppose à cette vision, revendiquant la primauté de l'humain et du politique, défendant la nécessité de réguler, réclamant la primauté du politique et de la démocratie sur les flux de capitaux, de personnes, de désirs, de consommation, est automatiquement calomnié comme fasciste par la gauche rose-fuchsia, pour qui tout ce qui ne se met pas au diapason avec le seigneur cosmopolite, dont ils sont les idiots utiles, est fasciste. Le paradoxe est le suivant, je le résume ainsi, cette gauche diffame tout ce qui s'oppose à l'ordre de la classe dominante sans-frontiériste, de la classe globocratique du capital, elle diffame comme fasciste l'idée de l'intervention de l'État dans l'économie, elle diffame comme fasciste le réveil des classes dominées, des opprimés qui, comme le disait Fichte, sont au-dessus de toute autorité qui prétend être supérieure.
 Il y a 80 ans, le 9 décembre 1940, Adriano Romualdi naissait à Forlì. Cet anniversaire est important pour se souvenir de cet intellectuel, demeuré jeune parce que décédé prématurément, le 12 août 1973, à la suite d'un accident de voiture. Son souvenir est resté gravé dans la mémoire de la jeune génération des années cinquante, confrontée à l'engagement politique et culturel des années soixante-dix. Adriano Romualdi était, pour cette génération, une sorte de grand frère, capable d'offrir à la vision néo-fasciste des raisons d'être plus profondes, puis d’emprunter de manière autonome les chemins d'un nouveau dynamisme culturel. Dans cette perspective, sa personnalité reste encore un exemple.
Il y a 80 ans, le 9 décembre 1940, Adriano Romualdi naissait à Forlì. Cet anniversaire est important pour se souvenir de cet intellectuel, demeuré jeune parce que décédé prématurément, le 12 août 1973, à la suite d'un accident de voiture. Son souvenir est resté gravé dans la mémoire de la jeune génération des années cinquante, confrontée à l'engagement politique et culturel des années soixante-dix. Adriano Romualdi était, pour cette génération, une sorte de grand frère, capable d'offrir à la vision néo-fasciste des raisons d'être plus profondes, puis d’emprunter de manière autonome les chemins d'un nouveau dynamisme culturel. Dans cette perspective, sa personnalité reste encore un exemple. Son idée d'un droit politique "non égalitaire" repose sur ces solides fondements spirituels, que je viens d’exposer ici. C'est en septembre 1972 qu'Adriano Romualdi, à l'occasion de la conférence annuelle de la revue L'Italiano, dirigée par son père Pino, figure historique du MSI, met en évidence la distinction entre la droite (politique et culturelle) et le qualunquisme, sous ses différentes formes (qualunquisme politique, patriotique, culturel).
Son idée d'un droit politique "non égalitaire" repose sur ces solides fondements spirituels, que je viens d’exposer ici. C'est en septembre 1972 qu'Adriano Romualdi, à l'occasion de la conférence annuelle de la revue L'Italiano, dirigée par son père Pino, figure historique du MSI, met en évidence la distinction entre la droite (politique et culturelle) et le qualunquisme, sous ses différentes formes (qualunquisme politique, patriotique, culturel). En dehors des contingences d'une situation politique et culturelle de cette époque d’avant 1973, qui sont nettement perceptibles dans certains passages de son œuvre écrite, inévitablement affectée par le temps qui a passé. Les bouleversements de notre époque ont changé la donne (il suffit de penser à la fin de l'URSS, à la crise de l'empire américain, à l'émergence de la mondialisation, à la montée des nouvelles économies asiatiques). Les propositions de Romualdi conservent leur valeur, dans la mesure où elles se nourrissent d'une vision profonde de la culture et donc de la politique, rejetant tout minimalisme et toute respectabilité rassurante.
En dehors des contingences d'une situation politique et culturelle de cette époque d’avant 1973, qui sont nettement perceptibles dans certains passages de son œuvre écrite, inévitablement affectée par le temps qui a passé. Les bouleversements de notre époque ont changé la donne (il suffit de penser à la fin de l'URSS, à la crise de l'empire américain, à l'émergence de la mondialisation, à la montée des nouvelles économies asiatiques). Les propositions de Romualdi conservent leur valeur, dans la mesure où elles se nourrissent d'une vision profonde de la culture et donc de la politique, rejetant tout minimalisme et toute respectabilité rassurante.




 N'étant guère enclin à nous faire procureurs en poésie ou en métaphysique, les postulants à ces titres douteux ne manquant pas, nous nous contenterons de percevoir, à travers les incertitudes maurrassiennes, dissimulées sous un ton péremptoire, le beau signe de la vérité qui nous est ainsi adressé. Cette vérité est la connaissance de nos limites. Le paradoxe de cette connaissance est d'être à la fois humble et orgueilleuse. Elle est humble, car elle présume que nous sommes essentiellement redevables de ce que nous sommes à notre tradition, à notre Pays et à notre langue. Ecrivain, moins que tout autre je ne peux oublier que ma pensée circule comme une sève dans le grand arbre héraldique et étymologique de la langue française et que ma liberté est constituée par celle de mes prédécesseurs. Chaque mot dont s'empare notre pensée s'irise de ses usages révolus. Notre orgueil n'est alors que la juste mesure de notre humilité: il nous hausse, par la reconnaissance que nous éprouvons, à la dignité d'intercesseurs. Maurras ne cesse de nous redire que notre legs est à la fois fragile et précieux. Si Maurras se fourvoie quelquefois lorsqu'il tente de définir ce qui menace, il discerne bien ce qui est menacé.
N'étant guère enclin à nous faire procureurs en poésie ou en métaphysique, les postulants à ces titres douteux ne manquant pas, nous nous contenterons de percevoir, à travers les incertitudes maurrassiennes, dissimulées sous un ton péremptoire, le beau signe de la vérité qui nous est ainsi adressé. Cette vérité est la connaissance de nos limites. Le paradoxe de cette connaissance est d'être à la fois humble et orgueilleuse. Elle est humble, car elle présume que nous sommes essentiellement redevables de ce que nous sommes à notre tradition, à notre Pays et à notre langue. Ecrivain, moins que tout autre je ne peux oublier que ma pensée circule comme une sève dans le grand arbre héraldique et étymologique de la langue française et que ma liberté est constituée par celle de mes prédécesseurs. Chaque mot dont s'empare notre pensée s'irise de ses usages révolus. Notre orgueil n'est alors que la juste mesure de notre humilité: il nous hausse, par la reconnaissance que nous éprouvons, à la dignité d'intercesseurs. Maurras ne cesse de nous redire que notre legs est à la fois fragile et précieux. Si Maurras se fourvoie quelquefois lorsqu'il tente de définir ce qui menace, il discerne bien ce qui est menacé. 





 Les festivités solsticiales de l’hiver ont été célébrées depuis des temps immémoriaux : ce furent les premiers rites romains des Saturnales, qui finirent par avoir mauvaise réputation mais qui, au départ, avaient le sens de la mesure et de la tenue. Dans le Nord de l’Europe, on célèbre notamment Iduna, déesse de la jeunesse et de la fertilité, des fruits et des pommiers, qui pourra à nouveau s’épanouir grâce au retour du Soleil. Parallèlement à ces cultes d’Europe du Nord et du Sud, la période de l’Empire romain a également connu l’existence d’une fête solsticiale mithraïque, apportée sous nos latitudes par les cavaliers sarmates engagés dans les légions romaines.
Les festivités solsticiales de l’hiver ont été célébrées depuis des temps immémoriaux : ce furent les premiers rites romains des Saturnales, qui finirent par avoir mauvaise réputation mais qui, au départ, avaient le sens de la mesure et de la tenue. Dans le Nord de l’Europe, on célèbre notamment Iduna, déesse de la jeunesse et de la fertilité, des fruits et des pommiers, qui pourra à nouveau s’épanouir grâce au retour du Soleil. Parallèlement à ces cultes d’Europe du Nord et du Sud, la période de l’Empire romain a également connu l’existence d’une fête solsticiale mithraïque, apportée sous nos latitudes par les cavaliers sarmates engagés dans les légions romaines.









 Selon Hésiode, c'était le premier âge mythique, où "une lignée de mortels ‘en or’ a créé dans les premiers temps les immortels qui habitaient l'Olympe". Ils vivaient au temps de Kronos, lorsqu'il régnait au ciel ; comme des dieux, ils passaient leur vie, l’âme sans angoisse, loin du labeur et de la misère ; et leur misérable vieillesse ne leur pesait pas... (Hésiode - Les travaux et les jours).
Selon Hésiode, c'était le premier âge mythique, où "une lignée de mortels ‘en or’ a créé dans les premiers temps les immortels qui habitaient l'Olympe". Ils vivaient au temps de Kronos, lorsqu'il régnait au ciel ; comme des dieux, ils passaient leur vie, l’âme sans angoisse, loin du labeur et de la misère ; et leur misérable vieillesse ne leur pesait pas... (Hésiode - Les travaux et les jours).











 Une telle opération n'est possible qu'en intervenant au niveau de la légitimation, dont le fonctionnement est décrit avec précision par Jean-François Lyotard dans le deuxième chapitre de La condition postmoderne avec un titre particulièrement emblématique : "Le problème". Le droit de décider de ce qui est vrai - par exemple, que la phrase "Je ne suis pas raciste mais" implique le rejet de la discrimination raciale - est pour Lyotard un problème essentiellement prospectif. Le droit de décider de ce qui est vrai ou faux (par exemple un sens), est étroitement lié au droit de décider de ce qui est juste et de ce qui est injuste. Dans un tel scénario, la science (la sémiotique) est étroitement liée à la politique et à l'éthique qui, selon Lyotard, reposerait sur un concept appelé "Occident". Lyotard conclut son chapitre par ce commentaire paradigmatique : "Qui décide de ce qu'est la connaissance (c'est-à-dire le sens à attribuer aux signifiants, ndA) ? La question de la connaissance à l'ère des technologies de l'information est plus que jamais la question du gouvernement".
Une telle opération n'est possible qu'en intervenant au niveau de la légitimation, dont le fonctionnement est décrit avec précision par Jean-François Lyotard dans le deuxième chapitre de La condition postmoderne avec un titre particulièrement emblématique : "Le problème". Le droit de décider de ce qui est vrai - par exemple, que la phrase "Je ne suis pas raciste mais" implique le rejet de la discrimination raciale - est pour Lyotard un problème essentiellement prospectif. Le droit de décider de ce qui est vrai ou faux (par exemple un sens), est étroitement lié au droit de décider de ce qui est juste et de ce qui est injuste. Dans un tel scénario, la science (la sémiotique) est étroitement liée à la politique et à l'éthique qui, selon Lyotard, reposerait sur un concept appelé "Occident". Lyotard conclut son chapitre par ce commentaire paradigmatique : "Qui décide de ce qu'est la connaissance (c'est-à-dire le sens à attribuer aux signifiants, ndA) ? La question de la connaissance à l'ère des technologies de l'information est plus que jamais la question du gouvernement".




 Si la vérification des faits était objective et ne constituait pas seulement un moyen d'attaquer, de dénigrer et de persécuter des informations indépendantes, elle constituerait une pratique bonne et souhaitable. C'est pourquoi j'ai rejoint le projet de Matteo Gracis du site nobufale.it, dont le but est de vérifier les nouvelles, y compris, toutefois, celles transmises par les médias, qui sont les premiers à se tromper, et non de vérifier les nouvelles et de diffuser de fausses nouvelles.
Si la vérification des faits était objective et ne constituait pas seulement un moyen d'attaquer, de dénigrer et de persécuter des informations indépendantes, elle constituerait une pratique bonne et souhaitable. C'est pourquoi j'ai rejoint le projet de Matteo Gracis du site nobufale.it, dont le but est de vérifier les nouvelles, y compris, toutefois, celles transmises par les médias, qui sont les premiers à se tromper, et non de vérifier les nouvelles et de diffuser de fausses nouvelles.





 Vauban et le chemin de fer
Vauban et le chemin de fer
 Le Rapport Meadows
Le Rapport Meadows "1984" de George Orwell
"1984" de George Orwell Elle vient d'un monde inique et pervers, qu'il faut réformer et un changement radical s'impose ! Profitons de cette occasion historique ! "Il s’agit, - clame d'en haut le tout-puissant Docteur Schwab, Président-Fondateur de Davos,- de rendre (le monde) moins clivant, moins polluant, moins destructeur, plus inclusif, plus équitable et plus juste que celui dans lequel nous vivions à l’ère pré-pandémique." Une véritable révolution ! Ni rouge ni noire, mais verte ! Elle rendra notre vie, déjà difficile, définitivement plate et sans oppositions.
Elle vient d'un monde inique et pervers, qu'il faut réformer et un changement radical s'impose ! Profitons de cette occasion historique ! "Il s’agit, - clame d'en haut le tout-puissant Docteur Schwab, Président-Fondateur de Davos,- de rendre (le monde) moins clivant, moins polluant, moins destructeur, plus inclusif, plus équitable et plus juste que celui dans lequel nous vivions à l’ère pré-pandémique." Une véritable révolution ! Ni rouge ni noire, mais verte ! Elle rendra notre vie, déjà difficile, définitivement plate et sans oppositions.




