vendredi, 26 décembre 2014
Le meilleur régime: une querelle millénaire

Le meilleur régime: une querelle millénaire
Proposer ou imposer un chef à sa Nation ne se fait jamais sans conséquences. Mais alors, quel système politique doit-on mettre en œuvre pour assurer la pérennité de ce (nouveau) Régime ? Et quel est le plus préférable ?
Dans son « Enquête » au sein du livre 3, Hérodote rapporte un dialogue entre trois « mages » au lendemain de la mort du roi de Perse, Smerdis, pour trouver quel serait le meilleur régime afin de gouverner le territoire. En réalité, ces « mages » ou encore appelés « servants » selon les textes, représentent les trois principaux régimes politiques.
- Otanes, faisant l’apogée de la démocratie, commence par attaquer la monarchie par ces mots : « Je crois que l’on ne doit plus désormais confier l’administration de l’État à un seul homme, le gouvernement monarchique n’étant ni agréable ni bon ». En réalité, Otanes s’insurge sur le fait que ce « monarque » n’agirait qu’à sa guise, selon l’impulsion donnée par son caractère capricieux, tout lui étant alors permis. Otanes préconise un gouvernement choisi par le peuple ce qui régirait le « principe d’isonomie ». Ce principe consiste en une soumission à une même loi pour tous. L’isonomie est concrétisée sur l’égalité des droits civiques avec l’idée de partage effectif du pouvoir.
- Mégabyse, favorable au système aristocratique, témoigne de son accord avec Otanes sur les dérives de la monarchie, régime tyrannique selon lui. Mais la démocratie ne vaut pas mieux en y regardant de plus près ! Mégabyse dira même que le système démocratique est bien pire que son opposant monarchique pour la simple et bonne raison que le tyran monarque sait ce qu’il fait, alors que la masse populaire ne le sait pas ! Pour lui, seul un gouvernement composé des hommes de savoir et d’éducation, peut se maintenir ! « Pour nous, faisons le choix des hommes les plus vertueux ; mettons-leur la puissance entre les mains : nous serons nous-même de ce nombre ; et, suivant toutes les apparences, des hommes sages et éclairés et ne donneront que d’excellents conseils ».
- Darius quant à lui se positionne pour la monarchie. Prenant la parole en dernier, et ayant soigneusement écouté ses comparses, il critique immédiatement Otanes et Mégabyse : Pour lui, le meilleur gouvernement ne peut être autre que celui du meilleur homme seul ! « Il est constant qu’il n’y a rien de meilleur que le gouvernement d’un seul homme, quand il est homme de bien ». L’oligarchie n’est pour lui que l’étape précédent la monarchie, d’où sa faiblesse : « Chacun veut primer, chacun veut que son opinion prévale » de sorte que les nobles se battraient pour gouverner. Cette situation ne déboucherait que sur le recours à un roi pour rétablir l’ordre social. Mais la démocratie ne vaut pas mieux selon le « mage » ! « Quand le peuple commande, il est impossible qu’il ne s’introduise beaucoup de désordre dans un État ». Cela ne conduirait qu’à une tyrannie – justement – pour rétablir brutalement l’ordre. Pour Darius, la monarchie apparait comme seul régime valable, ou du moins comme le moins mauvais.
Cette introduction nous permet d’enchaîner sur l’étude desdits systèmes politiques, non pas pour vanter les mérites de l’un sur les autres, mais pour en comprendre leurs fondements, leurs principes et leurs idéaux.
La démocratie
 L’une des meilleurs définitions a été donné par Aristote : « La liberté – ou démocratie – consiste dans le fait d’être tour à tour gouverné et gouvernant… »
L’une des meilleurs définitions a été donné par Aristote : « La liberté – ou démocratie – consiste dans le fait d’être tour à tour gouverné et gouvernant… »
La démocratie est le gouvernement du peuple, par le peuple et pour le peuple. Idéalement, la démocratie instaure une identité entre les gouvernants et les gouvernés. Les conditions nécessaires sont les suivantes :
- L’égalité : C’est l’idée que tous les citoyens, sans distinction d’origine, de race, de sexe ou de religion, sont égaux en droit. Les mêmes règles doivent s’appliquer aux citoyens qui sont placés dans une situation identique.
- La légalité : C’est l’idée d’une obéissance aux règles de droit. Les rapports entre les citoyens doivent être régis par des règles de droit qui, adoptées par tous, s’appliquent à tous.
- La liberté : C’est l’idée de la liberté de participation aux affaires publiques. Tous les citoyens sont libres de participer au gouvernement soit par la désignation des gouvernants – élection – soit par la prise directe de décision – référendum. C’est également l’idée d’une liberté d’opinion, ce qui induit le respect de plusieurs courants politiques.
Outre Otanès que nous avons évoqué en introduction, Périclès fait également l’éloge de la démocratie où l’égalité serait son fondement. Dans ce régime il ne doit y avoir aucune différence entre les citoyens ni dans leur vie publique ni dans leur vie privée. Aucune considération ne doit s’attacher à la naissance ou à la richesse, mais uniquement au mérite !
La démocratie est un régime de générosité et de fraternité, reposant sur la philanthropie (du grec ancien φίλος / phílos « amoureux » et ἄνθρωπος / ánthrôpos « homme », « genre humain ») est la philosophie ou doctrine de vie qui met l’humanité au premier plan de ses priorités. Un philanthrope cherche à améliorer le sort de ses semblables par de multiples moyens.
Cependant et après étude de ces éléments, nous sommes en droit de nous poser la question suivante : l’élection démocratique d’un dirigeant le force t-il nécessairement à être philanthrope ? À moins que la réponse ne soit déjà dans la question…
L’Oligarchie
L’oligarchie est le gouvernement d’un petit nombre de personnes, le pouvoir étant détenu par une minorité. L’oligarchie est également une catégorie générique qui recouvre plusieurs formes de gouvernement.
La forme oligarchique la plus répandue est l’aristocratie. C’est un gouvernement réservé à une classe sociale censée regrouper les meilleurs. L’aristocratie repose ainsi sur une conception élitiste du pouvoir.
Outre les institutions de la république romaine, rappelons que le système politique spartiate était bel et bien orienté vers l’oligarchie notamment avec la gérousie.
La gérousie est une assemblée composée de 28 hommes élus à vie et âgés de plus de 60 ans. Ces derniers sont choisis en fonction de leur vertu militaire mais force est de constater qu’ils appartiennent pour la plupart aux grandes familles de Sparte.
Il est intéressant de noter que dans cet exemple que seuls les membres de cette assemblée possèdent l’initiative des lois. Dans un système oligarchique on ne laisse que peu de place à l’aléatoire puisque seuls les « meilleurs » accèdent aux fonctions législatives, encore faut-il convenablement définir ce que sont « les meilleurs » dans un régime politique.
La monarchie
La monarchie est la forme de gouvernement dans laquelle le pouvoir est exercé par un seul homme (roi, empereur, dictateur).
La monarchie absolue est un courant de la monarchie qui, elle-même est un courant de la monocratie. La monarchie absolue donc, est le gouvernement d’un seul homme fondée sur l’hérédité et détenant en sa personne tous les pouvoirs (législatif, exécutif et judiciaire). La souveraineté du monarque est très souvent de droit divin.
Outre Darius, Isocrate défend cette idée de monarchie comme forme d’organisation du pouvoir. Il pense trouver le chef dans Philippe de Macédoine (père d’Alexandre le Grand), car il y voit le règne de l’efficacité et l’avènement de la modernité.
 Xénophon a réellement été l’initiateur du régime monarchique. « Ce qui fait les rois ou les chefs (…) c’est la science du commandement ». Le roi est comparable au pilote qui guide le navire. Xénophon décrit un homme qui détient une supériorité sur tous les autres, car il « sait ». On ne naît pas roi, on ne l’est pas non plus par le fait, ni encore par l’élection : on le devient ! La monarchie est un art qui, comme tous les autres arts, suppose un apprentissage, la connaissance des lois et des maîtres pour les enseigner.
Xénophon a réellement été l’initiateur du régime monarchique. « Ce qui fait les rois ou les chefs (…) c’est la science du commandement ». Le roi est comparable au pilote qui guide le navire. Xénophon décrit un homme qui détient une supériorité sur tous les autres, car il « sait ». On ne naît pas roi, on ne l’est pas non plus par le fait, ni encore par l’élection : on le devient ! La monarchie est un art qui, comme tous les autres arts, suppose un apprentissage, la connaissance des lois et des maîtres pour les enseigner.
L’éducation fait acquérir au roi un ensemble de talents et de qualités qui le rendront véritablement apte à exercer ses fonctions. Il ne doit pas imposer son pouvoir par la force, sinon il ne serait qu’un tyran, ce que Xénophon réprouve. Le roi devra être capable de susciter le consentement du peuple en se fondant sur la justice et la raison. Le chef est donc au service de ceux qu’il commande. « Un bon chef ne diffère en rien d’un bon père de famille ». Héritage grec oblige, Xénophon n’oublie pas de mentionner que le roi ne fera régner la justice qu’en respectant la primauté de la loi.
***
À l’étude de ces différents régimes proposant une gouvernance différente du territoire, sommes-nous en capacité de répondre à l’intitulé de cet article à savoir « Quel est le meilleur Régime politique ? » Chacun se fera son avis, chacun se fera son opinion ! Tout réside naturellement dans la capacité du « chef » à gouverner, mais aussi et surtout dans sa conception du pouvoir.
Napoléon Bonaparte a été très certainement l’un des empereurs les plus prestigieux de l’Histoire. Cependant était-il d’avantage un démocrate qu’un monarque ? Ou a-t-il réussi à faire ressortir une nouvelle façon d’exercer le pouvoir ? Pour approfondir le sujet, je vous invite à lire les articles de Christopher Lings et David Saforcada aux adresses suivantes :
- Moment d’histoire : Le coup d’Etat du 18 brumaire
- Le régime plébiscitaire des Napoléons comme remède à l’hérédité et à l’élection
Christopher Destailleurs
Nous avons besoin de votre soutien pour vivre et nous développer :
00:05 Publié dans Théorie politique | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : politologie, sciences politique, philosophie, théorie politique, philosophie politique, aristote, xénophon, antiquité grecque, hellenisme, grèce antique |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
jeudi, 25 décembre 2014
John Robb on Open Source Warfare
Robert Stark interviews John Robb on Open Source Warfare
Ex: http://www.starktruthradio.com
To listen to:
http://www.starktruthradio.com/?p=783
 Topics include:
Topics include:
John Robb’s book Brave New War: The Next Stage of Terrorism and the End of Globalization
The Four Generations of Warfare theory
How open source warfare became predominant when nuclear weapons deterred conflicts between major nations
How decentralization is the asset of non state actors such as ISIS
Why John does not view ISIS as a proxy for nations such as Saudi Arabia
How ISIS got it’s start during the Syrian conflict
His prediction that we will never win in Iraq
Hamas and Hezbollah
How an open source movement is not an organized organization
iWarfare
Why it’s inevitable that Open Source Warfare will spread to the West due to economic stagnation
How an economy based on financial institutions is unsustainable
How a managerial economy is a zero sum game
Why education and healthcare costs have gone up is because of an increase in loans
How the FDA shut down 23andme which does genetic testing and could of revolutionized medicine
The commercial use of drones
Edward Snowden
Click Here to download!
00:08 Publié dans Actualité, Entretiens, Livre | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : actualité, livre, john robb, guerre, guerre actuelle, états-unis, politique internationale |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Quelques rappels utiles sur l’histoire récente des Kurdes
Matthias Hellner :
Les Kurdes : un peuple sans Etat
Quelques rappels utiles sur l’histoire récente des Kurdes
C’est au 7ème siècle que le nom de « Kurde » apparaît pour la première fois dans les sources écrites musulmanes. Toutefois, le mot ne désigne pas, dans cette première littérature islamique, un peuple précis mais une pluralité de tribus nomades vivant à proximité de l’Iran actuel. Le territoire initial du peuple kurde se situe dans la région montagneuse du Caucase méridional. Aujourd’hui, la région qu’occupent les Kurdes s’étend aux confins de quatre pays : la Syrie, l’Iran, l’Irak et la Turquie.
Déjà au 7ème siècle, les régions kurdes tombent aux mains du Calife et bon nombre de Kurdes se convertissent rapidement à l’Islam sunnite. Malgré cette conversion rapide à la religion des tribus nomades sémitiques de la péninsule arabique, les siècles suivants seront ponctués de révoltes généralisées ou d’insurrections plus localisées contre le pouvoir des califes de Bagdad, comme en 838 ou en 905 dans les régions septentrionales de l’aire de peuplement kurde. On a vu alors certains clans kurdes se convertir au christianisme et faire cause commune avec l’Empire byzantin.
Après la chute de Constantinople, les Empires ottoman et séfévide se sont affrontés ; dans le cadre de cet affrontement, les Séfévides imposent le chiisme comme religion d’Empire en Perse, ce qui entraîne les Kurdes sunnites dans le camp des Ottomans qui, pour les récompenser de cette fidélité, les délivrent du devoir de payer tribut, du moins partiellement. Après la bataille de Tchaldiran en 1514, gagnée par les Ottomans et leurs alliés kurdes, les régions peuplées de Kurdes sont, malgré cette victoire, coincées dangereusement entre les deux empires. Au cours des décennies suivantes, les Séfévides ont dû régulièrement reculer devant les armées ottomanes. Beaucoup de Kurdes des régions frontalières de l’Empire ottoman ont quitté leurs villages d’origine. En migrant de la sorte, ces Kurdes pratiquaient aussi une politique de la terre brûlée dont pâtirent bon nombre d’antiques sites habités par leur peuple. En 1639, le long conflit qui avait opposé les Séfévides aux Ottomans se termine avec, entre autres résultats, la partition des régions habitées par les tribus kurdes. Cette partition du 17ème siècle a perduré jusqu’à nos jours : la séparation entre Kurdes de Turquie (et d’Irak) et Kurdes de Perse suit encore et toujours le même tracé, à quelques rares modifications près.
 A partir de 1847, l’Empire ottoman connaît une zone administrative nommé « Kurdistan » mais elle est dissoute en 1864. Après l’effondrement de l’empire ottoman en 1918, les Alliés occidentaux victorieux promettent aux Kurdes de leurs accorder un Etat propre et le droit à l’auto-détermination mais, en bout de course, de larges portions de l’aire de peuplement kurde ont été attribuées à la Syrie (sous mandat français) et surtout à l’Irak (sous mandat britannique). Par ailleurs, les Turcs de Mustafa Kemal, par leur victoire dans leur guerre d’indépendance, conservent le reste du Kurdistan et contraignent les franco-britanniques à accepter une révision du Traité de Sèvres. Sous l’impulsion d’Atatürk, leader des forces indépendantistes et nationalistes turques, de nombreux Kurdes se joignent au mouvement antioccidental parce qu’on leur promet simultanément de larges droits à l’autonomie dans l’Etat turc nouveau qui doit s’établir après la victoire des forces nationalistes. Les kémalistes avaient en effet promis aux Kurdes que cet Etat nouveau serait binational. Ces promesses n’ont pas été tenues : le jeune Etat, né de la victoire des armes kémalistes, ne reconnait pas les Kurdes comme minorité ethnique lors de la signature du Traité de Lausanne de 1923. La réaction ne se fait pas attendre : plusieurs insurrections éclatent entre 1925 et 1938 dans l’aire de peuplement kurde de la nouvelle Turquie. Toutes sont matées par l’armée turque, supérieure en nombre et en matériels.
A partir de 1847, l’Empire ottoman connaît une zone administrative nommé « Kurdistan » mais elle est dissoute en 1864. Après l’effondrement de l’empire ottoman en 1918, les Alliés occidentaux victorieux promettent aux Kurdes de leurs accorder un Etat propre et le droit à l’auto-détermination mais, en bout de course, de larges portions de l’aire de peuplement kurde ont été attribuées à la Syrie (sous mandat français) et surtout à l’Irak (sous mandat britannique). Par ailleurs, les Turcs de Mustafa Kemal, par leur victoire dans leur guerre d’indépendance, conservent le reste du Kurdistan et contraignent les franco-britanniques à accepter une révision du Traité de Sèvres. Sous l’impulsion d’Atatürk, leader des forces indépendantistes et nationalistes turques, de nombreux Kurdes se joignent au mouvement antioccidental parce qu’on leur promet simultanément de larges droits à l’autonomie dans l’Etat turc nouveau qui doit s’établir après la victoire des forces nationalistes. Les kémalistes avaient en effet promis aux Kurdes que cet Etat nouveau serait binational. Ces promesses n’ont pas été tenues : le jeune Etat, né de la victoire des armes kémalistes, ne reconnait pas les Kurdes comme minorité ethnique lors de la signature du Traité de Lausanne de 1923. La réaction ne se fait pas attendre : plusieurs insurrections éclatent entre 1925 et 1938 dans l’aire de peuplement kurde de la nouvelle Turquie. Toutes sont matées par l’armée turque, supérieure en nombre et en matériels.
Atatürk voulait en effet aligner son Etat sur le modèle jacobin français, en le dotant d’une forte centralisation. Dès lors, après la victoire sur les forces d’occupation alliées (françaises, anglaises, grecques et italiennes), Atatürk proclame la politique dite « d’Un Etat, Une Nation, Une Langue, Une Identité ». Automatiquement, il acceptait qu’un conflit permanent risquait de l’opposer aux chefs de clans kurdes qui voyaient vaciller leur autorité traditionnelle.
Après 1945, les mesures jacobines vexatoires et insultantes se multiplient (comme jadis en France) : le costume kurde, le Sal Sapik, est interdit ; ensuite vient le tour de l’usage officiel de la langue kurde (comme le breton, le francique-mosellan, l’alémanique du Sundgau ou le west-flamand en France). En 1967, l’Etat centralisateur turc interdit une nouvelle fois tout usage public de la langue kurde, de même que la musique, la littérature et les journaux kurdes.
Matthias Hellner.
(article paru dans « zur Zeit », Vienne, n°44/2014 ; http://www.zurzeit.at ).
00:05 Publié dans Actualité | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : kurdes, kurdistan, perse, empire ottoman, turquie, kémalisme, ethnologie, histoire, levant, moyen orient |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Il faut relire Soljénitsyne!
|
|
 Et il ne faut surtout pas le laisser penser et le plonger de façon permanente dans « …cette hâte et cette superficialité qui sont la maladie mentale du XXe siècle ». La presse est un maître puissant en la matière, qui suit « le vent du siècle », pratique la « sélection » et abreuve à tort et à travers, surtout à travers – c’est plus rentable – l’opinion publique. Soljénitsyne défend joliment ce « droit de ne pas savoir », qu’on ne connaît plus, de ne pas savoir l’inessentiel, l’accessoire, le superflu : ce droit « de ne pas encombrer son âme créée par Dieu avec des ragots, des bavardages, des futilités », qui nuisent à notre intériorité et annihile la saine réflexion et le nécessaire retour sur soi. Que dirait-il aujourd’hui, en ce temps de sur-communication permanente ?
Et il ne faut surtout pas le laisser penser et le plonger de façon permanente dans « …cette hâte et cette superficialité qui sont la maladie mentale du XXe siècle ». La presse est un maître puissant en la matière, qui suit « le vent du siècle », pratique la « sélection » et abreuve à tort et à travers, surtout à travers – c’est plus rentable – l’opinion publique. Soljénitsyne défend joliment ce « droit de ne pas savoir », qu’on ne connaît plus, de ne pas savoir l’inessentiel, l’accessoire, le superflu : ce droit « de ne pas encombrer son âme créée par Dieu avec des ragots, des bavardages, des futilités », qui nuisent à notre intériorité et annihile la saine réflexion et le nécessaire retour sur soi. Que dirait-il aujourd’hui, en ce temps de sur-communication permanente ?
00:05 Publié dans Littérature | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : alexandre soljénitsyne, russie, littérature, lettres, lettres russes, littérature russe |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Superbe trésor viking découvert en Ecosse
00:05 Publié dans archéologie | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : vikings, archéologie, écosse, moyen âge |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Le néo-nihilisme, nouveau mal français

Les Français sont abrutis par la propagande médiatique. Celle-ci véhicule un néo-nihilisme ahurissant.
Ce néo-nihilisme repose sur une négation des réalités. Négation des origines et de leur importance. Négation du Grand Remplacement de populations. Négation de l’existence même d’un peuple français historique. Négation de l’échec de tout processus d’assimilation des immigrés venus de loin. Négation de l’islamisation de la société et des mœurs. Négation de l’échec de la « conception citoyenne de la nation » devenue simple paravent du communautarisme.
Ce néo-nihilisme nie aussi les réalités anthropologiques. Il prétend déconstruire les différences de sexe. Tout en promouvant un « homosexualisme » militant, négateur du mariage et des liens de filiation. Sa vision est celle de l’immédiateté, du grand carnaval de l’Homo festivus et de la Gay Pride.
 Promu par les médias de l’oligarchie, ce néo-nihilisme est devenu l’idéologie dominante de la classe politique. Par connivence d’abord : journalistes et politiques déjeunent ensemble, voyagent ensemble, dînent ensemble… et plus si affinités. Par désir mimétique aussi : pour un politique, la recette pour se faire inviter à la télévision, c’est de tenir un discours média-compatible. Résultat : ceux qui devraient donner du sens se rallient – peu ou prou – au néo-nihilisme de l’État-spectacle et de l’Homo festivus. D’où le discrédit des partis politiques : Front de gauche, écolos, PS, UMP. À force de rechercher la dédiabolisation/banalisation, c’est le Front national lui-même qui pourrait perdre le crédit de sa différence. Or, suivre le vent n’est rien d’autre qu’« une ambition de feuille morte ».
Promu par les médias de l’oligarchie, ce néo-nihilisme est devenu l’idéologie dominante de la classe politique. Par connivence d’abord : journalistes et politiques déjeunent ensemble, voyagent ensemble, dînent ensemble… et plus si affinités. Par désir mimétique aussi : pour un politique, la recette pour se faire inviter à la télévision, c’est de tenir un discours média-compatible. Résultat : ceux qui devraient donner du sens se rallient – peu ou prou – au néo-nihilisme de l’État-spectacle et de l’Homo festivus. D’où le discrédit des partis politiques : Front de gauche, écolos, PS, UMP. À force de rechercher la dédiabolisation/banalisation, c’est le Front national lui-même qui pourrait perdre le crédit de sa différence. Or, suivre le vent n’est rien d’autre qu’« une ambition de feuille morte ».
Face à cette verticale du pouvoir médias/politiques, les réactions viennent des profondeurs du peuple. D’où l’ampleur des manifestations sociétales : de la Manif pour tous, du Printemps français, des Bonnets rouges et peut-être demain d’un PEGIDA (les mouvements anti-islamisation en Allemagne) à la française.
Les réactions viennent aussi des intellectuels. D’hommes et de femmes qui savent qu’ils ont le « devoir de vérité ». D’hommes et de femmes qui osent penser la radicalité : des essayistes comme Éric Zemmour ou Hervé Juvin, des écrivains comme Renaud Camus ou Richard Millet, des artistes ou critiques d’art comme Aude de Kerros, des esprits indépendants comme Robert Ménard ou Béatrice Bourges.
À eux de donner du sens. À eux de rappeler que la patrie (la terre des pères) n’a de sens que si elle porte une identité charnelle et civilisationnelle. À eux de rappeler qu’il n’y a pas de communauté nationale sans réalité substantielle, croyances communes, valeurs morales et sociales partagées et leur hiérarchie. À eux de rappeler qu’il y a des permanences anthropologiques et culturelles à respecter. À eux de rappeler que la souveraineté n’a de sens que si elle est enracinée.
Le renouveau ne passera pas par les structures anciennes tributaires des conformismes. Il viendra de la mise en forme par les intellectuels dissidents des aspirations profondes du peuple. Il sera possible grâce au contournement des médias par Internet et les réseaux sociaux.
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Manipulations médiatiques, Nouvelle Droite, Philosophie, Sociologie | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : nihilisme, france, actualité, nouvelle droite, sociologie, philosophie, jean-yves le gallou |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
mercredi, 24 décembre 2014
From Pagan Spirituality to Christian Consumerism

From Pagan Spirituality to Christian Consumerism
Solstice: the sun stands still. In temperate countries of the northern and southern hemispheres, every year there are two: summer and winter. The northern hemisphere’s summer solstice, which occurs on a day in the middle of the year (June 20 to 22, depending on the year), is the southern hemisphere’s winter solstice. Conversely, the southern hemisphere’s summer solstice, which occurs on a day in the third week of December (December 20 to 23, depending on the year), just prior to the New Year, is the northern hemisphere’s winter solstice. In the tropics, these astronomical events are not physically felt, except for the holiday celebration called Christmas that is associated with the northern’s hemisphere winter solstice and was brought by European Christian religions to countries like the Philippines, where I was born.
Dies natalis Solis invicti: Birthday of the unconquered Sun
Though we are more familiar now with the so-called Christmas season, connected with the winter solstice, there has always been something religious or spiritual about this time of year that antedates the Christian era. The traditions of caroling and midnight service, and common symbols in the celebration of Christmas, like mistletoes, decorated trees, candles and lights, wreaths and hollies, among others, were present in European paganism long before the advent of Christianity. Christmas is therefore the “Christianization” of the winter solstice celebration, whose institutionalization over time has led to the theft of most, if not all, of the major highlights from the pagan world.
 In the Hebrew scriptures of the Jewish religion, known as the Old Testament in the Christian Bible, there occurs a single instance of the word “solstice” that is not in any way associated with the annual summer and winter astronomical events. In the book of Joshua, chapter 10 and verses 12 to 14, it is reported that the tribal deity of ancient Israel, called YHWH, caused the sun to stand still in Gibeon to give the Israelites, known to be the people of the said tribal deity, the best opportunity to slaughter and annihilate, in broad daylight, an enemy tribe called the Amorites.
In the Hebrew scriptures of the Jewish religion, known as the Old Testament in the Christian Bible, there occurs a single instance of the word “solstice” that is not in any way associated with the annual summer and winter astronomical events. In the book of Joshua, chapter 10 and verses 12 to 14, it is reported that the tribal deity of ancient Israel, called YHWH, caused the sun to stand still in Gibeon to give the Israelites, known to be the people of the said tribal deity, the best opportunity to slaughter and annihilate, in broad daylight, an enemy tribe called the Amorites.
“Then Joshua spoke to the Lord in the day when the Lord delivered up the Amorites before the sons of Israel, and he said in the sight of Israel, ‘O sun, stand still at Gibeon, And O moon in the valley of Aijalon.’ So the sun stood still, and the moon stopped, Until the nation avenged themselves of their enemies. Is it not written in the book of Jashar? And the sun stopped in the middle of the sky and did not hasten to go down for about a whole day. There was no day like that before it or after it, when the Lord listened to the voice of a man; for the Lord fought for Israel.…”
This Lord, the sadistic tribal deity of ancient Israel, is a far cry from the god of love whose son, Jesus, is mythically believed by Christians to have been born sometime during the winter solstice and in whose honor Christians celebrate Christmas. By contrast to the murderous solstice of the Jewish story, the pagan winter solstice has always symbolized renewed hope, faith in the restorative cosmic forces and most of all, a love of life.
“In the depths of winter I finally learned there was in me an invincible summer.” – Albert Camus
The pagan winter solstice is an exaltation of the human spirit’s rebirth and revitalization, from “the dark nights of the soul” (“la noche oscura del alma”, with apologies to St. John of the Cross) into the energizing warmth of a radiant morning. It is the grandeur of this splendid background that the Christian religion stole for its prevailing celebration called Christmas, to the point of claiming: “It is not the birth of the Sun but rather that of the Son.”
Christianity, whose key figure, Jesus Christ, is a paragon of humility, should be humble enough not to monopolize the significance of the annual December 25 celebration. Deities from other religions whose births, in different periods, have been celebrated on the same date include: Attis and Dionysus, both of Greece; Mithra of Persia; Salivahana of Bermuda; Odin of Scandinavia; Crite of Chaldez; Thammuz of Syria; Addad of Assyria, and Beddru of Japan.
The winter solstice has influenced the lives of many generations of humanity, through the passing of different civilizations. Therefore the universalizing slogan “Jesus is the reason for the season,” is inaccurate. A more logically acceptable statement for Christians is: “Jesus is our reason for the season.” An all-encompassing claim that articulates ownership of the winter solstice celebration, by claiming that Jesus Christ is the season’s only source of meaning, is a blatant audacity of narrow-minded fundamentalist and evangelical Christians. Christians should be more sensitive not to monopolize the winter solstice celebration and should acknowledge the fact that most—if not all—material symbolisms in Christmas originate from the pagan realm. The legacy of the ancient pagans is still carried on by modern pagans who continue to use the ancient material symbolisms inherited from their precursors with comparable spiritual intensity and pomp.

It is tragic that the originally spiritual celebration of the pagan winter solstice has been ruined by the materialism of modern nominal Christianity. The modern winter solstice celebration has become commercialized and has lost, not only the graciousness originally associated with ancient pagan spirituality, but also the magnanimity of Christian virtues exemplified by the teachings of Jesus Christ.
“The black moment is the moment when the real message of transformation is going to come. At the darkest moment comes the light.” – Joseph Campbell
Even Christianity has been made seasonal by Christmas, which has become the only time of the year when nominal Christians affirm their shallow Christianity through their superficial adoration of their so-called Lord. I think that Christians, to be true to their commitment, should draw their inspiration and get moved to action not only during the Christmas season but also on a daily basis by the words of wisdom and example of Jesus. A truer spirit of Christianity might well reside in the pagan spirituality that has animated the ancient winter solstice celebration with its promise of renewed hope, faith in the restorative cosmic forces and love of life.
Merry Yuletide Season to All!
RUEL F. PEPA writes for News Junkie Post.
16:54 Publié dans Traditions | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : yule, noël, christmas, traditions, sol invictus, paganisme, solstice d'hiver |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Deutsche Geheimmission in Persien

Er hetzte zum Dschihad auf und ließ Ölpipelines sprengen: Hauptmann Fritz Klein führte im Orient einen Guerillakrieg gegen die Feinde des Kaiserreichs. Ein Historiker hat bislang unbekannte Dokumente des vergessenen Offiziers ausgewertet.
Die vier deutschen Soldaten waren verloren, Tausende Kilometer von der Heimat entfernt. Die Stadt Amara im heutigen Irak, umschlossen vom mächtigen Tigris und einem Überschwemmungsgebiet, wurde zur "Mausefalle", wie Anführer Hans Lührs es nannte. Die wichtigste Brücke war zerstört und aus der Ferne rückte schon der Feind an.
"Das Artilleriefeuer der Engländer kam immer näher", schreibt Lührs später. "Wir sahen in einer Flussbiegung bereits die Rauchfahnen der feindlichen Schiffe." Eine Granate schlug neben ihm ein, sein Hengst bäumte sich auf und galoppierte davon.
Fernab der Schlachtfelder in Europa lieferten sich die Kontrahenten des Ersten Weltkriegs auch im Orient einen unbarmherzigen Stellvertreterkrieg. Die Taktik auf beiden Seiten war ähnlich: neue Verbündete finden, Aufstände in gegnerischen Einflussgebieten anzetteln, feindliche Kräfte an der Kriegsperipherie binden.
Schulversager, Sitzenbleiber, Weltenbummler
Die Briten hatten für solche Aktionen Lawrence von Arabien. Der legendäre Archäologe und Geheimagent wiegelte die Araber gegen das wankende Osmanische Reich auf, den Bündnispartner des Kaiserreichs. Und die Deutschen? Nun, sie hatten - Hauptmann Fritz Klein aus dem westfälischen Siegerland.
"Klein von Arabien" hat den Mann glücklicherweise nie jemand genannt; es würde wohl auch lächerlich klingen. Aber: Kleins Männer haben ihre Aufgabe später zu Recht mit der von Lawrence von Arabien verglichen, und womöglich könnte ihre völlig unbekannte Mission nun etwas bekannter werden: Der Historiker Veit Veltzke hat eine Studie ("Unter Wüstensöhnen", Nicolai-Verlag) über die vergessene Orientmission geschrieben. Veltzke konnte dabei auf einen wahren Quellenschatz zurückgreifen: Der 95-jährige Sohn Fritz Kleins hatte dem Historiker den Nachlass seines Vaters übergeben - neben Aufzeichnungen auch rund 500 Fotos.
Veitzke spürte weitere Quellen auf, darunter das Kriegstagebuch der Expedition im Archiv des Auswärtigen Amtes. Am Ende stand für ihn fest: Fritz Kleins Mission war nicht nur die "vielseitigste" deutsche Orientexpedition - sondern auch die "mit dem greifbarsten Erfolg". Sie sei auch deshalb vergleichsweise erfolgreich gewesen, weil sich der eigensinnige Hauptmann nur bedingt an die Order seiner Vorgesetzten hielt.
"Schlag ins Herz der britischen Admiralität"
Klein träumte von einer engen deutsch-persischen Achse, die - und das war neu - möglichst unabhängig vom Einfluss des Osmanischen Reiches sein sollte. Konstantinopel verfolgte eigene imperialistische Ziele in der Region, die Klein ziemlich undiplomatisch als "geradezu blödsinnige Eroberungsgelüste" geißelte, weil sie jedes deutsch-persische Bündnis gefährden würden. Klein hingegen sah in Persien langfristig "ungeheure Kultur- und Wirtschaftsperspektiven" für das Kaiserreich.
Der Mann, der die Bevölkerung im heutigen Iran und Irak gegen die dort einflussreichen Briten und Russen aufwiegeln wollte, hatte schon als Kind seinen eigenen Kopf. Die Schulzeit war für ihn ein einziger "Bildungswahnsinn", angelerntes Wissen empfand er als "Ballast". Stattdessen habe er sich stets von seinem Menschenverstand und einem "unbezähmbaren Freiheitsdrang" treiben lassen - und fuhr damit erstaunlich gut: Klein reiste um die Welt, ging zur Armee und arbeitete ab 1911 für jeweils ein Jahr als Militärattaché in Rio de Janeiro, Kairo und Teheran.
Seine Erfahrungen dort halfen ihm, als das Auswärtige Amt nach dem Kriegsausbruch nach Personal für Geheimaufträge im Orient suchte. Klein brachte sich selbst ins Gespräch und wurde Ende 1914 zum Leiter eines verwegenen Kommandos: Die Deutschen sollten mithilfe arabischer Stämme die Ölpipelines der Briten am Persischen Golf sprengen - und damit die Treibstoff-Nachfuhr für die Marine kappen. Die Aktion sollte, so hoffte der Generalstab, "ein Schlag ins Herz der britischen Admiralität" werden.
So ungewöhnlich wie die Mission war auch ihre Zusammensetzung: Klein vertraute einer bunten Truppe von sprachgewandten Abenteurern, Archäologen, Kaufleuten und Ingenieuren. Zu seinem wichtigsten Mitarbeiter ernannte er Edgar Stern, den späteren Ullstein-Chefredakteur. 69 Männer machten den Kern seiner Expedition aus, zeitweise kamen noch 306 österreichisch-ungarische Soldaten hinzu, die aus russischer Gefangenschaft entflohen waren. Unterstellt waren sie der türkischen Armee, die damals von Bagdad aus Teile des heutigen Irak kontrollierte, allerdings schon von Briten und Russen bedrängt wurde.
Klein wollte in der Ferne mehr als nur Ölleitungen zerstören. Er improvisierte, sobald er ein Problem sah. Als der türkischen Flotte auf Euphrat und Tigris die Kohle ausging, fahndeten seine Männer nach neuen Kohlevorkommen. Geleitet wurde die hastig errichtete Mine von einem österreichischen Schlosser, die Logistik besorgte mit 1000 Kamelen ein deutscher Oberkellner. Kleins Ingenieure konstruierten auch lenkbare Flussminen und versuchten, wenig erfolgreich, ein Mittel gegen Heuschreckenplagen zu finden.
Vor allem aber hoffte Klein, "den Heiligen Krieg auch nach Persien hineinzutragen". Zwar hatte das sunnitische Osmanische Reich 1914 schon zum Dschihad gegen seine Feinde aufgerufen - aber was war mit den schiitischen Muslimen? Um auch sie für ein Bündnis mit dem Kaiserreich zu gewinnen, besuchte Klein 1915 - ohne Rücksprache mit der Botschaft in Konstantinopel - die schiitischen Glaubensführer in den heiligen Stätten von Nadschaf und Kerbela.
320 Millionen Liter Öl - verloren
"Unterwegs erkrankt [der Arzt] Dr. Schacht schwer, wird ohnmächtig, bekommt Darmblutungen", notierte Klein am 24. Januar 1915 über die beschwerliche Anreise nach Kerbala. "Eine Stunde vor K. empfangen uns zwei intelligent und vornehm aussehende Perser, um uns das Geleit zu geben. Der eine ist Sohn des Scheichs Mudschtahids Ali."
Scheich Ali bewirtete die Deutschen fürstlich mit "Hunderten von Schüsseln mit den verschiedensten orientalischen Sachen", wie der Hauptmann staunend festhielt. Nach zähen Verhandlungen sollte Klein schließlich sein Ziel erreichen: Im Februar 1915 riefen führende schiitische Geistliche, ermuntert auch durch 50.000 Reichsmark, zum Heiligen Krieg gegen die Feinde Deutschlands auf.
Obwohl sich der Hauptmann mit diesem Alleingang unbeliebt machte und zeitweise kaltgestellt wurde, gelang ihm wenige Wochen später sein größter Coup: Begleitet von türkischen Truppen sprengte ein Spezialkommando unter der Leitung von Hans Lührs am 22. März bei Ahvaz im heutigen Iran die britische Ölpipeline. Einem verbündeten arabischen Stamm gelangen in den folgenden Wochen weitere Anschläge auf die insgesamt 350 Kilometer lange Pipeline. Anhand des Jahresberichts der Anglo-Persian Oil Company schätzte der deutsche Generalstab den Gesamtverlust auf etwa 320 Millionen Liter Öl.
Eiternde Brandwunden
Ein Teil der Saboteure gerieten bald in die Defensive. Die Briten drängten die Türken aus der Region Ahvaz zurück, und ihre Kanonenboote eroberten Mitte 1915 die weiter westlich gelegene Stadt Amara, in die sich Lührs zurückgezogen hatte.
Auf der Flucht überquerte er mit seinen Kameraden Müller, Back und Schadow den reißenden Tigris. Eines ihrer Pferde ertrank. Verkleidet als Araber versuchten die Deutschen sich nun entlang des Flusses nach Norden durchzuschlagen. Die britischen Späher konnten sie täuschen, aber dann wurden sie von arabischen Banditen ausgeraubt. Einmal. Zweimal. Immer wieder. Erst verloren sie die Pferde, dann Uhren, Schuhe, Wäsche.
Nur mit Fetzen bekleidet taumelten die Männer barfuß über den heißen Lehmboden und bettelten um Brot, oft vergebens. Gegen die brüllende Hitze legten sie sich Tamariskenzweige auf den Kopf, die aber Unmengen von Moskitos und Sandmücken anzogen. "Auf unseren Schultern, Armen und Schenkeln bildeten sich große eiternde Brandwunden", erinnert sich Lührs. Sein Kamerad Schadow fiel immer wieder in Ohnmacht.
Ein "scheinheiliger Krieg"
Vielleicht ist es das größte Wunder der Mission Klein, dass Lührs und seine Männer ihre Odyssee überlebten. Nach mehr als hundert Kilometern Marsch erreichten sie bei Al-Gharbi mithilfe eines deutschfreundlichen Arabers eine türkische Einheit.
Klein selbst widmete sich nach dem Krieg der Philosophie. Den Heiligen Krieg, den er einst entflammen wollte, empfand er nun als "scheinheilig"; ebenso harsch kritisierte er jeglichen Imperialismus, den er früher mitgetragen hatte. In einem aber blieb er sich treu: Persien war zeitlebens das Land seiner Träume.
-

- Veit Veltzke:
Unter WüstensöhnenDie deutsche Expedition Klein im Ersten Weltkrieg
Nicolaische Verlagsbuchhandlung; 400 Seiten; 34,95 Euro.
00:05 Publié dans Histoire | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : histoire, allemagne, première guerre mondiale, perse, iran, capitaine klein |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Bulletin célinien n°369
Marc Laudelout : Bloc-notes [Christian Millau]
Stéphane Balcerowiak : Voyage au bout de l’Argonne
François Lecomte : Le parallèle Céline / Péguy
Vincent Tchamy Kouajie : Langage et narration chez Céline
M. L. : Trotsky – Céline
Éric Mazet : Lucienne Delforge et Louis Destouches (III)
M. L. : Hommage à Kléber Haedens
Le Bulletin célinien,
Abonnement annuel : 55 € (onze numéros). Courriel : bulletinlfc@gmail.com
00:05 Publié dans Littérature, Revue | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : céline, littérature, lettres, lettres françaises, littérature française, france |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Une révolution colorée imminente en Russie

Une révolution colorée imminente en Russie
La manipulation coordonnée des prix de l’énergie, sous l’égide de l’OTAN en Europe de l’est, et le retour des actions terroristes dans le sud Caucase apparaissent comme les éléments d’un scénario d’un événement plus large qui vise un renversement de pouvoir en Russie sur le modèle d’un « Maïdan russe ».
Les composantes nécessaires d’une action occidentale pour renverser l’ordre politique russe incluent un front politique de protestation dans les grandes villes du pays, aussi bien qu’une guerre économique globale destinée à mettre la population sous pression, le soutien à la dissidence aussi bien que l’organisation de manifestations par Washington et Wall Street dans les rues de la Russie. Une autre composante inclus l’armement des « opposants pacifiques » dans le but d’entraîner une escalade des manifestations, d’empêcher les forces de sécurité de rétablir l’ordre, afin de mener à bien leur renversement physique.
Ces éléments ont tous pu être observés dans l’Ukraine voisine – une nation dans laquelle les ingérences de l’OTAN et de l’Amérique constituent un sujet d’étude de longue date. Le journal The Guardian l’admettait dans un article de 2004 : « La campagne américaine derrière les tourments à Kiev », l’article ajoutait également :
« Alors que les avancées obtenues par la « révolution orange » sont ukrainiennes, la campagne est une création américaine,un exercice brillant et sophistiqué conçu par les agences de communication et de marketing occidentales, qui ont été utilisées en quatre ans dans quatre pays pour manipuler des élections truquées et renverser des régimes peu recommandables.
Fondé et organisé par le gouvernement US, utilisant des consultants US, des sondeurs et des diplomates, les deux grands partis politiques américains et des organisations non gouvernementales, ce type de campagne a d’abord été utilisée en Europe à Belgrade pour provoquer la défaite électorale de Slobodan Milosevic.
Richard Miles, l’ambassadeur américain à Belgrade, a joué un rôle clé. Et l’année dernière, en tant qu’ambassadeur à Tbilissi, il a répété l’opération en Géorgie, en aidant Mikhail Saakashvili à faire tomber Eduard Shevardnadze.
Dix mois après le succès de Belgrade, l’ambassadeur américain à Minsk, Michael Kozak, qui avait déjà conduit des opérations similaires en Amérique Centrale, notamment au Nicaragua, a organisé une campagne identique pour faire tomber l’homme fort de la Biélorussie, Alexander Lukashenko.
Cette opération échoua. « Il n’y aura pas de Kostunica en Biélorussie » déclara la président biélorusse en se référant au changement de régime à Belgrade.
Mais l’expérience accumulée lors des opérations en Serbie, Géorgie et Biélorussie, a été inestimable dans la tentative de renverser le régime de Léonid Kuchma à Kiev.
L’opération, de l’ingénierie démocratique passant par des scrutins électoraux et la désobéissance civile, est maintenant parfaitement au point et la méthode fait figure de modèle pour gagner n’importe quelle élection. »
Comme le révèlent d’autres sources du Guardian, ce n’est pas seulement l’Ukraine qui a souffert ces dernières années de la déstabilisation américaine, de ces changements de régime, des manipulations et subversions, mais toute l’Europe de l’est. Lorsqu’on considère ces faits documentés, de telles manœuvres de Wall Street et Washington contre la Russie n’apparaissent plus seulement comme un fait envisageable, elles ont déjà eu lieu par le passé, et sont inévitables à l’avenir.
Il y a déjà une manipulation coordonnée des prix du pétrole. La chute des cours du pétrole révèle que l’industrie pétrolière entière est manipulée non pas par les forces du marché mais par l’agenda US et ses partenaires au Moyen-Orient et particulièrement la dictature saoudienne. Bien que toute nation possède les capacités de supporter de telles mesures économiques sur le long terme comme l’ont prouvé l’Iran et Cuba, sur le court terme, l’instabilité économique est un signe avant-coureur de la subversion politique et les manifestations de mécontentement peuvent être imputées par ceux qui perçoivent cette instabilité comme relevant de la responsabilité du gouvernement en place plutôt que comme la conséquence des attaques économiques étrangères.
Le front politique russe
Le front politique qui aura la charge de descendre dans les rues de Russie a été identifié depuis longtemps. Il inclut les mêmes branches de nationalistes extrémistes et les groupuscules d’extrême droite qui ont détruit l’ordre politique ukrainien. Cela inclut des néo-nazis. L’une des figures à la solde des états-unis et régnant sur l’ultra-droite russe s’appelle Alexey Navalny, présenté par l’occident comme un « activiste anti-corruption ». Il s’agit en réalité d’un néo-fasciste qui opère ouvertement pour le compte de Wall Street. Navalny est membre du programme YaleWordfellows (NDT : il s’agit d’un programme de séminaires développé par l’université de Yale et destiné aux jeunes leaders étrangers dans le but de « créer un réseau de partenaires ayant les mêmes opinions ». On retrouve parmi les sponsors du programme l’Open Society de Georges Soros…)
Voici sa présentation telle qu’elle apparaît sur son profil :
« Navalny est le fer de lance des actions juridiques menées au nom des actionnaires minoritaires dans les grandes entreprises russes, incluant Gazprom, BankVTB, Sberbank, Rosneft, Transneft, et Surgutneftegaz, à travers l’Union des Actionnaires Minoritaires. Il a forcé avec succès des entreprises à communiquer davantage d’information à leurs actionnaires minoritaires et a poursuivi plusieurs cadres de grandes entreprises pour des pratiques alléguées de corruption. Navalny est également le cofondateur du mouvement pour l’Alternative Démocratique et a été vice-président de la branche moscovite du parti Yabloko. Il a lancé RosPil, un projet public financé par une campagne d’appel de fonds sans précédent. En 2011, Nvalny a lancé RosYama, qui combat la fraude dans le secteur de la construction routière. »
L’Alternative démocratique, DA!, est financée par la Natinoal Endowment for Démocratie, NED, qui dépend du département d’état, ce qui implique qu’Alexey Navalny est un agent de sédition US. Le département d’état mentionne lui même DA! parmi la liste des mouvements de la jeunesse qu’il soutient en Russie.
« DA! : Mariya Gaydar, la fille de l’ancien premier ministre Yegor Gaydar, dirige DA!. Elle est un ardent promoteur de la démocratie mais réaliste quant aux obstacles auxquels elle doit faire face. Gaydar affirme que DA! mène des activités non partisanes conçues pour sensibiliser le monde politique. Elle a reçu des financements de la NED, un fait dont elle ne souhaite pas faire la publicité pour ne pas paraître compromise avec les états-unis. »
Le fait que ce financement n’apparaisse nulle part sur le site web de la NED indique qu’il ne s’agit pas d’une opération transparente et que la NED est engagée dans un financement clandestin.
Navalny a été directement impliqué dans la création d’un mouvement financé par le département d’état et à ce jour les mêmes personnes qui ont fondé DA! le défendent à travers les médias occidentaux. La mention du co-fondateur Mariya Gaydar est également révélatrice, du fait qu’elle ait collaboré depuis longtemps, et occasionnellement été arrêtée avec Ilia Yashin, un autre leader d’un groupe d’opposition russe financé par la NED.
Ilia Yashin dirige la branche moscovite du Parti pour la Liberté du Peuple et est un des leaders de la campagne « Stratégie 31 » dont les rangs sont infiltrés par des activistes entraînés et coordonnés par des ONG financées par la NED. La référence au financement de « Stratégie 31 » a été supprimée du site web officiel de la NED :
« Groupe d’assistance de Moscou pour la mise en place des accords d’Helsinki : 50000$
Pour focaliser davantage l’attention sur les résultats de l’Assemblée de la Liberté en Russie et le mouvement « Stratégie 31 »qui cherche à protéger ce droit fondamental. L’organisation va promouvoir un réseau d’activistes régionaux et coordonner leurs activités à travers des mini séminaires et des visites sur le terrain et conduire une campagne d’information par des conférences de presse, des posters, et des documents éducatifs relatifs à l’Assemblée de la Liberté distribués au grand public par des partenaires régionaux. »
Egalement supprimé, « Democraty Digest », un article intitulé « Stratégie 31 : un signe de résilience de la société civile ». A l’intérieur, le « groupe de Moscou-Helsinki » est explicitement déclaré comme l’initiateur des marches de Stratégie 31 et comme un « bénéficiaire de longue date de la NED ».
Les multiples suppressions concernant les connexions de la NED avec les activistes russes, leur financement massif et leur téléguidage, sont également un autre signe de subversion imminente. Ce nettoyage a été effectué dans l’espoir que les liens avec les activistes ne pourront pas être établis aussi vite que l’agitation se déroulera et qu’ils ne pourront pas saper la légitimité d’une nouvelle subversion pilotée par les états-unis.
Le Parti de la Liberté du Peuple de Yashin est lié non seulement avec les financements de la NED pour la « jeunesse » mais également avec des politiciens de carrière et des businessmen oeuvrant pour des intérêts étrangers. Parmi eux on trouve Vladimir Ryzkhov, un membre du Mouvement Mondial pour la Démocratie, financé par la NED et basé à Washington (dont le profil a été également supprimé récemment). Il y a aussi Boris Nemtsov dont le conseiller, Vladimir Kara-Murza (de Solidarnost) a participé à un événement sponsorisé par la NED le 14 septembre 2011 intitulé « Les élections en Russie : votes et perspectives ».
Il s’agit d’un front politique entièrement créé par le département d’état US et qui se positionne comme le porteur des aspirations du peuple russe alors qu’il s’agit en réalité de la création et de la perpétuation des aspirations de Wall Street et Washington.
Sous l’agitation créée par ce front se trouve un autre front armé constitué de l’ultra-droite et de néo-nazis, sur le modèle ukrainien, mais également des terroristes armés chapeautés par l’Arabie Saoudite.
Un petit aperçu du manuel de « sédition » américain
L’usage d’éléments armés pour assister les tentatives de subversion politique US n’est pas une invention. Au contraire, il s’agit d’une stratégie documentée incluse dans les plans établis pour saper et renverser les gouvernements étrangers. Dans un document de politique US de 2009 intitulé « Quel chemin pour l’Iran ? » publié par la Brookings Institution et qui concerne le changement de régime en Iran il est spécifiquement mentionné :
« Une méthode qui pourrait avoir des chances de succès consisterait à augmenter les actions par procuration visant à un changement de régime dans l’espoir que Téhéran conduise des représailles ouvertes ou semi-ouvertes qui pourraient être ensuite présentées comme des agressions iraniennes infondées. »
Les stratèges US conspirent ici ouvertement pour organiser une provocation envers une nation étrangère par la subversion politique. L’ « acte d’agression » qui doit en résulter sera présenté comme sans rapport avec la politique étrangère US exactement comme l’a été l’implication de la Russie vis à vis de l’Ukraine ainsi que toutes les actions entreprises par Moscou depuis que les états-unis et l’OTAN ont décidé de déclencher une confrontation militaire.
Le document aborde également ouvertement les conditions pour fomenter des troubles politiques. Dans une section intitulée littéralement « Trouver les bonnes procurations », on peut lire :
« L’un des points les plus ardus pour fomenter une révolution, ou seulement des troubles, consiste à trouver les bons partenaires locaux. »
Après avoir admis ouvertement l’objectif de « fomenter une révolution »ou des « troubles » le document détaille quels soutiens apporter à ces partenaires locaux :
« … les étudiants et les autres groupes ont besoin d’un support officieux pour leurs manifestations. Ils ont besoin de fax. Ils ont besoin d’accès Internet, de financements pour photocopier des documents, et de financements pour rester vigilants quant à leur sécurité. Au delà de ça, les médias sous notre influence peuvent mettre en lumière les lacunes du régime et donner de l’importance aux critiques du régime. Les états-unis pilotent déjà des satellites de télévision en langue iranienne (La Voix de l’Amérique) et des radios (Radio Farda) qui donnent des informations non filtrées aux iraniens (ces dernières années ces médias ont absorbé la majeur partie des fonds américains pour promouvoir la démocratie en Iran). La pression économique US (et peut-être également militaire) peut discréditer le régime et rendre la population désireuse d’un changement politique. »
Le rapport mentionne finalement les groupes armés en soutien de la subversion américaine :
« Ceux qui souhaitent fomenter un changement de régime en Iran mettent en avant le fait qu’il est utopique d’espérer une révolution de velours. A l’inverse, ils estiment que les états-unis devraient se tourner vers les groupes d’opposition qui existent déjà, qui ont déjà montré leur volonté de combattre le régime et qui semblent disposés à accepter l’assistance américaine. Cette stratégie fait le pari que ces groupes d’opposition hétéroclites pourront se transformer en un puissant mouvement qui pourrait être capable de renverser le régime. »
Ce qui est troublant à propos de ce rapport de 2009, c’est que chaque conspiration qu’il contient est non seulement confirmée par ces auteurs comme devant être utilisée contre l’Iran, mais qu’il est maintenant clair que des stratégies similaires ont été utilisées contre la Syrie, la Chine, et la Russie elle-même. Le « printemps arabe » était un peu plus complexe que ce mode opératoire utilisé à l’échelle régionale, mais ce qui a été fait en Syrie et en Ukraine est presque un Verbatim tiré des pages de ce manuel.
Concernant la campagne menée contre Moscou, c’est probablement le même manuel qui sera employé une fois encore. Exposer la criminalité insidieuse des géostratèges US qui conspirent ouvertement sur la manière de provoquer les autres nations et de les entraîner dans des conflits, qui manipulent la perception de l’opinion publique afin de maintenir leur primauté morale, constitue une première étape afin d’éviter la déstabilisation et l’ébranlement de la Russie et de toutes les autres nations qui se trouvent dans le collimateur de Wall Street et Washington.
Alors que l’Ouest continue à présenter la Russie comme l’agresseur, selon le script de la politique étrangère américaine, on peut voir que ces accusations constituent seulement une petite partie d’un plan gigantesque, insidieux et trompeur. Dépeindre la Russie comme l’agresseur permet de justifier de nouvelles mesures destinées à engager des actions de subversion politique contre cette dernière.
Cela vise également à justifier les liens directs avec les groupes d’opposition lorsque ceux-ci sont finalement révélés, mais aussi les interventions extraordinairement agressives de supplétifs armés et des forces de l’OTAN elles-mêmes destinées à soutenir les groupes d’opposition.
Les « invasions » spectaculaires telles que nous les imaginons, comme le blitzkrieg nazi en Europe de l’Ouest, appartiennent au passé. Les invasions au sein de la guerre de quatrième génération utilisent des faux groupes d’opposition, des soutiens militaires agissant sous couverture, et une guerre économique, politique et informationnelle à large spectre. La Russie a construit des défenses contre ce type de guerre, confondant l’occident, mais en définitive la morale et tous les avantages qui en découlent ne peuvent être l’apanage que d’un seul camp. Peut-être qu’en exposant la vérité, les procédés et l’agenda de l’occident, la Russie pourra sortir victorieuse, sinon l’Ouest continuera ses manœuvres de déstabilisation et dans ce cas elle sera laminée.
- Source : Tony Cartalucci-Traduction Ender
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Affaires européennes, Géopolitique | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : actualité, affaires européennes, europe, russie, politique internationale, géopolitique, révolution colorée, subversion, guerres indirectes |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
De Taliban, verdwaalde restant van de Koude Oorlog

De Taliban, verdwaalde restant van de Koude Oorlog
door Johan Sanctorum
Ex: http://www.doorbraak.com
Waarom het bloedbad van Peshawar tot enkele ongemakkelijke bedenkingen leidt over de historische rol van de VS en Pakistan.
Te walgelijk voor woorden, dat is onze eerste bedenking bij de executie door de Pakistaanse Taliban van 132 kinderen in een school nabij Peshawar, terwijl er ‘Allah is groot!’ werd gescandeerd. De naam Taliban schijnt zoiets te betekenen als ‘theologiestudenten’: wat moet men zich voorstellen bij een godsdienst die dit soort leerlingen voortbrengt en in de 21ste eeuw tot dit soort acties inspireert. Benieuwd weerom hoe snel en hoe radicaal de moslimgemeenschappen in de beschaafde wereld hiervan afstand zullen nemen, want voorlopig is het weer zeer stil in die hoek. Alsof men meer de perceptieschade betreurt dan de 132 kinderlijken. Of erger, horresco referens: alsof er zelfs heimelijk gesympathiseerd wordt met deze strijders van de goede zaak.
Dat mag ons allemaal niet beletten om een en ander in een historisch perspectief te plaatsen, en uit te vlooien waar die godvruchtige Taliban eigenlijk vandaan komt. Een korte terugblik.
Van ‘freedom fighters’ tot terroristen
Afghanistan is een land dat geografisch en etnisch niet centraal te besturen valt. ‘Onherbergzaam’ is de naam die wij klassiek gebruiken voor zo’n droge steenwoestijn, heet in de zomer, ijskoud in de winter. Krijgsheren maken er traditioneel de dienst uit en liggen voortdurend met elkaar overhoop: stamoorlogen zijn de enige echte nationale sport. Eén economische sector floreert van oudsher: de kweek en handel van opium.
In de 19de eeuw raakte deze negorij in de Britse invloedssfeer, zonder dat de Engelsen er een echte beschaafd gewest van konden maken waar men thee drinkt en cricket speelt, zoals in Indië. Neen, de Afghanen bleven de ongenode gasten de rug toekeren, vochten op feestjes om een geitenkarkas, en bestreden tussendoor ook elkaar. Dat zou niet anders zijn met de Russische bezetting, we zijn dan al 1979, in volle Koude Oorlog. De toenmalige Sovjetleider Leonid Breznjew besliste het land binnen te vallen, na een mislukte politiek van Moskougezinde stromannen. Rusland heeft nu eenmaal graag volgzame satellieten aan zijn grenzen, dat is de hoeksteen van een defensieve strategie.
De Russen maakten echter dezelfde fout als de Britten: ze dachten de Afghanen te kunnen beschaven en transformeren tot met hamer en sikkel getooide bewoners van de Marxistische heilstaat. De geitenhoeders en kamelendrijvers lustten er geen pap van en bleven verknocht aan hun eeuwenoude ongeschreven, maar door de Koran gewettigde gebruiken. De grote steun aan het anti-Sovjet-verzet kwam echter van buitenaf, en wel van een andere grote broer die verder weg lag: de Verenigde Staten.
Onder invloed van zijn radicale adviseur Zbigniew Brzeziński, die een grootscheeps Russisch offensief richting Perzische Golf meende te ontwaren, ging president Jimmy Carter de Afghaanse moslimrebellen - die het koosnaampje 'Freedom Fighters' kregen - militair ondersteunen. Lokaal werden ze Moedjahedien genoemd, waaruit de latere Taliban zou ontstaan. Om de Amerikaanse betrokkenheid te verhullen gebeurde die steun via omwegen: de CIA kocht in alle uithoeken van de wereld Sovjet- en Oostblokwapens (!) op en leverde die aan de opstandelingen.
Pakistan nam in deze strategie met verve de rol op van regionaal steunpunt. Het werd daarin ruim gedragen door de met de rebellen sympathiserende moslimbevolking, maar het leverde het land ook militaire VS-steun op in zijn wedijver met oervijand India. De Taliban kregen in Pakistan hun guerilla-opleiding en leerden daar de Amerikaanse hightechwapens bedienen. Tegelijk werd het religieus radicalisme gepromoot, als een belangrijke mentale stimulans die maakte dat men een krijger werkelijk alles kon vragen tot en met een zelfmoordactie. Bewust gebruikte Washington de Koranscholen en hun ‘theologiestudenten’ als anti-Sovjet-wapen, nog niet beseffende welke doos van Pandora men daarmee had geopend.
Na de Russische terugtrekking viel het land ten prooi aan een complete chaos, waarin de Taliban uiteindelijk triomfeerden en als een stuurloos geworden projectiel om zich heen sloegen. De inval in 2001 van een door de VS geleide NAVO-legermacht bezorgde hen tenslotte een nieuwe vijand op het terrein waarop ze onklopbaar waren. Pakistan bleef de vluchtheuvel van die fanatieke groupuscules. Op 2 mei 2011 liquideerden Amerikaanse elitetroepen er Osama Bin Laden, het brein achter de aanslag op de Twin Towers. Een puur symbolische overwinning: Al Qaida was al lang uitgezaaid naar Irak en omstreken, de Islamitische Staat stond in de steigers.
Europese ongebondenheid
Zo groeide een verdwaalde restant van de koude oorlog uit tot een planetaire splijtbom. De historische verantwoordelijkheid van de VS is hier enorm. Washington blijkt in de jaren ‘80 een politiek-religieuze stroming in het leven geroepen te hebben, die twintig jaar later verantwoordelijk zou zijn voor de grootste en bloedigste terroristische aanslag op Amerikaans grondgebied, ‘9/11’. Het zegt iets over het intellectueel niveau en het kortetermijndenken dat domineert in het Pentagon en het Witte Huis. We hebben hier te maken met klungelende presidenten, van Carter tot George Bush Jr., varend op een populistisch-paranoide veiligheidsdoctrine (war on terror), mondiaal bemoeizuchtig, met slechte raadgevers en een geheime dienst die opereert als een staat-in-de-staat, zie ook de huidige afluisterschandalen. Met zo’n bondgenoten heb je geen vijanden nodig.
Minstens even hachelijk is de morele vraag die Pakistan zichzelf moet stellen: in hoeverre heeft het land zelf deze adder niet aan zijn borst gekoesterd, die het bloedbad van Peshawar zou veroorzaken? De prijs voor deelname aan het wereldwijde geostratego van de grootmachten is hoog, te hoog. Men zou zich kunnen afvragen hoe onze wereld er zou uitgezien hebben zonder de inval van de Sovjet-Unie in Afganistan en zonder het tegenoffensief van de VS, zonder de met valse voorwendsels goedgeprate invasie van Irak. Zouden Bin Laden en Al Qaida groot geworden zijn? Zou 11 september 2001 plaats gevonden hebben? Vermoedelijk niet. Zouden we nu met een radicaliseringsprobleem zitten in onze steden? Ik betwijfel het. Zouden de 132 Pakistaanse schoolkinderen nog leven? Allicht wel.
De ultieme les van de Peshawar-tragedie zou voor ons, Europeanen, kunnen gelegen zijn in een kritische herziening van het NAVO-bondgenootschap. De Pentagon-logica is de onze niet. Wij hoeven de brokken niet op te ruimen die door Amerika worden gemaakt. En als het over democratie en mensenrechten gaat: de VS zouden misschien toch beter eerst voor eigen deur vegen, gelet op de lamentabele rechtspositie van hun gekleurde staatsburgers. Er vallen overigens per jaar meer doden door de kogel in het vrije Amerika dan in het achterlijke Afghanistan.
De idee alleen al dat de CIA ook vandaag compleet onder de waterlijn wereldwijd allerlei schimmige constructies opzet, zogezegd in naam van vrijheid en democratie, moet ons tot de grootste argwaan nopen. Een onafhankelijk Vlaanderen zou hier de status van de Belgische NAVO-vazal kunnen overstijgen en een koers van neutraliteit,- ik spreek liever van ongebondenheid,- aanhouden. Het absoluut vermijden van geïmporteerde conflicten hoort daarbij, evenals het verwijderen van alle gevaarlijke rommel die hier niet thuis hoort.
Dat doet er me aan denken: al meer dan vijftig jaar liggen er kernbommen op de luchtmachtbasis van Kleine Brogel, die minstens tien keer de kracht van de atoombom op Hiroshima hebben. Officieel mogen we zelfs niet weten dat ze er liggen, hoewel de VS onlangs hebben aangedrongen om ze te ‘moderniseren’. Vanuit welk strategisch oogpunt is onbekend, tenzij de Amerikaanse wapenindustrie een zetje in de rug nodig heeft.
Nogmaals: dat maakt onze belangen niet uit. De nieuwe Europese republieken moeten zich durven afkeren van het Amerikaans militair dictaat. Een onderling bondgenootschap, gebaseerd op intelligente diplomatie, wordt dan een reële optie. Voor de Koude Oorlog weer een hete wordt.
(c) Reporters
00:05 Publié dans Actualité | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : politique internationale, géopolitique, actualité, afghanistan, talibans, pakistan, terrorisme, islamisme, djihadisme, services secrets, services secrets américains, cia |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
La neutralité suédoise pendant la seconde guerre mondiale
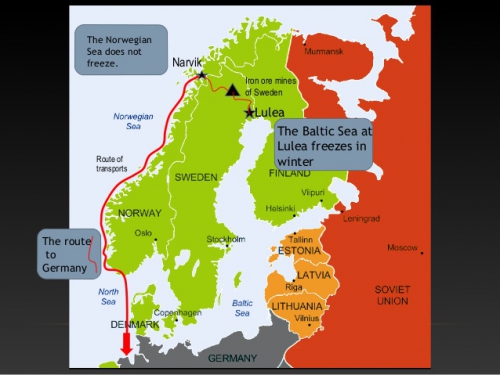
Erich Körner-Lakatos :
La neutralité suédoise pendant la seconde guerre mondiale
La Suède exportait du minerai de fer et importait du charbon
Le 5 février 1940, le conseil de guerre suprême des Alliés décide d’envoyer trois à quatre divisions à hauteur du port de Narvik. D’une part, leur intention est d’apporter une aide aux Finlandais menacés par les Soviétiques et, d’autre part, d’occuper les mines de fer suédoises, et c’est vraisemblablement là que réside la raison principale de cette manœuvre car cela aurait privé l’ennemi allemand de ses approvisionnements en un minerai stratégique de la plus haute importance. La Norvège et la Suède étaient deux puissances neutres mais prendre ce statut en considération n’entrait pas dans les intentions des Alliés occidentaux.
Dans le texte anglais du 6 avril, relatif à l’occupation programmée des zones de minerais de fer dans le nord de la Suède, on lit clairement que « si l’occasion se présente, le commandement envisage de faire entrer nos troupes en Suède et d’occuper les mines de fer de Gällivare… ». Il ne s’agissait donc pas de franchir la frontière suédoise sur une profondeur réduite car ces mines se trouvent à une centaine de kilomètres à l’intérieur du pays.
Ce qui rend l’opération problématique, c’est que les voies de chemin de fer ont été minées par les forces suédoises en dix-sept endroits. Le Reich, pour sa part, envisage lui aussi une occupation partielle : en décembre 1939, la Kriegsmarine élabore un plan pour l’occupation du sud de la Suède, la région de Scanie, afin que l’Allemagne puisse contrôler la totalité de la Mer Baltique. Cependant, le corps expéditionnaire britannique embarque le 7 avril et, le jour suivant, les Anglais commencent à miner la zone de trois miles devant Narvik. Les forces allemandes réagissent alors à la vitesse de l’éclair : l’Action Weserübung (« exercice sur la Weser ») est amorcée dès le 8 avril en soirée et réduit à néant les projets des Alliés. L’édition vespérale du 9 avril 1940 de la « Neue Zürcher Zeitung » suisse informe ses lecteurs sur les événements du jour en titrant « La contre-attaque allemande ».
 Avant de signer le « Traité de transit » du 8 juillet 1940 a été précédé en Suède d’un crise politique interne. Les sociaux-démocrates sont contre cet accord qui sera finalement signé avec l’Allemagne tandis que les partis conservateurs y sont favorables (voir annexe). Il a fallu que le chef de l’Etat, le Roi Gustave V (photo) -qui officiellement porte le titre de « Roi des Suédois, des Goths et des Vandales »- menace d’abdiquer pour que le premier ministre Per Albin Hansson réussisse à convaincre les sociaux-démocrates d’accepter les clauses du traité.
Avant de signer le « Traité de transit » du 8 juillet 1940 a été précédé en Suède d’un crise politique interne. Les sociaux-démocrates sont contre cet accord qui sera finalement signé avec l’Allemagne tandis que les partis conservateurs y sont favorables (voir annexe). Il a fallu que le chef de l’Etat, le Roi Gustave V (photo) -qui officiellement porte le titre de « Roi des Suédois, des Goths et des Vandales »- menace d’abdiquer pour que le premier ministre Per Albin Hansson réussisse à convaincre les sociaux-démocrates d’accepter les clauses du traité.
Quand la fortune des armes abandonne les Allemands au cours de la seconde guerre mondiale, les Suédois se mettront à battre froid leurs voisins allemands du Sud. Le 29 juillet 1943, Stockholm renonce au Traité de transit. Peu de temps avant la fin des hostilités sur les fronts européens, les sociaux-démocrates, à leur tour, influencent la politique du premier ministre Hansson qui, sous leur pression, menace de faire donner l’armée suédoise si les unités allemandes présentes au Danemark et en Norvège transforment ces deux territoires nationaux scandinaves un théâtre d’opérations militaires. Le courage guerrier des Suédois ne s’est donc affirmé que contre un adversaire potentiel déjà presque totalement liquidé par les Alliés occidentaux et par les Soviétiques, alors qu’à peine plus tard, ces mêmes suédois sociaux-démocrates tombent à genoux devant les menaces soviétiques dans la question du droit d’asile. En janvier 1946, en effet, les socialistes suédois livrent aux bourreaux staliniens de nombreux Baltes qui s’étaient réfugiés en Suède.
Comment se sont déroulés les relations économiques entre la Suède et le Reich pendant la seconde guerre mondiale ? L’Allemagne a un besoin impératif du minerai de fer suédois, réputé de très haute qualité. Le transport de ce minerai s’effectue pour partie par la Mer Baltique et pour une autre partie par le port norvégien de Narvik, où deux millions de tonnes de minerai de fer avaient été expédiées par voie maritime en Allemagne entre septembre 1939 et mars 1940.
La Suède, elle, avait un besoin permanent de charbon allemand. L’Angleterre et la Pologne (qui, en 1937, livrait 40% du charbon consommé en Suède) ne fournissaient plus ce charbon. C’est pourquoi les Suédois ont été contraints d’importer quatre millions de tonnes de charbon et 1,7 million de tonnes de coke en provenance des mines allemandes en 1941.
A la fin de l’année 1941, les Suédois réclament aux Allemands la livraison de 110 canons (de type Howitzer) avec 300.000 munitions ad hoc. Vu l’énorme besoin en armes qu’exigeait le front soviétique, le Reich n’a pu faire face à cette exigence suédoise que très lentement : en mars 1943, seulement 40 howitzers et 80.000 munitions sont livrés effectivement à l’armée suédoise. Par la suite, la Suède a reçu chaque mois quatre de ces pièces d’artillerie.
A partir d’août 1943, les premières failles dans la livraison du minerai de fer suédois surviennent, surtout parce que les ports allemands de la Mer du Nord sont pilonnés systématiquement par les aviations anglo-saxonnes et que le débarquement des minerais prend plus de temps. Mais il y a une autre cause à ce ralentissement qui réside en Suède : la voie de chemin de fer transportant le minerai vers Narvik a été sur-sollicitée et a réclamé réparations et remises en état, interrompant ainsi provisoirement le transport du fer vers la côte norvégienne.
Les Suédois se montrent aussi de plus en plus récalcitrants parce que les mesures visant à protéger le pays contre tout blocus portent leurs fruits : les Suédois disposent désormais de réserves de charbon et de coke pour près de six mois et ont commencé aussi à solliciter les immenses réserves de bois dont dispose naturellement le pays. Ensuite, autre facteur, les stocks de pétrole sont bien fournis et largement suffisants, tandis que l’on mobilise également les produits substitutifs comme les carburants tirés du schiste argileux et de la tourbe.
Malgré tout la Suède livre encore de janvier à mai 1944 près de deux millions de tonnes de minerai de fer au Reich. Après les échanges sont quasiment réduits à néant car le transport du charbon vers le Nord s’est avéré de plus en plus difficile. Les deux partenaires avaient prévu des négociations en décembre 1944, qui devaient régler les échanges économiques à partir de janvier 1945. Les Suédois n’y participeront pas car la situation n’était plus claire.
Erick Körner-Lakatos.
(article paru dans « zur Zeit », Vienne, n°50/2014 ; http://www.zurzeit.at ).
Le Traité du transit: de la Norvège à la Carélie soviétique
Le « Trait du transit », signé avec l’Allemagne en juillet 1940 permettait d’acheminer à travers le territoire suédois des éléments de la Wehrmacht (au maximum un train par jour dans les deux sens). Le Parlement suédois, dominé par les sociaux-démocrates, accepte le 25 juin 1941, trois jours après l’entrée des troupes allemandes (hongroises, finlandaises et roumaines) en Union Soviétique, que passe par le territoire suédois une division entière de la Wehrmacht (la 163ème DI), qui venait d’Oslo et se rendaient en Finlande. Jusqu’à la moitié de l’été 1943, les chemins de fer suédois ont ainsi transporté 2,14 millions de fantassins allemands et 100.000 wagons de marchandises destinées aux armées du Reich entre la Norvège et la Finlande et retour. 300 élèves officiers suédois serviront dans la Waffen-SS et 30 volontaires suédois sortiront de l’école d’aspirants officiers de cette organisation située à Bad Tölz en Bavière.
 Pourquoi une telle situation a-t-elle été possible ? Le chef de l’armée suédoise, le Général Olof Thörnell (photo) croit en une victoire allemande sur les Soviétiques, au plus tard à l’été 1942. Thörnell et le Parti Conservateur ne pourront toutefois pas faire interdire le parti communiste suédois, malgré leurs demandes réitérées. Dans l’armée suédoise pourtant, les conscrits réputés communistes, les syndicalistes les plus engagés et certains sociaux-démocrates de gauche ont été isolés dans des « compagnies de travail » spéciales pour les empêcher, en cas de conflit, de déserter et de rejoindre les rangs de l’armée soviétique. Cependant, cette politique était risquée : lors des élections pour la deuxième chambre du Parlement suédois en septembre 1944, le parti communiste a obtenu un score non négligeable, beaucoup plus important qu’habituellement : 10,3%, ce qui leur a permis de quintupler leurs sièges, de trois à quinze.
Pourquoi une telle situation a-t-elle été possible ? Le chef de l’armée suédoise, le Général Olof Thörnell (photo) croit en une victoire allemande sur les Soviétiques, au plus tard à l’été 1942. Thörnell et le Parti Conservateur ne pourront toutefois pas faire interdire le parti communiste suédois, malgré leurs demandes réitérées. Dans l’armée suédoise pourtant, les conscrits réputés communistes, les syndicalistes les plus engagés et certains sociaux-démocrates de gauche ont été isolés dans des « compagnies de travail » spéciales pour les empêcher, en cas de conflit, de déserter et de rejoindre les rangs de l’armée soviétique. Cependant, cette politique était risquée : lors des élections pour la deuxième chambre du Parlement suédois en septembre 1944, le parti communiste a obtenu un score non négligeable, beaucoup plus important qu’habituellement : 10,3%, ce qui leur a permis de quintupler leurs sièges, de trois à quinze.
EKL.
00:02 Publié dans Histoire | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : histoire, suède, scandinavie, seconde guerre mondiale, deuxième guerre mondiale, minerai de fer suédois, fer suédois |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
mardi, 23 décembre 2014
Traité transatlantique: les Etats européens paient déjà le prix fort

Traité transatlantique: les Etats européens paient déjà le prix fort
Dans le cadre du débat public sur le projet de traité commercial Europe-États-Unis (connu sous l'acronyme TAFTA ou TTIP), il est beaucoup question des mécanismes de protection des investisseurs que celui-ci pourrait inclure. Ces mécanismes - dits ISDS - pourraient donner aux multinationales le pouvoir de poursuivre des gouvernements devant des tribunaux privés lorsque ces derniers adoptent des législations nuisibles à leur taux de profit. Comme le révèle une étude approfondie des Amis de la terre Europe, des dispositifs de ce type sont déjà en vigueur en Europe. Et des entreprises - parmi lesquelles EDF, GDF, Vivendi, Servier ou Orange - y ont déjà eu recours pour obliger des gouvernements, principalement en Europe de l'Est, à leur verser de copieuses compensations financières.
L'équivalent du salaire annuel de 230 000 infirmières : c'est ce qu'a dû payer la Pologne en compensations financières à de gros investisseurs s'estimant lésés. Soit 2,2 milliards d'euros en tout. En 2010, un chèque de 219,9 millions a d'abord été signé à l'industrie pharmaceutique française. En cause : une réforme de l'autorisation de mise sur le marché de médicaments qui a entraîné l'interdiction de plusieurs molécules commercialisées, d'où une plainte de plusieurs sociétés françaises, dont les laboratoires Servier, tristement célèbres depuis l'affaire du Mediator. Le comble est que cette réforme mise en œuvre en 2001 était exigée par la Commission en vue de l'adhésion de la Pologne à l'Union européenne. En 2003, c'est la compagnie d'assurance néerlandaise Eureko qui attaque la Pologne pour son refus de privatiser totalement l'ancienne compagnie d'assurance publique PZU. Varsovie a dû s'acquitter d'un chèque de 2,19 milliards d'euros à Eureko, qui souhaitait devenir l'actionnaire majoritaire de l'assureur polonais.
Ces exemples, et quelques autres en Allemagne, en République tchèque ou en Roumanie, sont détaillés dans un rapport publié le 4 décembre par les Amis de la Terre Europe, réseau indépendant qui rassemble une trentaine d'organisations écologistes. Ce rapport, intitulé « les coûts cachés des traités commerciaux européens », illustre très concrètement les effets pervers des « règlements des différends » entre investisseurs et États.
Ces dispositifs, associés à un accord commercial entre États, permettent à une multinationale ou à un fonds d'investissement d'exiger des compensations financières en cas de réformes, de nouvelles législations sociales et environnementales, ou de refus de privatiser certains secteurs. Ces « différends » sont jugés devant un tribunal d'arbitrage privé, à l'aune des traités commerciaux bilatéraux qui ont été conclus. Ce sont ces mêmes dispositifs qui sont tant décriés pour les traités commerciaux en cours de négociation entre l'Union européenne et les États-Unis en vue d'un grand marché transatlantique (Tafta/TTIP) ou avec le Canada (Ceta). En France, sénateurs et députés ont voté fin novembre des résolutions invitant le gouvernement à renoncer à ce type de mécanismes.
Dans une affaire sur cinq, le jugement n'est même pas rendu public !
Le rapport des Amis de la Terre Europe recense, sur les 20 dernières années, 127 conflits commerciaux de ce type, concernant vingt pays, au sein de l'Union européenne. Les demandes de compensation formulées par les investisseurs dépassent les 30 milliards d'euros. L'Europe de l'Est est particulièrement touchée : les trois-quarts des demandes de compensations sont adressés aux nouveaux pays membres. Sur ces 127 affaires, 60 % concernent le secteur de l'environnement : énergies fossiles et nucléaire, recyclage des déchets, agriculture... Et représenteraient au moins 12 milliards d'euros de demande de compensation. Le dossier à suivre de près est l'action intentée en 2012 contre l'Allemagne par l'énergéticien suédois Vattenfall. L'entreprise demande 4,7 milliards d'euros de compensation à l'Allemagne pour avoir décidé de sortir du nucléaire et de fermer progressivement ses centrales, dont deux appartiennent à Vattenfall.
C'est l'une des 46 affaires encore en cours sur 127. Les autres ont donné lieu à un arbitrage en faveur de l'investisseur dans 18 % des cas, à un règlement à l'amiable - une compensation est cependant payée par le pays à l'investisseur - dans 16 % des affaires et à une victoire de l'État dans 17 % des dossiers. Qu'en est-il des autres ? Dans un cas sur quatre, la procédure a été interrompue. Et dans 20 % des affaires, le résultat de l'arbitrage n'a pas été rendu public ! Ce qui révèle le niveau de transparence de cette « justice » commerciale...
Ce dispositif de règlement des différends « compromet la capacité des autorités nationales et locales de réglementer dans l'intérêt général et constitue une attaque inacceptable et inutile contre la démocratie », alerte le rapport. (« Et ce sont les contribuables eux-mêmes qui devront payer la facture pour les risques pris par les investisseurs privés »). Privatisation des profits, socialisation des pertes...
- Source : Ivan du Roy, Nathalie Pedestarres
00:07 Publié dans Actualité, Affaires européennes, Géopolitique | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : europe, affaires européennes, actualité, politique internationale, géopolitique, traité transtlantique, atlantisme |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Immigration clandestine: l’ONU tance le gouvernement hollandais

Immigration clandestine: l’ONU tance le gouvernement hollandais pour sa fermeté
AMSTERDAM (NOVOpress via Bulletin de réinformation)
Ex: http://fr.novopress.info
Comme tous les pays d’Europe, les Pays‑Bas comptent des dizaines de milliers de clandestins. Environ 8 000 demandeurs d’asile déboutés refusent chaque année de rentrer dans leur pays. Nombre d’entre eux vivent dans la rue, des squats ou des logements mis à disposition par des organismes de charité ou certaines municipalités sans le soutien du gouvernement central. Le gouvernement néerlandais a en effet refusé de débloquer la somme de 15 millions d’euros aux 60 municipalités les plus infestées qui réclamaient une aide financière.
Une situation intolérable pour un comité d’experts de l’ONU !
Un groupe de rapporteurs spéciaux des Nations Unies, spécialistes des droits de l’homme, a sommé mardi les Pays‑Bas de bien vouloir fournir des abris d’urgence cet hiver aux migrants vivant sur le sol hollandais. Le rapporteur spécial de l’ONU Philip Aston a déclaré « En ces sombres jours précédant Noël, il est effrayant de constater que le gouvernement néerlandais ne souhaite pas consacrer moins de 0,01 % de son budget annuel pour aider des gens vivant dans la misère et la pauvreté absolue ». On notera qu’il est autorisé d’utiliser Noël lorsqu’il s’agit de culpabiliser les nations européennes. Leilani Farha, le rapporteur spécial des Nations Unies sur le droit à un logement convenable (sic) a pour sa part rajouté « Les services d’urgence tels que les refuges pour itinérants, et des alternatives de logement adéquat, doivent être mis à la disposition des migrants, indépendamment de leur statut juridique dans le pays ».
Quelle est la position du gouvernement hollandais ?
Le gouvernement néerlandais a rejeté ces vertueux appels. Le secrétaire d’Etat à la Justice Fred Teeven ne souhaite pas mettre ce budget à disposition, craignant de miner le système de demande d’asile en récompensant ceux qui n’acceptent pas l’expulsion. Le rapporteur spécial de l’ONU sur les droits humains des migrants, François Crépeau lui a répondu, estimant que : « Les politiciens des Pays‑Bas essaient de gagner des voix dans le débat national sur l’immigration au détriment des migrants irréguliers sans‑abri », et ajoutant : « Les flux de migration ne changeront pas en laissant des migrants dormir dans la rue ».
On peut lui rétorquer que la très ferme politique anti‑immigrationniste du gouvernement australien a quant à elle porté ses fruits : il n’y a plus aucun immigré clandestin au pays des kangourous…
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Affaires européennes | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : politique internationale, immigration, immigration clandestine, pays-bas, europe, affaires européennes, onu |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
“Eric Zemmour is het slachtoffer van een media-fatwa”

“Eric Zemmour is het slachtoffer van een media-fatwa”
Gesprek met Jean-François Kahn
Door Alexandre Devecchio
Ex: http://www.doorbraak.be
In een onderhoud dat hij toestond aan FigaroVox, neemt Jean-François Kahn de verdediging op van Éric Zemmour, en hekelt hij de onmogelijkheid om in Frankrijk nog sereen debat te voeren.
Jean-François Kahn is een Franse journalist en auteur, historicus van opleiding. In 1984 stichtte hij L'Événement du jeudi, en in 1997 het weekblad Marianne, waarvan hij directeur was tot 2007. Zijn jongste boek, Marine Le Pen vous dit merci! verscheen bij Plon.
Devecchio: Bent u geschokt door het feit dat i-Télé aan Éric Zemmour de bons heeft gegeven naar aanleiding van een polemiek die Jean-Luc Mélenchon op gang had getrokken, en die werd opgepikt door de patron van de PS-afgevaardigden, tevens minister van Binnenlandse Zaken?
Kahn: Ja, ten zeerste geschokt, en wel om drie redenen. Vooreerst kan men door het ongehoorde succes van zijn boek zien dat een belangrijk deel van de bevolking zich kan vinden in wat Éric Zemmour schrijft. Men kan dit betreuren, en soms doe ik dat ook. Maar kan men zich in de ontkenning verschuilen? Kan men in ernst een zo sterke stroming in het land op die manier wegcijferen? In zekere zin sluit de zaak Zemmour aan bij de algemene verkiezingen. Kan men in ernst zich erover verheugen dat een partij die 19% van de stemmen haalt, door amper twee verkozenen vertegenwoordigd wordt in de Assemblée nationale? De zaak Zemmour toont het probleem aan van het gebrek aan pluralisme in onze democratie.
Ten tweede vind ik het schokkend dat i-Télé wijkt voor een perscampagne die grenst aan een mediatieke lynchpartij. Éric Zemmour vertelt niets nieuws. Onderhand twintig jaar onderhoudt hij hetzelfde discours. Bij i-Télé wist men wat men deed toen ze hem aanwierven, overigens misschien precies omdat hij die ideeën verdedigde. Waarom hem dan nu wegsturen? Omwille van een ‘woord’ dat hij niet eens heeft uitgesproken. Verachtelijk vind ik het procedé dat erin bestaat een ‘woord’ of een ‘zinsnede’ te gebruiken, vaak uit hun verband gerukt, om zo iemand uit te schakelen. Ik zeg dit des te liever, omdat ikzelf al het slachtoffer werd van die methode.

En tenslotte wens ik eraan te herinneren dat «Ça se dispute», een debatprogramma was waar Éric Zemmour een tegenstem moest trotseren. Het was niet zo dat hij een vrije tribune ter beschikking kreeg. In een debat is het normaal dat er twee invalshoeken zijn. Het gaat niet op te beslissen dat één ervan ongepast is, en eruit moet. Wat mij bij de televisie vandaag choqueert, zijn niet de debatten waar een echte ideologische confrontatie plaatsheeft, maar die waar iedereen met iedereen akkoord gaat. In de media vandaag zien we de liberaal-modernistische houding overheersen, die Alain Minc omschreef als de “club van de redelijkheid.” Die gedachtegang is niet noodzakelijk verkeerd, maar als ze even hegemoniaal blijft, kan dat afschrikkende gevolgen hebben.
Devecchio: Zou u zeggen dat Marine Le Pen dankjewel mag zeggen aan al diegenen die liever verbieden dan weerwerk te bieden?
Kahn: Door Zemmour aan de deur te zetten doet men niets anders dan voedsel geven aan de wrok bij een deel van de bevolking, dat terecht zich niet meer vertegenwoordigd voelt. Dat is inderdaad een geweldig cadeau voor Marine Le Pen. Vanzelfsprekend geeft dit legitimiteit aan haar discours tegen het systeem. Mag ik eraan toevoegen dat ook voor Éric Zemmour dit een formidabel cadeau is, want nu heeft hij makkelijk spel als hij zich voor martelaar van de politieke correctheid wil uitgeven. Wees maar zeker dat hij nu nog 40 000 boeken meer zal verkopen, en dat het hem in zijn statuut van rebel tegen het establishment zal sterken, en daar is hij dol op.
Devecchio: Hebt u er begrip voor als organisaties vragen dat een journalist geen tribune meer krijgt?
Kahn: Daar alweer verwijderen we ons verder en verder van de grondbeginselen van de democratie. Wie benoemt en verkiest die organisaties? Hun politiek gewicht lijkt me niet in verhouding te staan tot hun representativiteit. Volstaat het om twaalf man bijeen te brengen en communiqués te schrijven, om voor legitiem door te gaan? Die organisaties, dat zijn onbenoemde imams, overigens niet altijd onbenoemd, die dan fatwa’s lanceren.
Devecchio: Zijn er niet toch grenzen aan de vrijheid van meningsuiting? Heeft Éric Zemmour die overschreden?
Kahn: Er bestaan wetten, met name wat betreft racisme en het vergoelijken van oorlogsmisdaden. Maar zodra iemand, zonder de wet te schenden een sterke stroming vertegenwoordigt, moet hij mogelijkheid krijgen om zich uit te drukken. Vandaag is dat niet het geval, zeker wat economische en sociale thema’s betreft, als iemand zich voorneemt om af te wijken van de liberaal-modernistische consensus. Zo bijvoorbeeld is de vraag rond de exit uit de Euro taboe. Men zal zich ook herinneren dat 90% van de media zich in 2005 uitspraken voor een ‘Ja’ bij het referendum over het grondwettelijk verdrag, waarbij ze in het voorbijgaan ook elke vorm van tegenstand diaboliseerden. Nochtans heeft het ‘nee’-kamp het gehaald, al was het slecht vertegenwoordigd.

Devecchio: Is debatteren vandaag nog mogelijk?
Kahn: Om te beginnen wil ik opmerken dat het boek van Zemmour nogal moeilijk leest. Voor wie nog andere bezigheden heeft, neemt het een week in beslag. Maar de dag dat het verscheen waren er in de linkse pers al lange bladzijden te lezen over Le Suicide français. Duidelijk was dat de meeste journalisten maar een paar uittreksels gelezen hadden. Wat we dus bijwoonden, was een aanzwellende polemiek, uitgaande van een boek dat niemand gelezen had. Men raakte gepolariseerd rond een oninteressant hoofdstuk gewijd aan Vichy, terwijl heel wat passages veel interessanter waren. Ik denk dan speciaal aan het hoofdstuk over de Crif, dat de communautaristische wending van veel Franse joden op de korrel neemt. Over die kwestie ging evenwel niet één artikel.
Als reactie op de ontketende linkse pers, heeft de rechtse pers eerder de lof gezongen van het boek. Nochtans is het zonneklaar dat zij het evenmin gelezen hadden. Want inderdaad, laat Le Suicide français het meest reactionaire boek zijn sinds lang, het is tegelijk ook een antiliberaal pamflet. Op sociaaleconomisch gebied is het een waar neomarxistisch manifest, waarin Zemmour tekeergaat tegen het financieel kapitalisme, dat volgens hem verantwoordelijk is voor alles wat misgaat. Wat men moet lezen zijn de tien pagina’s gewijd aan een lofzang op Georges Marchais, of het dithyrambische hoofdstuk waarin hij zijn steun betuigt aan de sociale beweging tegen de wetten Juppé van 1996. Dit alles zegt veel over het ideologische debat vandaag: lezen doet men niet meer, men redeneert afgaand op etiketten, en banvloeken lanceert men al na een paar slagzinnetjes.
Vertaling: Marc Vanfraechem
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Affaires européennes, Entretiens | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : éric zemmour, actualité, france, europe, affaires européennes, immigration, médias, presse, censure, liberté d'expression, politique internationale, jean-françois kahn |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Pourquoi la Russie a-t-elle décidé de mettre un terme au projet South Stream?

Pourquoi la Russie a-t-elle décidé de mettre un terme au projet South Stream?
« Le projet South Stream était voué à l’échec dès le départ »
Propos recueillis par Thomas Gras
Ex: http://www.lecourrierderussie.com
Entretien avec Said Gafourov, économiste spécialiste de l’Orient et conseiller auprès du gouvernement russe.
Le 1er décembre, le président russe Vladimir Poutine a déclaré, lors d’une visite d’État en Turquie, que Moscou stoppait la réalisation du projet de gazoduc South Stream. La raison invoquée est la « position non constructive » de l’Union européenne. Vladimir Poutine a également annoncé que, pour répondre aux besoins de l’économie turque, la Russie était prête à construire un nouveau pipeline vers la Turquie et à le prolonger, si nécessaire, jusqu’en Grèce. Qu’est-ce qui se cache derrière la fermeture de South Stream ? Le Courrier de Russie a posé la question à Said Gafourov, économiste spécialiste de l’Orient et conseiller auprès du gouvernement russe.
Le Courrier de Russie : Comment avez-vous réagi à l’annonce de l’abandon de la construction du gazoduc South Stream ?
Said Gafourov : J’ai été surpris par cette décision, même s’il fallait s’y attendre. Le projet South Stream, selon moi, était voué à l’échec dès le départ, car beaucoup trop cher [le coût du projet était estimé à quelque 25 milliards d’euros, ndlr]. La construction d’un gazoduc sous l’eau est une entreprise très onéreuse, et dangereuse. С’est une opération requérant d’importantes garanties sur le long terme et un partage des risques entre les parties. L’acheteur endosse la responsabilité de la demande, au cas où elle diminuerait, alors que le vendeur, ici Gazprom, est responsable du maintien des prix, s’ils venaient à monter.
LCDR : L’Europe est-elle d’accord pour partager ces risques ?
S.G. : En Europe, si les acheteurs sont des compagnies privées, les conditions sont fixées par Bruxelles. Et elles sont loin d’être équitables pour les fournisseurs, qu’il s’agisse de la Russie ou d’un autre pays. La position de l’UE consiste à dire : Vous amenez le gaz chez nous à vos frais, et nous le prenons au prix que nous voulons et sans garantie sur le long terme. Bien évidemment, cette situation ne peut pas satisfaire la Russie qui, dans le projet South Stream, se heurte en outre à un autre obstacle majeur : le troisième paquet énergie européen, interdisant aux producteurs de gaz de posséder des pipelines en Union européenne. Ce paquet contraint Gazprom à permettre à n’importe quel autre fournisseur d’utiliser son gazoduc pour livrer du gaz en Europe. Résultat, même si aucun autre acteur du marché ne se manifeste, la compagnie russe ne pourra pas utiliser le South Stream à pleine capacité, elle devra laisser une partie des pipelines en réserve, ce qui affecte grandement la rentabilité du projet et le rend économiquement peu fiable pour la partie russe. Le paquet énergie a été utilisé par l’UE comme une arme, et la Russie en a eu assez.
LCDR : Le Premier ministre hongrois Viktor Orban a d’ailleurs ouvertement accusé l’Union européenne, le 5 décembre, d’avoir fait échouer le projet de gazoduc.
S.G. : L’Union européenne n’est pas « unique » : elle est constituée de points de vue politiques multiples et très différents. On y trouve notamment un groupe de bureaucrates qui se sont opposés à la réalisation du South Stream au nom de leurs intérêts personnels. Leur but n’était pas tant de faire du mal à Gazprom que de contrôler les flux monétaires liés au gaz afin de pouvoir s’en servir comme moyen de pression sur les compagnies et hommes politiques. Ces individus ne voulaient pas en arriver à la fermeture du projet, mais nous y sommes. Ce ne sont ni plus ni moins que des manœuvres et négociations secrètes de type mafieux.
LCDR : Doit-on définitivement faire une croix sur South Stream ?
S.G. : Non. Il y a des chances que le projet ne disparaisse pas complètement, bien que Gazprom affirme le contraire. La question centrale est de savoir quels changements auront lieu à Bruxelles dans les mois à venir. Les individus dont je parlais doivent être remplacés. Il faut briser cette bureaucratie mafieuse à Bruxelles. Les personnes chargées de la sécurité et de la livraison de gaz en Europe n’ont pas à commettre de tels actes irresponsables. Ensuite, la réouverture du projet dépendra beaucoup de l’évolution d’un certain nombre de facteurs, tels que la variation du coût du matériel de construction sous-marine, de l’obtention de garanties sur la demande et de la levée des sanctions contre Gazprom. D’ailleurs, les compagnies européennes impliquées [l’italien Eni, le français EDF et l’allemand Wintershall, ndlr] n’ont pas entériné la fin du South Stream et feront tout pour qu’il aboutisse.
LCDR : Le nouveau projet de Gazprom envisage de traverser la Turquie par un nouveau gazoduc afin d’aller jusqu’à la Grèce, où serait construit un hub à la frontière. Pourquoi cette route rencontrerait-elle plus de succès que le tracé par la Bulgarie ?
S.G. : Premièrement, le projet est moins cher, puisqu’il est principalement terrien, et deuxièmement, la Turquie ne suit pas le régime des sanctions. N’oublions pas que Gazprom est touché par les sanctions occidentales et ne peut obtenir de crédits à long terme auprès des banques européennes. Ensuite, la Grèce dispose de plus de pouvoir au sein de l’UE que la Bulgarie. D’autant que la prochaine élection présidentielle grecque [avancée au 17 décembre, ndlr] devrait être remportée par un représentant du parti de gauche, Syriza [très opposé à la politique de Bruxelles, ndlr].
LCDR : Quel rôle joue la Turquie dans cette affaire ?
S.G. : La Turquie compte devenir le principal centre de transit du gaz en direction de l’Europe du Sud, à la place de l’Ukraine. Gazprom a présenté un contrat intéressant à Ankara, lui accordant une ristourne sur le gaz. Bien que le prix de vente soit tenu secret, je pense que les Turcs pourraient payer moins de 300 dollars les 1 000 m3, alors que la moyenne européenne oscille entre 300 et 500 dollars. Le projet proposé par Gazprom n’est néanmoins pas une réalité, mais une possibilité. L’Union européenne doit maintenant prendre une décision quant à sa réalisation. Si Bruxelles est honnête d’un point de vue concurrentiel, elle acceptera le projet russo-turc, car elle doit être heureuse qu’il existe, outre l’Ukraine, une nouvelle route gazière au Sud.

00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Affaires européennes, Entretiens, Géopolitique | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : actualité, europe, russie, poutine, affaires européennes, politique internationale, géopolitique, entretien, hydrocarbures, gazoducs, south stream, mer noire, espace pontique, union européenne |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Gladio B and the Battle for Eurasia
Gladio B and the Battle for Eurasia
TRANSCRIPT AND SOURCES: http://www.corbettreport.com/?p=12947
‘Operation Gladio B’--the continuation of the old NATO Gladio program--covers a tangled web of covert operatives, billionaire Imams, drug running, prison breaks and terror strikes. Its goal: the destabilization of Central Asia and the Caucasus. In this presentation to Studium Generale in Groningen on November 19, 2014, James Corbett lifts the lid on this operation, its covert operatives, and the secret battle for the Eurasian heartland.
00:05 Publié dans Actualité | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : actualité, politique internationale, eurasie, caucase, james corbett, géopolitique, special ops, gladio, asie centrale, asie, affaires asiatiques |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Así se combatía la corrupción pública en la antigua Roma
Gürtel, Operación Púnica, los ERE de Andalucía, la familia Pujol, Bárcenas o el caso Noos son el pan nuestro de cada día. Desayunamos, comemos y cenamos con ellos en las noticias. Como explica el escritor y ensayista italiano Carlo Alberto Brioschi, en el siglo XXI, la corrupción se ha convertido en una especie de bacilo de la peste que, sin embargo, padecemos desde hace siglos. Y así es, porque delitos tan actuales como el cohecho, el tráfico de influencias, el robo de las arcas del Estado, la extorsión, la adjudicación de obras públicas a amigos poderosos o la compra de votos colapsaron a muchos gobiernos de la antigua Roma, que tuvieron que establecer toda una serie de leyes para perseguirla.
Durante algún tiempo, las estructuras del Estado romano se resistieron a esta corrupción sin sufrir grandes contratiempos. Era parte de un sistema social y político basado en el clientelismo, el abuso de poder, las mordidas y el enriquecimiento personal. La codicia de los funcionarios públicos no tenía límite y estos delitos fueron creciendo a ritmo de las conquistas. Pero llegó un momento en que el gobierno se hizo impracticable y el derecho romano tuvo que introducir cambios.
 Sin embargo, la convivencia entre buenos propósitos y acciones deshonestas por parte de los gobernantes fue siempre una de las características de Roma. Un ejemplo de esto fue Licinio Calvo Estolón, tribuno de la plebe en el 377 a.C., que introdujo una fuerte limitación a la acumulación de tierras por parte de un único propietario, además de una severa reglamentación para los deudores, pero luego fue acusado de haber violado sus propias leyes.
Sin embargo, la convivencia entre buenos propósitos y acciones deshonestas por parte de los gobernantes fue siempre una de las características de Roma. Un ejemplo de esto fue Licinio Calvo Estolón, tribuno de la plebe en el 377 a.C., que introdujo una fuerte limitación a la acumulación de tierras por parte de un único propietario, además de una severa reglamentación para los deudores, pero luego fue acusado de haber violado sus propias leyes.
Las «quaestiones perpetuae»
Durante el periodo republicano (509 a.C. - 27 a.C.), el propio sistema electoral facilitaba, de hecho, la corrupción, que se agravó a partir de la expansión territorial y marítima producida después de la Segunda Guerra Púnica. Los gobernadores comenzaron a enriquecerse sin escrúpulos a través del cobro de impuestos excesivos y la apropiación de dinero de la administración pública. Como denunció en aquella época el historiador romano Salustio, «los poderosos comenzaron a transformar la libertad en licencia. Cada cual cogía lo que podía, saqueaba, robaba. El Estado era gobernado por el arbitrio de unos pocos».
La primera ley que se estableció fue la «Lex Calpurnia» (149 a.C.), como consecuencia del abuso del gobernador de la provincia de Lusitania, Servio Sulpicio Galba, al que se acusó de malversación de fondos y fue juzgado por un jurado procedente de la orden senatorial, algo que era toda una novedad. Sin embargo, esta primera ley no imponía ninguna pena pública, sino la devolución del dinero que había sustraído.
En el 123 a.C., se establecieron una serie de tribunales permanentes, llamados «quaestiones perpetuaes», cuyo cometido fue el de investigar todas estas malas prácticas y extorsiones de los gobernadores provinciales que habían sido denunciadas por los ciudadanos. Al principio no tuvieron el éxito deseado, pero fueron importantes porque con ellos se definió legalmente el «crimen repetundarum», que hizo alusión a los delitos de corrupción, cohecho o tráfico de influencias.
Este sistema se fue perfeccionando con la definición de nuevos delitos. El «crimen maiestatis», por ejemplo, definía los abusos de poder por parte de los senadores y magistrados. Era considerado el acto más grave contra la República y fue castigado, incluso, con la pena de muerte o el exilio voluntario. El «crimen peculatus» hacía referencia a la malversación y apropiación indebida de fondos públicos por parte de un funcionario, así como la alteración de moneda o documentos oficiales. O el «crimen ambitus», que describía la corrupción electoral, especialmente la compra de votos.
Leyes anti-corrupción
Todos estos y otros delitos trajeron consigo nuevas leyes, que querían dar respuesta a los diferentes cambios políticos, económicos y morales que se iban produciendo. La «Lex Acilia» –que apareció al mismo tiempo que los «quaestiones perpetuaes»–, subió la pena para los delitos de malversación de fondos y cohecho de la «Lex Calpurnia», estableciendo una multa del doble del valor del daño causado por el funcionario. Es una de las más conocidas, porque se ha conservado gran parte de su texto original.
 Otras leyes importantes fuero la «Lex Sempronia» (122 a.C.) o la «Lex Servilia de Repetundis» (111 a.C.), que establecieron penas más severas para los delitos de cohecho. La segunda, en concreto, fue la primera ley que introdujo la pérdida de los derechos políticos. Ambas fueron completadas con otras como la «Lex Livia Iudiciaria» (91 a.C.), que impuso una corte especial para los juicios contra los jueces corruptos que hubieran cometido extorsión, o la «Lex Cornelia», que aumentaba las condenas para los magistrados que aceptaran dinero en un juicio por cohecho. Esta última debe su nombre al dictador Lucio Cornelio Sila, que la estableció tres años antes de morir.
Otras leyes importantes fuero la «Lex Sempronia» (122 a.C.) o la «Lex Servilia de Repetundis» (111 a.C.), que establecieron penas más severas para los delitos de cohecho. La segunda, en concreto, fue la primera ley que introdujo la pérdida de los derechos políticos. Ambas fueron completadas con otras como la «Lex Livia Iudiciaria» (91 a.C.), que impuso una corte especial para los juicios contra los jueces corruptos que hubieran cometido extorsión, o la «Lex Cornelia», que aumentaba las condenas para los magistrados que aceptaran dinero en un juicio por cohecho. Esta última debe su nombre al dictador Lucio Cornelio Sila, que la estableció tres años antes de morir.
La corrupción, sin embargo, seguía imparable. En esta época, el gobernador de Sicilia, Verres, se convirtió de alguna manera en el arquetipo originario del «corruptócrata» incorregible. Se calcula que robó al erario público más de cuarenta millones de sestercios y depredó literalmente su provincia. Y no fue una excepción. El mismo Cicerón, que no le tenía especial simpatía y se esforzaba en presentarlo como un caso claro de avidez de poder, afirmó, por el contrario, que su conducta representaba la norma en buena parte del imperio romano.
Julio César, en las puertas del Tesoro
Cuando aún era cónsul, Julio César fue el que propuso la última y más severa ley republicana contra los delitos de corrupción, la «Lex Iulia», que incluía penas de multas desorbitadas y el destierro. Es curioso que fuera él, pues poco antes no había dudado en recurrir a cualquier medio para acceder al consulado. «Cuando el tribuno Metello trató de impedirle que tomase dinero de las reservas del Estado, citando algunas leyes que vetaban tocarlo, él respondió que el tiempo de las armas es distinto al de las leyes… y se encaminó hacia las puertas del Tesoro», contó de él el historiador Plutarco. Eso no le impidió establecer más de cien capítulos en su ley, la mayoría de ellos destinados a los magistrados e, incluso, jueces que se hubieran dejado sobornar para favorecer a un acusado en un delito de corrupción.
El contenido de todas estas leyes demuestra el grado de corrupción que se vivía en Roma. Con la llegada del Imperio en el 27 a.C., éste no solo no se redujo, sino que se incrementó. Los políticos siguieron sobornando a los funcionarios para conseguir puestos en la administración, mientras que a los ciudadanos se les asfixiaba cada vez con más impuestos y se veían obligados a pagar propinas a cambio de que se les agilizara algún trámite solicitado.
A partir de Augusto, el erario público fue perdiendo importancia e independencia, al ser sustituido por la caja privada del emperador. Esto facilitó, sin duda, la corrupción, a la que se intentó poner remedio. Durante la época del emperador Adriano (24-76 d.C.), por ejemplo, se amplió «crimen repetundarum» a todos los actos de malversación realizados por los funcionarios públicos y los sancionó incluso con penas de muerte. Y junto a este crimen, aparecieron otros como la «concussio» (concusión), una de las prácticas favoritas de los gobernadores provinciales, consistente en exigir a los ciudadanos una contribución no establecida por la ley o aumentar otra sí existente de manera desorbitada.
Pero la historia de Roma parece que ya había sido escrita por el escritor y político romano Petronio, cuando se preguntó, impotente, en el siglo I: «¿Qué pueden hacer las leyes, donde sólo el dinero reina?».
Fuente: ABC
00:05 Publié dans Histoire, Théorie politique | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : corruption, corruption politique, rome, rome antique, antiquité romaine, théorie politique, politologie, sciences politiques, histoire |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Raspail, Zemmour, Houellebecq ou le « Grand Remplacement » en littérature

Houellebecq, prix Goncourt 2010 (pour La Carte et le Territoire), se prenant pour Destouches – jusqu’à cultiver la ressemblance physique avec le père de Bardamu – mais sans jamais parvenir à être génialement Céline, aime l’odeur de la poudre. Grâce à un plan « communication » subtilement étudié, l’auteur de L’Extension du domaine de la lutte annonce à ses lecteurs la parution, à l’orée 2015, d’un roman mêlant anticipation et politique-fiction. Intitulé d’un claquant Soumission, le livre promet de faire couler beaucoup d’encre.
Celui qui, peu après le 11 septembre, déclara que « la religion la plus con, c’est quand même l’islam» a imaginé un scénario dont on ne sait s’il doit faire sourire ou pleurer. D’après les premiers bruissements médiatiques, le livre raconte comment, en 2022, le mahométan Mohammed Ben Abbes est élu à l’Élysée avec le concours de son parti, Fraternité musulmane, associé à un front « républicain » UMP-UDI-PS opportunément constitué pour faire barrage à Marine Le Pen. Le nouveau président nommera même François Bayrou comme Premier ministre. Parallèlement, on suivra la conversion progressive d’un prof bobo obsédé sexuel qui finira par épouser la religion de son souverain.
Coïncidence ou conséquence d’une lecture déjà métabolisée, Bruno Roger-Petit, de L’Obs, augurait récemment l’extinction « démographique » des « adeptes du zemmourisme politiquement remplacés par des citoyens français plus ouverts, en prise avec la mondialisation et les formidables opportunités qu’elle offre, et qui n’auront pas peur […] avant la fin de ce siècle, [d’élire] un président de la République française dont le prénom sera Mohammed, ou Ahmed, ou Norredine. »

Aux côtés des nombreux essayistes (Tribalat, Caldwell, Sarrazin, Marchand, Bat Ye’or, etc.), on ne compte plus, depuis quelques années, les écrivains talentueux qui se sont essayés au genre littéraire du futurisme politique et civilisationnel dans ses extrapolations les plus sombres. Avec Poitiers demain, Philippe Randa modernisait la version ibérique de la Reconquista quand son épique Apocalypse yankee décrivait la résistance d’une Europe vaincue par les États-Unis. Dans un genre plus discret mais tout aussi corrosif, le Petit Frère d’Éric Zemmour entreprenait la satire politique et sociale d’une époque dont les prodromes immigrationnistes et antiracistes des années 1980 annonceront les douloureuses déconvenues multiculturalistes du XXIe siècle. On pourrait également citer le gauchisant – tendance Michéa – Jérôme Leroy, auteur d’un Bloc particulièrement réaliste ou encore l’eschatologique Mosquée Notre-Dame de Paris, année 2048 de la sulfureuse Elena Tchoudinova.
Témoins implacables de leur temps, ces contempteurs du réensauvagement – « cette situation d’un peuple dans le peuple, des musulmans au milieu des Français [qui] amènera le chaos et la guerre civile » qu’Éric Zemmour, horresco referens, osa dénoncer, il y a peu, dans un journal transalpin – s’élèvent par la plume contre le dogme totalitaire des lendemains métissés. En cela, ils sont les dignes épigones d’Orwell, Huxley et Bradbury.
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Affaires européennes, Littérature | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : actualité, france, grand remplacement, littérature, lettres, lettres françaises, littérature française, eric zemmour, michel houellebecq, renaud camus, europe, affaires européennes, immigration |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
lundi, 22 décembre 2014
La France est allée trop loin dans la désindustrialisation

Jean-Luc Ginder: «La France est allée trop loin dans la désindustrialisation»
Ex: http://fortune.fdesouche.com
Le déclin relatif de l’industrie est une tendance naturelle, de la même manière qu’il y a eu un déclin de l’activité agricole remplacée par l’industrie. Ainsi l’activité industrielle tend à être remplacée par le secteur des services.
Une société qui se développe et se sophistique consomme davantage de services et moins de produits industriels. Mais comme ce sont les produits industriels qui portent les gains de productivité remarquables, les prix de production et de vente sont à la baisse. Des exemples dans notre quotidien : téléviseurs, téléphones..
Le problème ne vient pas de cette évolution générale mais vient du rétropédalage industriel de la France depuis les 15 dernières années. Il faut en finir avec l’accumulation des politiques contradictoires.
Les résultats français sont inférieurs à ceux des pays qui ont une fiscalité moindre et à ceux qui ont une fiscalité plus lourde, inférieurs à ceux qui ont des lois sociales plus généreuses ou mois généreuses, et inférieurs à ceux qui ont un État fort ou un État faible. Mauvaise élève face à tous ses voisins depuis 15 ans et même au-delà : le choc de la désindustrialisation a été plus violent en France qu’ailleurs et cela a commencé vers les années 80.
Entre 1979 et 1984, on remarque une première vague de désindustrialisation. D’une violence extrême, elle fait perdre à la France 1/3 de son potentiel industriel. Pour comprendre ce qui s’est passé il faut prendre en compte le dualisme de l’économie française.
A côté des très grandes entreprises qui s’étaient formidablement développées, certaines dans le giron de l’État, existaient un tissu fort de PME sous capitalisées, sous investies. Ces dernières ont subi de plein fouet le choc des crises des années 70.
On a alors assisté à une forte mortalité des entreprises dans les secteurs des biens d’équipement, celui de la machine outil, celui des chantiers naval, et il y e a d’autres. on a assisté à une véritable hécatombe industrielle.
Les plans de sauvetage mis en place face à l’hécatombe industrielle n’ont eu pour effet que d ‘accompagner le déclin des secteurs en difficulté sans jamais permettre le rebond industriel.
Et au milieu des années 80, la France a fait le choix européen, du marché unique et de l’euro sans prendre en compte les conséquences de ces choix. Dans un premier temps cela a été un formidable marché, l’euro a même permis d’évacuer les risques de change.
Sauf que. Il n’a pas été pris en compte que le modèle inflationniste de la France, financé par l’État et régulé par les dévaluations périodiques ne pouvaient plus dès lors fonctionner à partir du moment où la monnaie était monnaie unique dans un marché devenu unique. La France se devait d’appréhender les nouvelles dynamiques de compétitivité, de maîtrise interne, de concurrence fiscale.
Et que. Ces nouveaux paramètres n’ont pas été pris en compte. Il était capital de maîtriser les dépenses publiques dans un temps où l’on faisait le choix stratégique majeur de la mondialisation, de l’intégration européenne et de l’euro. Il était capital de se demander dans le même temps si on pouvait continuer à gérer comme avant.
On peut estimer cette situation à l’application d’une politique keynésolibérale. Keynésienne d’un côté car chaque fois qu’il y a une crise conjoncturelle, on dit que c’est une insuffisance de la demande et qu’il faut donc relancer cette dernière, avec bien entendu de la dette publique, de la dépense publique et quand cela devient insupportable on monte les impôts, qui eux pèsent sur les entreprises tout en dégradant la compétitivité
On assiste bien à l’application d’une solution keynésienne à toutes les crises conjoncturelles et dans le même temps d’une solution de type libéral qui considère que les problèmes industriels et productifs doivent être réglés par le biais du marché et de la concurrence.
Ce raisonnement et le temps ont eu pour effet d’accumuler un formidable écart au niveau des taux de marge des entreprises. Aujourd’hui, 10 points d’écart séparent les entreprises allemandes et les entreprises françaises. Pour corriger cette situation, il faudrait faire un transfert de 100 milliards de l’État vers le secteur privé sous forme d’aides et d’allègements. Aujourd’hui l’État en promet 40, et en apporte concrètement 5.
Et jour après jour, secteur après secteur, la rentabilité industrielle s’effondre.
La solution de la désindustrialisation passe avant tout par de la cohérence ! ….plutôt que de chercher à protéger le caractère national du contrôle du capital des entreprises françaises par des capitaux français. La nationalité du capital prévaut-elle sur le développement des compétences françaises, sur le développement de l’activité sur le sol français ? l’important est de préserver le développement de la recherche française, et des marques françaises.
Il est donc nécessaire et vital pour l’économie française d’avoir enfin une cohérence et un alignement des politiques.
Il faut en finir avec l’accumulation des politiques contradictoires (politique fiscale qui dissuade l’investissement dans le même temps que les 34 plans sectoriels…). Il faut en finir avec la politique placebo qui a pour effet d’affaiblir davantage les entreprises par le poids des charges sociales, réglementaires, fiscales pour qui on invente le crédit d’impôt lorsqu’on constate qu ‘elles ne peuvent plus respirer, ou encore la CICE pour colmater les brèches.
Il faut d’urgence et impérativement à la France un objectif productif qui considère toutes les politiques et qui fixe les priorités.
Le souhait formulé du pays est d’engager les moyens dans la troisième révolution industrielle, celle du numérique, du digital. Et le pays constate que sa base industrielle a perdu sa compétence manufacturière et n’a plus la capacité de transformer ses innovations en produits, qui seraient aussi les produits industriels de demain.
Le constat est alarmant, simple : la France est allée trop loin dans la désindustrialisation pourtant avec la science de nouvelles révolutions arrivent. De fait nos enfant ne vivrons pas comme nous. Nous sommes à un moment de notre histoire économique ou les repères vont changer….de révolution technologique en révolution économique avec l’aide de la science (révolution agricole, révolution biotechnologique, révolution énergétique, et révolution numérique).
(Merci à Percy)
00:09 Publié dans Actualité, Affaires européennes | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : france, politique internationale, désindustrialisation, délocalisation, libéralisme, crise européenne, europe, affaires européennes |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Renseignement: nos principaux partenaires sont nos principaux prédateurs

Renseignement: nos principaux partenaires sont nos principaux prédateurs, États-Unis en tête
La délégation parlementaire au renseignement a rendu un rapport de 180 pages présenté par les députés Urvoas, PS, et Miard, UMP. L'espionnage industriel et financier pille la France. La responsabilité en incombe à l'insouciance française et aux prédateurs internationaux que sont nos principaux partenaires économiques, États-Unis en tête.
Jean Jacques Urvoas et Lucien Miard, en présentant leur rapport de la délégation parlementaire au renseignement, composée de parlementaires tous habilités au «secret-défense», ont choisi de mettre particulièrement en lumière l’espionnage économique. Et tout au long des cent quatre-vingt pages l’évidence s’impose, « nos principaux partenaires sont nos principaux prédateurs », comme le souligne Urvoas. L’accusation n’excepte personne, ni Russes, ni Chinois. On vient ainsi de découvrir un centre d’écoute chinois dans le Val de Marne. Emporiums, litchis frais et pousses de soja sont des couvertures toujours efficaces (Le phénomène n’est pas neuf. Déjà en 2012, le rapport Bockel recommandait d’éviter tout matériel d’origine chinoise dans les infrastructures stratégiques publiques et privées). Mais les USA arrivent sans conteste en tête des prédateurs qui pillent l’économie française. Selon Urvoas, « les Américains ou les Israéliens sont très souvent les plus agressifs, pas seulement sur un plan commercial ».
Prédateurs tous azimuts, un pillage général
Le nombre des affaires découvertes surprend. En septembre 2011, les policiers spécialisés de la sous-direction de la protection du patrimoine économique, basée à Levallois-Perret, ont révélé près de 5.000 « cas » en quatre ans. Durant cette période, 3.189 entreprises ont été visées. L’Île-de-France, où 144 cas d’ingérence ont été mis au jour en 2013, concentre près de 20 % des attaques. L’objet du pillage est très divers. Il y a d’abord les secteurs sensibles : l’énergie, l’aérospatiale, les télécommunications, la robotique, la santé ou la recherche fondamentale. Mais la curiosité des agents de renseignement économique s’étend bien au-delà et ne dépend pas de la taille des entreprises : les pme innovantes sont particulièrement surveillées. Et l’administration n’est pas en reste, à commencer par celle des finances. Or celle-ci, particulièrement visée, est aussi particulièrement fragile. « Nous sommes effarés par l’absence de culture de sécurité dans les ministères des Finances et de l’Economie », déplorent en chœur les deux présentateurs du rapport parlementaire. Malgré la « progression inquiétante » de l’espionnage économique, à Bercy, les fonctionnaires « ne tiennent pas compte des informations stratégiques qui circulent dans les ministères », bref, la « protection » est insuffisante.
Les moyens déployés par les services étrangers pour espionner l’économie française sont variés… Piratages de données, infiltration, déstabilisation, vol d’ordinateur dans des chambres d’hôtel, disparition de brevets dans le Thalys entre Paris et Bruxelles, pénétration d’agents à l’occasion d’une visite, piratage de technologies, utilisation offensive du droit, etc… Les bonnes vieilles méthodes barbousardes mises en honneur par le roman policier servent toujours. Un cadre supérieur d’une entreprise de Défense raconte ainsi : « Quand on part négocier un dossier sensible dans certains pays étrangers, on sait que nos chambres d’hôtel sont sonorisées, peu importe l’enseigne. Quand on parle, c’est pour les micros et les seuls documents qui traînent sont ceux dont on voudrait qu’ils soient lus. » Selon lui, telle est la vie quotidienne des délégations françaises en matière de contrats d’armement.

Internet et l’informatique principales sources de renseignement
Mais l’utilisation de l’informatique est devenue plus payante et beaucoup plus répandue. Elle est particulièrement efficace en France en raison d’abord de l’insouciance des Français, dont le ministère des finances offre un exemple flagrant, et ensuite du manque de moyens en matière de cyberdéfense. Alors que seize agences américaines consacrent dix milliards de dollars (au moins : c’est la part budgétée) par an à la chose, l’ANSSI, l’Agence nationale de la sécurité des systèmes informatiques n’a que 750 millions d’euros à consacrer à ses 500 agents. Elle consacre ses moyens à des cibles particulièrement importantes, par exemple l’Elysée, récemment visé par une cyber-attaque américaine. Or la fréquence des incursions ennemies s’accroît. Déjà en 2011, la sous-direction de la protection du patrimoine économique qui dépend de la DCRI déplorait en moyenne « une attaque toutes les sept heures » Et ça ne ralentit pas. Dans son chapitre intitulé Le monde après les révélations d’Edward Snowden, le rapport de la DPR insiste sur « l’incroyable investissement des États-Unis dans les moyens dédiés au renseignement technique » et sur son « intensité agressive à l’égard de notre pays ». Le rapport, d’une manière générale, souligne « l’utilisation croissante du vecteur internet ». Par qui a été inventé internet ? Par l’armée américaine. A qui sert d’abord internet? Au renseignement américain.
Les USA utilisent leurs lois pour piller la France
Mais une autre spécialité américaine, non moins payante, est l’utilisation du « droit comme puissant instrument de prédation ». Selon Jean-Jacques Urvoas, « la première arme de pillage c’est la loi, le droit américain par exemple ». Le juge Charles Prats, qui a enseigné l’usage offensif du droit à l’Ecole de guerre économique (EGE) dès l’an 2000 explique : « A partir des années 60, les Etats-Unis ont entrepris d’extra-territorialiser leur droit de la concurrence ». Puis en 1977, le Foreign Corrupt Practices Act a été promulgué. Ces lois permettent à un plaignant américain « d’adresser des demandes de pièces au défendeur afin de cibler son action en justice », C‘est une façon de contraindre des entreprises étrangères à livrer des informations sensibles dans un pays où le Département de la Justice semble souvent « au service des intérêts économiques ». Sans doute le procédé a-t-il été utilisé quand Alstom négociait avec Général Electric la vente de sa branche énergie, alors que le groupe français faisait l’objet de poursuites dans une affaire de corruption aux Etats-Unis.
Le rapport détaille ces procédures. D’abord la procedure Discovery fondée sur la common law américaine. Les demandes de pièces sont souvent si vastes qu’elles prennent le surnom de fishing expeditions (parties de pêche) et ouvrent la porte à l’espionnage économique. Même chose pour le « deal of justice », qui permet au Department of Justice (DOJ) d’éperonner de grandes entreprises pour infraction aux lois américaines en matière de corruption qui «s’appuie principalement sur le Foreign Corrupt Practices Act de 1977 et sur les lois de sanctions économiques contre des pays (Cuba, Iran, Libye, Soudan, Syrie…) » Cette procédure frappe « dans 90 % des cas (des) entreprises étrangères, dont certains grands groupes français, à l’image de la récente affaire impliquant BNP Paribas ».
Le rapport parlementaire descend très loin dans l’analyse
Cette dernière affaire vaut un développement particulier, car le rapport parlementaire sur le renseignement en livre l’explication. Le groupe français, accusé de transactions avec des pays sous embargo économique américain, a reconnu le 30 juin, devant un tribunal de New York, deux chefs d’accusation : « falsification de documents commerciaux » et « collusion ». Verdit : 6,5 milliards d’euros d’amende alors qu’on avait parlé de onze. Mais la réduction de l’amende initiale comprend une contrepartie très forte : « L’entreprise doit reconnaître sa culpabilité et négocier le montant de l’amende infligée. En contrepartie, le DOJ renonce aux poursuites pour une période de trois ans, période pendant laquelle l’entreprise doit faire preuve d’un comportement exemplaire. Pour prouver sa bonne foi, et là réside le principal problème, elle doit accepter la mise en place d’un moniteur en son sein, moniteur qu’elle choisit mais dont la désignation définitive est soumise à l’approbation des États-Unis. Le moniteur aura accès à l’intégralité des informations de l’entreprise afin de rédiger un rapport annuel extrêmement détaillé. » Il aura donc la possibilité de recopier la comptabilité, lire les échanges de courriels, la documentation stratégique, exiger le détail des notes de frais. Ou dévoiler les démarches commerciales à l’étranger. Or la délégation parlementaire relève que les services secrets américains peuvent « solliciter toute information nécessaire, y compris les rapports de monitorat » en invoquant le Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act. En somme, le droit ouvre la porte de l’entreprise et les espions ramassent.
Bien entendu, la France n’est pas totalement désarmée face ces pratiques. Une « loi de blocage » a été promulguée en 1968 sous De Gaulle, puis amendée en 1980. Elle prévoit des poursuites pénales contre quiconque communiquerait à une puissance étrangère des données économiques sensibles. Elle est censée permettre à un dirigeant français de se soustraire au droit américain en invoquant le risque pénal encouru en France s’il se soumet aux procédures intrusives. Las, « ce moyen reste mal connu », déplore le juge Charles Prats, et il n’est surtout pas sûr qu’il convainque les juges américains. La justice des USA est au service du business et des grands groupes, ce que n’est pas sa consoeur française. Qui plus est, les services secrets aussi ont partie liée avec le business, au point que la CIA a créé et gère un fonds d’investissements, In-Q-Tel, dont la mission est de capter des informations industrielles. Face à de tels prédateurs, le savoir-faire des entreprises françaises semble bien vulnérable.
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Affaires européennes, Géopolitique | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : services secrets, services secrets américains, nsa, espionnage, europe, affaires européennes, politique internationale, géopolitique, actualité, économie, espionnage économique |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
Robert Stark interviews Paul Gottfried on Dugin & Neoconservatives
Robert Stark interviews Paul Gottfried on Dugin & Neoconservatives
Ex:
http://www.starktruthradio.com
Audio:
http://www.starktruthradio.com/?p=934
 Paul Gottfried recently retired as Professor of Humanities at Elizabethtown College, PA. He is the author of After Liberalism, Multiculturalism and the Politics of Guilt and The Strange Death of Marxism His most recent book is Leo Strauss and the Conservative Movement in America.
Paul Gottfried recently retired as Professor of Humanities at Elizabethtown College, PA. He is the author of After Liberalism, Multiculturalism and the Politics of Guilt and The Strange Death of Marxism His most recent book is Leo Strauss and the Conservative Movement in America.
Topics include:
Alexander Dugin and Martin Heidegger
The definition of Liberalism
The Eurasian school of thought
National Review’s Hit Piece on Dugin
How Neoconservatives attack their enemies such as Dugin as Fascist or Nazis
How Neoconservatives are a faction of the left
The Neoconservative View toward Russia
The Cold War and whether it was a mistake
The conflict with Russia in the Ukraine
Why Paleoconservatives tend to dislike Israel
Paul Gottfried’s upcoming book Fascism: The Career of a Concept
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Entretiens, Eurasisme, Nouvelle Droite, Théorie politique | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : politique internationale, nouvelle droite, nouvelle droite russe, alexandre douguine, paul gottfried, russie, entretien, théorie politique, sciences politiques, politologie, philosophie, philosophie politique, eurasisme |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
L'homme sans liens...
L'homme sans liens...
Ex: http://metapoinfos.hautetfort.com
Nous vous signalons la publication du douzième numéro de la revue Perspectives libres consacré à l'anomie qui frappe nos sociétés. La revue Perspectives libres, dirigée par Pierre-Yves Rougeyron, est publiée sous couvert du Cercle Aristote et est disponible sur le site de la revue .

Présentation du numéro
« L’anomie de nos sociétés est aujourd’hui un fait sinon largement admis du moins globalement constaté avec une sorte de trépignement qui peut inquiéter. Ces germes de pourrissement social attirent à intervalles réguliers tout ce que la France et les sociétés dites avancées possèdent comme faune sociologique, entomologistes sociaux et autres inspecteurs de dépôt de bilan civilisationnel. Il y a quelque chose d’impudique – comme un fantasme de ruine – à contempler la tragédie avec gourmandise en priant de pouvoir abaisser le puce comme dans les arènes romaines devant la grande curée terminale censée emporter notre communion humaine dégradée en vulgaire vivre-ensemble.
C’est de cet homme délié car déraciné et par la même désincarné que nous allons esquisser un portrait ici. Délié face à ses semblables, face à tout destin collectif, il est désorienté dans le temps et de l’espace ; venu de rien, il n’entend aller nulle part. Déraciné car ne pouvant plus avoir de rapport à la terre et aux morts ; inapte à se figurer dans une société qui, comme l’avait souligné Auguste Comte, est faite de « plus de morts que de vivants ». Désincarné car ce qui fait de nous des êtres charnels, c’est ce qui nous distingue de l’autre à l’échelle individuelle, comme notre peau, ou à l’échelle collective, comme les clans, les nations, les frontières. Comment en sommes-nous arrivés là ?
[…]
Contre cette inhumanité qui vient, dominée par les puissances maîtrisant l’immatériel et l’approche réticulaire de la puissance, il faut reprendre la seule querelle qui vaille, « celle de l’homme » comme le disait le général de Gaulle. A cette fin, contre l’autonomie de l’individu auto-centré dans son néant, il faut redécouvrir l’incomplétude de nos sociétés. En effet, comme dans les théorèmes mathématique la solution se trouve peut-être à l’extérieur du problème : comme nos sociétés ne peuvent être leur propre référent, elles ont besoin de quelque chose qui les entoure, les pénètre et les unie, une transcendance civique ou religieuse. Cette transcendance doit être issue de notre histoire, de notre Tradition. Ce qui n’implique nullement une logique de passéisme mais une logique de transmission arrimée sur une nostalgie et sur une véritable conscience du passé. Il ne s’agit pas là des caricatures d’appartenance des idéologues du bien (parti espagnol/impérial, islamistes) mais d’une affirmation de soi tranquille et politique qui doit passer par des étapes de reprise en compte de soi et de mise à distance (la distance du dialogue) des autres. Commencer par se rendre compte que pour qu’il y ait eux et nous, il faut d’abord prendre conscience que la vraie fraternité implique que tous les hommes ne soient pas frères.
Pour ce faire, nous devons reprendre fierté et foi en nous et dans notre lignée. Pour préserver notre humanité, nous devons affirmer notre particularisme en tant que Français et le travailler jusqu’à le ressentir réellement, en nous rappelant que l’éthique est quelque chose de concret : prendre soin des siens d’abord. Politiquement, nous devons refaire communauté et nous battre pour la souveraineté et la gloire pour des objectifs clairement politiques. Comme à chaque fois où la France a failli être détruite, un camp des politiques doit se lever, car en la sauvant, nous sauvrons une part du génie humain, celui de nos ancêtres.
Les temps qui arrivent seront terribles, mais « [p]ourtant, à la fin des fins, la dignité des hommes se révoltera » »
Pierre-Yves ROUGEYRON, directeur de la rédaction.
Sommaire
Pierre-Yves ROUGEYRON : « Fraternité perdue »
Dossier : L’Homme sans liens
Marie-Céline COURILLEAULT : « L’Homme sans liens »
Michael Allen GILLESPIE : « La question de la Modernité et des possibilités de l’essor humain »
Jérémy-Marie PICHON : « L’Homo Canal +. Enquête sur un fascisme accompli : le Cool »
Maria VILLELA-PETIT : « Simone Weil et « L’Enracinement » »
Anthony ELLIOTT : « La Réinvention dans un monde au-delà des liens »
Jean-François GAUTIER : « Avec et sans lien(s) »
Stéphane VINOLO : « Le prisme diffractant du lien social »
Pierre-Antoine CHARDEL : « Une herméneutique sociologique dans la société liquide. Lecture de Zygmunt Bauman »
Libres pensées
Erik S. REINERT : « Le futur de la société d’information en Europe : contributions au débat »
Libres propos
Julien FUNNARO : « 1989 : l’anniversaire oublié »
Charles ROBIN : « « Mon ex est quelqu’un de bien ». Éloge de la décence amoureuse »
Dossier : Jean-François Mattéi
Pierre-Yves ROUGEYRON : « Jean-François Mattéi, le maître et le compagnon »
Marc HERCEG : « Esthétique et métaphysique dans l’œuvre de Jean-François Mattéi »
Jérôme PALAZZOLO : « La famille contemporaine face à la globalisation mondiale : approche systémique et anthropologique »
Marc ALPOZZO : « Entretien avec Jean-François Mattéi »
Pierre LE VIGAN : « Albert Camus, une vision grecque du monde »
00:05 Publié dans Philosophie, Revue | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : philosophie, revue, jean-françois mattéi |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
La «Grande Séparation»: du citoyen à l’homme de rien…

 J’ai écrit La Grande Séparation parce que je suis affolé de la perte de notre mémoire historique qui accompagne la perte de notre identité nationale. Le monde dans lequel nous vivons encore est dessiné par des frontières, par des nations, qui nous donnent notre citoyenneté et notre identité. Le principe de la souveraineté nationale garantit aux citoyens la liberté de décider de leurs lois, de leurs mœurs, de leur destin, sur leur territoire et à l’intérieur de leurs frontières. Les conditions d’acquisition de la citoyenneté assurent l’unité de la nation, et la transmission entre les générations. La séparation est géographique, respectueuse des cultures, des civilisations, de la diversité collective des peuples.
J’ai écrit La Grande Séparation parce que je suis affolé de la perte de notre mémoire historique qui accompagne la perte de notre identité nationale. Le monde dans lequel nous vivons encore est dessiné par des frontières, par des nations, qui nous donnent notre citoyenneté et notre identité. Le principe de la souveraineté nationale garantit aux citoyens la liberté de décider de leurs lois, de leurs mœurs, de leur destin, sur leur territoire et à l’intérieur de leurs frontières. Les conditions d’acquisition de la citoyenneté assurent l’unité de la nation, et la transmission entre les générations. La séparation est géographique, respectueuse des cultures, des civilisations, de la diversité collective des peuples.
La Grande Séparation qui vient affirme que rien n’existe que l’individu absolu. Elle invente l’homme hors-sol, sans histoire, sans origine, sans sexe, sans âge, sans race. Elle nous sépare de nos territoires, de nos identités, de nos origines. Elle célèbre l’homme de nulle part, le migrant perpétuel, sans identité, sans appartenance et sans liens. Et elle nous coupe de l’histoire, elle célèbre le consommateur pour effacer le citoyen, elle laisse la propriété et le marché dévorer la nation et l’identité.
Des forces puissantes agissent en faveur de cette Grande Séparation. Les intérêts qui veulent remplacer la société par le contrat privé, le marché et l’individu de droit ne manquent pas. Ceux qui considèrent que la nation et l’État ne sont que des entraves à l’exploitation de toutes les ressources disponibles sur la planète non plus. Qui sont ces gens qui s’opposent à ce qu’on creuse leur sol pour y exploiter le gaz de schiste ? Qui sont ceux qui entendent préserver leurs espèces animales et végétales endémiques, quand les usines du vivant leur promettent de meilleurs rendements ? Et qui sont ces indigènes qui s’opposent aux colons qui tirent plus d’argent de leurs terres, de leurs mers et de leur vie ?
J’ai voulu contribuer à alerter les Français. Nous vivons un nouvel épisode de la colonisation. Ce sont les ONG, les fondations, les fonds d’investissement qui s’y emploient. Cette fois, c’est nous qui sommes victimes, comme ils l’ont été, eux du Congo, du Maroc ou de Chine. Mais la réalité n’a pas changé. Nous vivons aussi un nouvel épisode de la guerre de toujours, celle de la liberté des peuples à décider de leur destin. Cette fois, des États-Unis dont l’autorité morale est ruinée, dont la prétention à détenir le secret de la réussite est épuisée, et qui n’ont plus que leur force militaire pour écraser le monde, constituent la première menace pour la paix mondiale et pour notre liberté. Mais ne nous y trompons pas. La religion scientiste, l’idée folle de construire un homme nouveau, libéré de la mort, de l’histoire et de toute identité est la première menace à laquelle nous devons faire face, hommes de notre terre, de notre France, et qui savons dire « Nous ».
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Livre, Livre, Philosophie | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : grande séparation, hervé juvin, actualité, livre, philosophie |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook
dimanche, 21 décembre 2014
Val van Putin betekent groot gevaar voor het Westen

Zware klappen voor Europese export door sancties tegen Rusland
DIW-Instituut Berlijn: Kans van 33% op Russisch staatsbankroet
Als Putin valt is de kans dat hij wordt opgevolgd door een ultranationalist aanzienlijk. De gevolgen voor met name Europa zouden dan wel eens verschrikkelijk kunnen zijn.In Berlijn en Brussel gaan steeds meer stemmen op om de sancties tegen Rusland te herzien, ook al wordt er meteen bij gezegd dat deze niet de oorzaak zijn van de huidige chaos in Rusland. Maar ook het vijandbeeld van president Vladimir Putin wordt gerelativeerd. De reden: als Putin valt, dan dreigen radicale nationalisten aan de macht te komen, waardoor de rekening voor het Westen wel eens veel hoger kan uitpakken dan van tevoren werd ingeschat. Europa zou zelfs in een oorlog om Oekraïne gesleurd kunnen worden.
De dreigende economische instorting van Rusland baart Europa grote zorgen. Plotseling verklaarde een woordvoerder van de EU-Commissie dat ‘niemand er belang bij heeft dat Rusland in een diepe Depressie wordt gestort’. De Duitse bondskanselier Angela Merkel uitte onlangs nog zware kritiek op Putin, maar prees afgelopen week plotseling de goede banden met Rusland.
Export naar Rusland stort in
De Europese sancties tegen Rusland vanwege de situatie in Oekraïne hebben enorme gevolgen voor de Europese en vooral Duitse export. Sommige analisten schatten dat de export naar Rusland eind dit jaar met 20% tot 25% zal zijn gedaald. Alleen al in Duitsland zal dat 50.000 mensen hun baan kosten.
De enige oplossing is het opheffen van de sancties, zodat buitenlands kapitaal weer naar Rusland stroomt en er weer wordt geïnvesteerd in het land. Dan zal ook de Europese export naar het land aantrekken.
‘Kans dat Rusland instort 33%’
De president van het DIW-Instituut in Berlijn, Marcel Fratscher, schat de kans dat Rusland bankroet gaat op 33%. Zolang de sancties intact blijven wordt het risico dat Rusland daadwerkelijk instort steeds groter. Zo hebben de VS en bondgenoten de Russische banken en bedrijven feitelijk van de internationale aandelenmarkten afgesneden, waardoor ze zonder kapitaal komen te zitten. Een financiële handelaar sprak zelfs van een ware ‘financiële oorlog’ tegen Rusland.
EU zwaar getroffen, VS nauwelijks
De Verenigde Staten lijken echter niet van plan Rusland en Europa te hulp te schieten. Sterker nog, Obama onderstekende gisteren een nieuw pakket met zwaardere sancties, die Europa nog harder zullen raken. Het is dan ook de vraag hoe lang de EU dit over zijn kant zal laten gaan, omdat Amerika zelf nauwelijks door de sancties wordt getroffen.
‘Putin is goed voor het Westen’
Inmiddels begin in Brussel langzaam het besef door te dringen dat Putin nog niet de slechtste Russische leider is, en dat zijn val wel eens voor een zeer gevaarlijke situatie kan zorgen, omdat dan ultranationalisten aan de macht dreigen te komen. Die leunen traditioneel op de kracht van het Russische leger en vooral het enorme aantal kernwapens dat het land heeft.
George Friedman, hoofd van de private Amerikaanse inlichtingendienst Stratfor, is op dit moment in Moskou en schrijft dat het Westen het eigenlijk erg goed getroffen heeft met Putin. Het alternatief, de ultranationalisten, betekent vrijwel zeker de totale instorting van Rusland, met zeer pijnlijke gevolgen voor de EU. Bovendien kan Rusland dan wel eens een oorlog beginnen om Oekraïne, waar Europa bij betrokken kan raken – tenminste, zolang Brussel netjes aan de leiband van Washington blijft lopen.
‘Obama geeft Europa op’
Misschien is het de Amerikaanse regering wel om beide te doen, namelijk het tegelijkertijd fors verzwakken van zowel de Russische als de Europese economie. Hierdoor zal de Amerikaanse economie weer kunnen floreren.
De onafhankelijke Amerikaanse analist Webster Tarpley, deze eeuw bekend geworden vanwege zijn forse kritiek op president George Bush, noemde in 2008 de verkiezing van Obama ‘catastrofaal’ voor de wereld. Volgens Tarpley zou Obama uiteindelijk een oorlog met Rusland en China veroorzaken, en daarbij zonder met zijn ogen te knipperen Europa opgeven. Het begint er steeds meer op te lijken dat Tarpley gelijk begint te krijgen.
Europese elite koos islam in plaats van Rusland
In plaats van dat Europa samen met het orthodoxe Rusland een vuist maakt tegen het islamitische extremisme, heeft de Europese elite in al zijn wijsheid uitgerekend de islam als bondgenoot gekozen tégen Rusland. Daarmee hebben Brussel en alle eurofielen moedwillig de stabiliteit, toekomst en welvaart van ons hele continent in groot gevaar gebracht.
Xander
(1) Deutsche Wirtschafts Nachrichten
Zie ook o.a.:
16-12: Olie-oorlog: Financiële markten speculeren over staatsbankroet Rusland
00:05 Publié dans Actualité, Affaires européennes, Géopolitique | Lien permanent | Commentaires (0) | Tags : géopolitique, politique internationale, rouble, russie, europe, affaires européennes |  |
|  del.icio.us |
del.icio.us |  |
|  Digg |
Digg | ![]() Facebook
Facebook













